Ch 28 Reading guide
... 6. Draw the product of the reaction catalyzed by acetyl CA carboxylase. Which cofactor does it require? How much ATP is required? Why is this the regulatory enzyme for fatty acid synthesis? 7. In the first step of fatty acid synthesis, malonyl Coa condenses with acetyl CoA and releases the CO2 that ...
... 6. Draw the product of the reaction catalyzed by acetyl CA carboxylase. Which cofactor does it require? How much ATP is required? Why is this the regulatory enzyme for fatty acid synthesis? 7. In the first step of fatty acid synthesis, malonyl Coa condenses with acetyl CoA and releases the CO2 that ...
Nutritional Assessment & Clinical Application Part 2
... – use of a metabolic monitor/cart – measures respiratory gas exchanges – Differences in oxygen and carbon dioxide content between air going in and air coming out respiratory exchange energy expenditure (Ref: Mann & Truswell(ed) Essentials of Human Nutrition, Chap. 5) ...
... – use of a metabolic monitor/cart – measures respiratory gas exchanges – Differences in oxygen and carbon dioxide content between air going in and air coming out respiratory exchange energy expenditure (Ref: Mann & Truswell(ed) Essentials of Human Nutrition, Chap. 5) ...
ATP
... • used to make cheese and yogurt • during strenuous exercise not enough oxygen from blood creates an “oxygen debt” • lactic acid accumulates in muscle; leads to fatigue ...
... • used to make cheese and yogurt • during strenuous exercise not enough oxygen from blood creates an “oxygen debt” • lactic acid accumulates in muscle; leads to fatigue ...
Cell Respiration
... • As the concentration of H ’s build up they are sucked back into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase • Oxygen is the final e- acceptor, it bonds with H+ to make water (which is released) • 32-34 ATP’s are produced** ...
... • As the concentration of H ’s build up they are sucked back into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase • Oxygen is the final e- acceptor, it bonds with H+ to make water (which is released) • 32-34 ATP’s are produced** ...
Pre-workout / Nitric Oxide : SUPERNOVA 282GR
... Presenting the active ingredients of the product according to functional groups: Supernova Blend contains active ingredients which enhance nitrogen monoxide production in your body and carnosine production in your muscles, as well as a unique combination of two kinds of L-arginine, L-citrulline mala ...
... Presenting the active ingredients of the product according to functional groups: Supernova Blend contains active ingredients which enhance nitrogen monoxide production in your body and carnosine production in your muscles, as well as a unique combination of two kinds of L-arginine, L-citrulline mala ...
Cell Respiration
... • As the concentration of H ’s build up they are sucked back into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase • Oxygen is the final e- acceptor, it bonds with H+ to make water (which is released) • 32-34 ATP’s are produced** ...
... • As the concentration of H ’s build up they are sucked back into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase • Oxygen is the final e- acceptor, it bonds with H+ to make water (which is released) • 32-34 ATP’s are produced** ...
A chemist has discovered a drug that blocks
... 7. A new species has been discovered and it was found that they possessed some mitochondria with unfolded cristae. What generalizations can you make about this organisms metabolism? 8. Sports physiologists at an Olympic training center wanted to monitor athletes to determine at what point their mus ...
... 7. A new species has been discovered and it was found that they possessed some mitochondria with unfolded cristae. What generalizations can you make about this organisms metabolism? 8. Sports physiologists at an Olympic training center wanted to monitor athletes to determine at what point their mus ...
Unit 3 Homework
... molecules and one __________ molecule. These last four molecules are electron carriers. Since each glucose molecule splits, two acetyl CoA molecules go through the citric acid cycle, bringing the total yield per glucose molecule to _____ ATP, _____ NADH, and _____ FADH2. So that the cell can use the ...
... molecules and one __________ molecule. These last four molecules are electron carriers. Since each glucose molecule splits, two acetyl CoA molecules go through the citric acid cycle, bringing the total yield per glucose molecule to _____ ATP, _____ NADH, and _____ FADH2. So that the cell can use the ...
IIIb
... 5. (12 Pts) Unlike most organs, muscle uses three specific amino acids as energy sources. What are these amino acids (structures)? Choose one and draw its degradation pathway. ...
... 5. (12 Pts) Unlike most organs, muscle uses three specific amino acids as energy sources. What are these amino acids (structures)? Choose one and draw its degradation pathway. ...
Guided Reading Unit 3
... molecules and one __________ molecule. These last four molecules are electron carriers. Since each glucose molecule splits, two acetyl CoA molecules go through the citric acid cycle, bringing the total yield per glucose molecule to _____ ATP, _____ NADH, and _____ FADH2. So that the cell can use the ...
... molecules and one __________ molecule. These last four molecules are electron carriers. Since each glucose molecule splits, two acetyl CoA molecules go through the citric acid cycle, bringing the total yield per glucose molecule to _____ ATP, _____ NADH, and _____ FADH2. So that the cell can use the ...
Cellular Respiration: - Multiple Choice Questions Answer all
... Phosphofructokinase is an important control enzyme in the regulation of cellular respiration. Which of the following statements describes a function of phosphofructokinase? A ...
... Phosphofructokinase is an important control enzyme in the regulation of cellular respiration. Which of the following statements describes a function of phosphofructokinase? A ...
Human Metabolism Compared to Other Species
... For example, there is life deep down on the ocean floor. ...
... For example, there is life deep down on the ocean floor. ...
Amino Acid Metabolism
... Metabolic Pool of Amino Acids • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N co ...
... Metabolic Pool of Amino Acids • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N co ...
1 Amino Acid Metabolism
... Metabolic Pool of Amino Acids • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N co ...
... Metabolic Pool of Amino Acids • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N co ...
Cellular Respiration
... WHAT IS CELLULAR RESPIRATION? It is a PROCESS ALL organisms (including plants) perform cell respiration! • Cellular Respiration is how every cell changes Glucose into ATP. ATP is the cell’s energy molecule. • ATP is used by cells to perform ALL biological activities! (STRANGER-C) ...
... WHAT IS CELLULAR RESPIRATION? It is a PROCESS ALL organisms (including plants) perform cell respiration! • Cellular Respiration is how every cell changes Glucose into ATP. ATP is the cell’s energy molecule. • ATP is used by cells to perform ALL biological activities! (STRANGER-C) ...
Chapter 6 Cellular Energy
... Citric Acid (Kreb’s) Cycle – creates CO2 from pyruvate 2 molecules of pyruvate become 2 molecules of acetyl CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle Energy yield is 2 ATP, 6 NADH & 2 FADH2 Provides electrons for respiration ...
... Citric Acid (Kreb’s) Cycle – creates CO2 from pyruvate 2 molecules of pyruvate become 2 molecules of acetyl CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle Energy yield is 2 ATP, 6 NADH & 2 FADH2 Provides electrons for respiration ...
File
... provided. After each molecule is made, the group will come together and follow the instructions and answer the questions regarding carbohydrates. Monosaccharide’s (single molecules of sugar) A single molecule of sugar is called a monosaccharide. The prefix “Mono” means one. However, the one molecule ...
... provided. After each molecule is made, the group will come together and follow the instructions and answer the questions regarding carbohydrates. Monosaccharide’s (single molecules of sugar) A single molecule of sugar is called a monosaccharide. The prefix “Mono” means one. However, the one molecule ...
AP Biology Notes Outline Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Cellular R
... When oxygen is NOT present, glycolysis is followed by a different pathway called fermentation. o Fermentation releases energy from food molecules in the absence of oxygen o Because fermentation does not require oxygen, it is said to be anaerobic The 2 main types of fermentation are: o alcoholic ...
... When oxygen is NOT present, glycolysis is followed by a different pathway called fermentation. o Fermentation releases energy from food molecules in the absence of oxygen o Because fermentation does not require oxygen, it is said to be anaerobic The 2 main types of fermentation are: o alcoholic ...
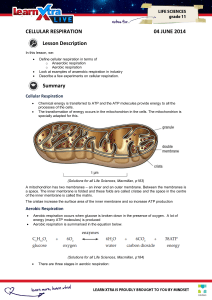
CELLULAR RESPIRATION 04 JUNE 2014 Lesson Description
... In the presence of oxygen, all cells synthesize ATP via the process of glycolysis. Many cells also can metabolize pyruvate if oxygen is not present, via the process of: A. ...
... In the presence of oxygen, all cells synthesize ATP via the process of glycolysis. Many cells also can metabolize pyruvate if oxygen is not present, via the process of: A. ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... The long chains of fatty acids are broken down into two-carbon units and metabolized by the enzymes of the citric acid (Krebs) cycle into CO2 and H2O, releasing large amounts of energy. ...
... The long chains of fatty acids are broken down into two-carbon units and metabolized by the enzymes of the citric acid (Krebs) cycle into CO2 and H2O, releasing large amounts of energy. ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.