Chemistry of Life
... It has 4 valence electrons It can form up to 4 covalent bonds These can be single, double, or triple cov. Bonds It can form large molecules. These molecules can be chains, ring-shaped, or branched ...
... It has 4 valence electrons It can form up to 4 covalent bonds These can be single, double, or triple cov. Bonds It can form large molecules. These molecules can be chains, ring-shaped, or branched ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration 1 Photosynthesis and Respiration
... 16. Explain the process by which pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA. What electron carrier is produced during this reaction? 17. Where does the Kreb’s Cycle occur? 18. Explain the difference between Oxidative Phosphorylation and Substrate Level Phosphorylation? When does each process occur? 19. For ...
... 16. Explain the process by which pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA. What electron carrier is produced during this reaction? 17. Where does the Kreb’s Cycle occur? 18. Explain the difference between Oxidative Phosphorylation and Substrate Level Phosphorylation? When does each process occur? 19. For ...
Cellular Energetics
... of light and become excited when their e- gain energy • Photosystem 2 (P680) absorbs light and e- are excited • e- are now boosted to a higher level and must be replaced • H2O is split (photolysis) and the e- are replaced (and oxygen is produced) • e- pass down an ETC and ATP is produced by chemiosm ...
... of light and become excited when their e- gain energy • Photosystem 2 (P680) absorbs light and e- are excited • e- are now boosted to a higher level and must be replaced • H2O is split (photolysis) and the e- are replaced (and oxygen is produced) • e- pass down an ETC and ATP is produced by chemiosm ...
File
... enzymes have an active site; that fits the substrate precisely; changes in the chemical environment of the enzyme can lead to a shape / conformational change in the protein; leading to a change in the shape of the active site; may interfere with the binding of the substrate with the active site; alt ...
... enzymes have an active site; that fits the substrate precisely; changes in the chemical environment of the enzyme can lead to a shape / conformational change in the protein; leading to a change in the shape of the active site; may interfere with the binding of the substrate with the active site; alt ...
Lecture 6
... • This means – We must get plenty of CHO prior to and even during activity – Liver supplements this ...
... • This means – We must get plenty of CHO prior to and even during activity – Liver supplements this ...
Lecture 9: Citric Acid Cycle/Fatty Acid Catabolism
... Metabolism Lecture 9 — CITRIC ACID CYCLE/FATTY ACID CATABOLISM — Restricted for students enrolled in MCB102, UC Berkeley, Spring 2008 ONLY ...
... Metabolism Lecture 9 — CITRIC ACID CYCLE/FATTY ACID CATABOLISM — Restricted for students enrolled in MCB102, UC Berkeley, Spring 2008 ONLY ...
Module 1 (Review)
... They increase the volume of the lungs, allowing more oxygen to be inhaled. They increase the surface areas of the lungs, allowing efficient gas exchange. ...
... They increase the volume of the lungs, allowing more oxygen to be inhaled. They increase the surface areas of the lungs, allowing efficient gas exchange. ...
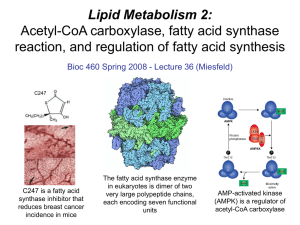
Lecture 36 - Lipid Metabolism 2
... coenzyme in redox reactions, and the building block is malonyl-CoA. • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is the key regulated enzyme in fatty acid synthesis and is responsible for generating malonyl-CoA in a carboxylation reaction using acetyl-CoA. • The fatty acid synthase protein complex consists of six enzym ...
... coenzyme in redox reactions, and the building block is malonyl-CoA. • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is the key regulated enzyme in fatty acid synthesis and is responsible for generating malonyl-CoA in a carboxylation reaction using acetyl-CoA. • The fatty acid synthase protein complex consists of six enzym ...
1 All cells can harvest energy from organic molecules. To do this
... NADH and FADH2 (produced during glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the Krebs cycle) donate high energy electrons to an electron transport chain As the electrons are passed along the ETC, their energy is used to make ATP by chemiosmosis At the end of the ETC, electrons join with oxygen and 2H+ t ...
... NADH and FADH2 (produced during glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the Krebs cycle) donate high energy electrons to an electron transport chain As the electrons are passed along the ETC, their energy is used to make ATP by chemiosmosis At the end of the ETC, electrons join with oxygen and 2H+ t ...
The risks and benefits of feeding intact male swine in the United
... suggeststhat for this age group, the maximumingestivecapacitylies between2.0-2.2kg per day,and that diets of 3350-3465 kcal DE(14070-14550kJ)are required to maximize protein and fat growth. On a typical westernCanadian diet which lacks corn but is based on wheat, barley, and soybean meal as the grai ...
... suggeststhat for this age group, the maximumingestivecapacitylies between2.0-2.2kg per day,and that diets of 3350-3465 kcal DE(14070-14550kJ)are required to maximize protein and fat growth. On a typical westernCanadian diet which lacks corn but is based on wheat, barley, and soybean meal as the grai ...
AP Biology Summer Assignment Chapter 3 Quiz 2016-17
... groups below except a. positively charged and hydrophilic. b. negatively charged and hydrophilic. c. uncharged hydrophilic. d. positively charged and hydrophobic. 8. In an alpha helix, the coiling is stabilized by a. the hydrophobic nature of the R chains, which causes the chain to coil with the R g ...
... groups below except a. positively charged and hydrophilic. b. negatively charged and hydrophilic. c. uncharged hydrophilic. d. positively charged and hydrophobic. 8. In an alpha helix, the coiling is stabilized by a. the hydrophobic nature of the R chains, which causes the chain to coil with the R g ...
Chapter 3: Energy for Cells
... Stages of Cellular Respiration At the end of the cycle, a new molecule of oxaloacetate is formed. (This is why it's called a cycle...the molecule you start with is reformed at the end, so it can be reused.) *Remember: two pyruvic acids are formed during glycolysis, so the Krebs cycle happens ...
... Stages of Cellular Respiration At the end of the cycle, a new molecule of oxaloacetate is formed. (This is why it's called a cycle...the molecule you start with is reformed at the end, so it can be reused.) *Remember: two pyruvic acids are formed during glycolysis, so the Krebs cycle happens ...
Muscles
... of glycogen followed by glycolysis and anaerobic respiration results in the production of ATP at a rate faster than can be achieved by the TCA cycle and the cytochrome chain. Anerobic respiration can supply muscles with high levels of ATP in a very short time period but only in short bursts eg in th ...
... of glycogen followed by glycolysis and anaerobic respiration results in the production of ATP at a rate faster than can be achieved by the TCA cycle and the cytochrome chain. Anerobic respiration can supply muscles with high levels of ATP in a very short time period but only in short bursts eg in th ...
lect4
... Excess or insufficient dietary amino acid intake leads to the catabolism of amino acids Excess amino acids can be used for energy Insufficient dietary amino acids lead to the catabolism of proteins Insufficient dietary energy leads to the catabolism of proteins ...
... Excess or insufficient dietary amino acid intake leads to the catabolism of amino acids Excess amino acids can be used for energy Insufficient dietary amino acids lead to the catabolism of proteins Insufficient dietary energy leads to the catabolism of proteins ...
Which Protein is Best?
... bodies. The researchers explained the high thermic effect of whey protein might be due to the amino acid composition. Whey is high in leucine, a branchedchain amino acid, which has been shown to stimulate muscle protein synthesis and muscle turnover. The study tested the metabolic rate, satiety and g ...
... bodies. The researchers explained the high thermic effect of whey protein might be due to the amino acid composition. Whey is high in leucine, a branchedchain amino acid, which has been shown to stimulate muscle protein synthesis and muscle turnover. The study tested the metabolic rate, satiety and g ...
Document
... • In many animals, carbon dioxide is carried to the lungs to be released during breathing. • Some of the energy produced during cellular respiration is released as heat. • Much of the energy produced is transferred to ATP. • C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + chemical energy ...
... • In many animals, carbon dioxide is carried to the lungs to be released during breathing. • Some of the energy produced during cellular respiration is released as heat. • Much of the energy produced is transferred to ATP. • C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + chemical energy ...
5.19.06 Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation Reading
... This cartoon is adapted from fig. 2 of Cross. The 3 shades of red represent the 3 different conformational states of the catalytic subunits. The central asymmetric black object represents the gamma subunit which is caused to rotate by themitochondrial proton efflux. This rotation drives the conforma ...
... This cartoon is adapted from fig. 2 of Cross. The 3 shades of red represent the 3 different conformational states of the catalytic subunits. The central asymmetric black object represents the gamma subunit which is caused to rotate by themitochondrial proton efflux. This rotation drives the conforma ...
Cellular Respiration
... or ethanol and carbon dioxide, with no further yield of ATP. 3.7.4 Explain that, during aerobic cell respiration, pyruvate can be broken down in the mitochondrion into carbon dioxide and water with a large yield of ATP. ...
... or ethanol and carbon dioxide, with no further yield of ATP. 3.7.4 Explain that, during aerobic cell respiration, pyruvate can be broken down in the mitochondrion into carbon dioxide and water with a large yield of ATP. ...
The Name Game - UCSD Course Websites
... but sometimes… not so good. Anyway, a simple example of this idea can be seen with 2-keto-propane, or 2-propanone, which we usually refer to as “acetone” (on the right). The fancier names are completely unambiguous; if you had never seen the pictured molecule, you would still know how to draw it fro ...
... but sometimes… not so good. Anyway, a simple example of this idea can be seen with 2-keto-propane, or 2-propanone, which we usually refer to as “acetone” (on the right). The fancier names are completely unambiguous; if you had never seen the pictured molecule, you would still know how to draw it fro ...
Biosketch - NC State University
... 1. Muoio DM, Awad AB, Horvath P, Leddy J and Pendergast DR. Effect of dietary fat on metabolic adjustments to maximal Vo 2 and endurance in trained runners. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise. ...
... 1. Muoio DM, Awad AB, Horvath P, Leddy J and Pendergast DR. Effect of dietary fat on metabolic adjustments to maximal Vo 2 and endurance in trained runners. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise. ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.