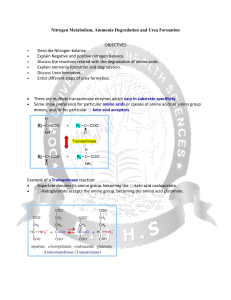
FACTORS AFFECTING ENZYME ACTION
... • 3-D structure - the amino acid sequence causes bonds to form and the polypeptide to fold into a 3D shape. • The 3D shape causes the enzyme to form an active site - this is a “hole” that forms and is able to bind onto other molecules by forming temporary bonds between them. • The molecule that the ...
... • 3-D structure - the amino acid sequence causes bonds to form and the polypeptide to fold into a 3D shape. • The 3D shape causes the enzyme to form an active site - this is a “hole” that forms and is able to bind onto other molecules by forming temporary bonds between them. • The molecule that the ...
6.8-6.10 Citric acid cycle and Oxidative phosphorylation
... 6.10 Oxidative phosphorylation • At this point in Cellular Respiration only 4 ATP molecules have been produced – 2 in glycolysis – 2 in the citric acid cycle ...
... 6.10 Oxidative phosphorylation • At this point in Cellular Respiration only 4 ATP molecules have been produced – 2 in glycolysis – 2 in the citric acid cycle ...
2017 Product Guide
... This focus and commitment to quality continues today and it is the reason why the Max Muscle Nutrition brand has been trusted by millions of nutritional supplement consumers over the past 25 years! Max Muscle Nutrition guarantees our customers the highest quality supplements in order to get you the ...
... This focus and commitment to quality continues today and it is the reason why the Max Muscle Nutrition brand has been trusted by millions of nutritional supplement consumers over the past 25 years! Max Muscle Nutrition guarantees our customers the highest quality supplements in order to get you the ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
1. What is the best definition of rate of reaction? A. The time it takes
... propanone and the iodine, as the reaction can happen without a catalyst. Hannah’s hypothesis was that as the catalyst is involved in the reaction, the concentrations of the propanone, iodine and the hydrogen ions will all affect the rate. They carried out several experiments varying the concentratio ...
... propanone and the iodine, as the reaction can happen without a catalyst. Hannah’s hypothesis was that as the catalyst is involved in the reaction, the concentrations of the propanone, iodine and the hydrogen ions will all affect the rate. They carried out several experiments varying the concentratio ...
Fourth Progress Report
... PQR file. The rational behind this script is to obtain a file that is compatible to the Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver. PQR format incorporates van der Waals radii and partial charge. We then have successfully written a script that can successfully call to APBS to calculate free energies. It shou ...
... PQR file. The rational behind this script is to obtain a file that is compatible to the Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver. PQR format incorporates van der Waals radii and partial charge. We then have successfully written a script that can successfully call to APBS to calculate free energies. It shou ...
IB496-April 10 - School of Life Sciences
... to altered gene expression profiles to: (1) provide new insights into the regulatory network underlying the metabolic dysfunctions; (2) enable the assembly of disparate gene expression events into functional pathways that was not feasible by transcriptomic analysis alone. This was illustrated in par ...
... to altered gene expression profiles to: (1) provide new insights into the regulatory network underlying the metabolic dysfunctions; (2) enable the assembly of disparate gene expression events into functional pathways that was not feasible by transcriptomic analysis alone. This was illustrated in par ...
biomedical therapy
... In general, intermediary catalyst preparations are indicated in all cellular phases – that is, in the impregnation, degeneration, and dedifferentiation phases to the right of Reckeweg’s “Biological Section”. To a large extent, these preparations can be administered independent of specific symptoms. ...
... In general, intermediary catalyst preparations are indicated in all cellular phases – that is, in the impregnation, degeneration, and dedifferentiation phases to the right of Reckeweg’s “Biological Section”. To a large extent, these preparations can be administered independent of specific symptoms. ...
LP - Columbia University
... 45 kcal/mole we got from converting glucose to two lactates. The lactic acid that we are throwing away at the end could be used for more energy, but in the absence of oxygen there is no way to use it. With oxygen, it's another story .............and our next chapter. [To review glycolysis and fermen ...
... 45 kcal/mole we got from converting glucose to two lactates. The lactic acid that we are throwing away at the end could be used for more energy, but in the absence of oxygen there is no way to use it. With oxygen, it's another story .............and our next chapter. [To review glycolysis and fermen ...
Studies on the Fate of Isotopically Labeled
... resents the micro-atoms of carbon of the substrate, in this instance glucose, converted to CO2 per gram of dry tissue per hour. This value can be easily calculated from the amounts and relative specific activities of the respiratory carbon dioxide. The normal tissues fall into two groups: those with ...
... resents the micro-atoms of carbon of the substrate, in this instance glucose, converted to CO2 per gram of dry tissue per hour. This value can be easily calculated from the amounts and relative specific activities of the respiratory carbon dioxide. The normal tissues fall into two groups: those with ...
Amino acid metabolism: Disposal of Nitrogen
... (a TCA cycle intermediate and glucogenic compound) Valine and isoleucine are branched-chain amino acids They generate propionyl CoA that is converted to succinyl CoA by biotin- and vitamin B12– requiring reactions Threonine is dehydrated to α-ketobutyrate, which is converted to propionyl CoA and the ...
... (a TCA cycle intermediate and glucogenic compound) Valine and isoleucine are branched-chain amino acids They generate propionyl CoA that is converted to succinyl CoA by biotin- and vitamin B12– requiring reactions Threonine is dehydrated to α-ketobutyrate, which is converted to propionyl CoA and the ...
respiration review
... Is respiration endergonic or exergonic? What does this term mean? Respiration is exergonic. The reactants possess more free energy than the products. Energy is released as the reactants are converted into products. ...
... Is respiration endergonic or exergonic? What does this term mean? Respiration is exergonic. The reactants possess more free energy than the products. Energy is released as the reactants are converted into products. ...
Enzymes Problem Set 1 A) What concentration of the substrate
... kinase activity is directly related to the rate at which NADH disappears from the solution. The following solutions are mixed: 200L 400 L 50L 50L 50L 50L 50L 50L ...
... kinase activity is directly related to the rate at which NADH disappears from the solution. The following solutions are mixed: 200L 400 L 50L 50L 50L 50L 50L 50L ...
A1981MS54300001
... would prove useful to others too. "It seemed that PAL was a logical candidate to be a control enzyme for phenylpropanoid metabolism, but among the difficulties with this hypothesis was the extreme variability of enzyme activity. It seemed as if every stimulus imaginable caused enzyme levels to chang ...
... would prove useful to others too. "It seemed that PAL was a logical candidate to be a control enzyme for phenylpropanoid metabolism, but among the difficulties with this hypothesis was the extreme variability of enzyme activity. It seemed as if every stimulus imaginable caused enzyme levels to chang ...
Carbonyl group is a functional group of (Aldehyde, Ketone)
... compounds of human body, here is some of them:①-Monosaccharides: Monosaccharide's are carbohydrates which can not be hydrolyzed to small molecules, contain carbons with functional aldehyde or keto group are present in nature. Aldohexose is glucose, Fructose is ketohexose respectively. Glucose is pre ...
... compounds of human body, here is some of them:①-Monosaccharides: Monosaccharide's are carbohydrates which can not be hydrolyzed to small molecules, contain carbons with functional aldehyde or keto group are present in nature. Aldohexose is glucose, Fructose is ketohexose respectively. Glucose is pre ...
Variation in the link between oxygen consumption and ATP
... ETC) situated within the inner mitochondrial membrane and then to the final acceptor, oxygen. The electron flow through the ETC allows the proton (Hþ) pumps to expel Hþ from the matrix to the mitochondrial inter-membrane space. The accumulation of Hþ within this inter-membrane space generates an ele ...
... ETC) situated within the inner mitochondrial membrane and then to the final acceptor, oxygen. The electron flow through the ETC allows the proton (Hþ) pumps to expel Hþ from the matrix to the mitochondrial inter-membrane space. The accumulation of Hþ within this inter-membrane space generates an ele ...
Cell Respiration
... • In the absence of O2 (oxygen debt), the 2 molecules of pyruvic acid from the end of glycolysis are converted into 2 molecules of lactic acid • Anaerobic fermentation most commonly occurs in active skeletal muscle cells when they use O2 faster than it can be delivered by the respiratory and circula ...
... • In the absence of O2 (oxygen debt), the 2 molecules of pyruvic acid from the end of glycolysis are converted into 2 molecules of lactic acid • Anaerobic fermentation most commonly occurs in active skeletal muscle cells when they use O2 faster than it can be delivered by the respiratory and circula ...
Photosynthesis Modeling Activity
... ● four rectangles, each with one of these chemical formulas: C6H12O6, CO2, H2O, and O2, and the name of the molecule that each chemical formula represents ● one rectangle with → to represent a chemical reaction ● two rectangles with + ● one rectangle with sunlight 1. Arrange the eight rectangles for ...
... ● four rectangles, each with one of these chemical formulas: C6H12O6, CO2, H2O, and O2, and the name of the molecule that each chemical formula represents ● one rectangle with → to represent a chemical reaction ● two rectangles with + ● one rectangle with sunlight 1. Arrange the eight rectangles for ...
Accelerated Analysis of Amino Acids in Physiological
... Figure 1. Plasma sample containing unusual amino acids. 570nm and 440nm channel. ...
... Figure 1. Plasma sample containing unusual amino acids. 570nm and 440nm channel. ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.