Fall 2009 Chem 306 Exam II KEY
... 45. Electrophoresis is a laboratory method a. used to determine enzyme activity b. that allows for the identification of amino acids and proteins. c. that is based on the differential migration of charged species within an electrical field. d. which is used to help diagnose diseases such as sickle ...
... 45. Electrophoresis is a laboratory method a. used to determine enzyme activity b. that allows for the identification of amino acids and proteins. c. that is based on the differential migration of charged species within an electrical field. d. which is used to help diagnose diseases such as sickle ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism - BITS Academic Resource Center
... Carbohydrate Metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism is a fundamental biochemical process that ensures a constant supply of energy to living cells. The most important carbohydrate is glucose, which can be broken down via glycolysis, enter into the Kreb's cycle and oxidative phosphorylation to generate A ...
... Carbohydrate Metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism is a fundamental biochemical process that ensures a constant supply of energy to living cells. The most important carbohydrate is glucose, which can be broken down via glycolysis, enter into the Kreb's cycle and oxidative phosphorylation to generate A ...
Practice photosynthesis/Respiration
... A) energy released as electrons flow through the electron transport system B) No external source of energy is required because the reaction is exergonic. C) energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase D) energy released from substrate-level phosphorylation E) energy released from A ...
... A) energy released as electrons flow through the electron transport system B) No external source of energy is required because the reaction is exergonic. C) energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase D) energy released from substrate-level phosphorylation E) energy released from A ...
Physiology 8 Endocrine and Gastroenterology
... a) standard unit of heat energy necessary to raise the temperature of 1L of water 1° from 15-16°C b) standard unit of heat energy necessary to raise the temperature of 1gm of mercury 1° from 17-18°C c) the standard unit of heat energy necessary to raise the temperature of 1gm of water 1° from 17-18° ...
... a) standard unit of heat energy necessary to raise the temperature of 1L of water 1° from 15-16°C b) standard unit of heat energy necessary to raise the temperature of 1gm of mercury 1° from 17-18°C c) the standard unit of heat energy necessary to raise the temperature of 1gm of water 1° from 17-18° ...
Glucose
... Glycogen is stored hydrated with water; thus the water makes glycogen large, cumbersome, and unsuitable for long-term energy storage. The 70-kg "average" man stores only an IS-hour fuel supply as glycogen, compared with a 2-month supply stored as fat. If all human energy stores were glycogen, humans ...
... Glycogen is stored hydrated with water; thus the water makes glycogen large, cumbersome, and unsuitable for long-term energy storage. The 70-kg "average" man stores only an IS-hour fuel supply as glycogen, compared with a 2-month supply stored as fat. If all human energy stores were glycogen, humans ...
DIETARY GUIDANCE SYSTEM
... about food products, including dietary supplements. • If you think you have suffered a ...
... about food products, including dietary supplements. • If you think you have suffered a ...
Krebs Cycle - USD Home Pages
... • Szent-‐Gyorgyi determined the catalytic affect of small amounts of future TCA intermediates • Knoop (also key in fatty acid metabolism) the formation of citrate form OAA and Pyruvate • Krebs found a ...
... • Szent-‐Gyorgyi determined the catalytic affect of small amounts of future TCA intermediates • Knoop (also key in fatty acid metabolism) the formation of citrate form OAA and Pyruvate • Krebs found a ...
Industrial Biotechnology
... • In case of isosteic inhibition the inhibitor and substrate have the same molecular conformation. • Feedback inhibition can be explained on an enzymatic level by the structure of the enzyme molecule. • Such enzymes have two type of protein sub-units. • The binding site on the sub-unit binds to the ...
... • In case of isosteic inhibition the inhibitor and substrate have the same molecular conformation. • Feedback inhibition can be explained on an enzymatic level by the structure of the enzyme molecule. • Such enzymes have two type of protein sub-units. • The binding site on the sub-unit binds to the ...
Advances around technologies investigating mitochondrial function
... The mitochondrion is an intracellular organelle that plays a central role in the metabolism. Here are the Krebs cycle enzymes and the electron transfer chain (ETC) enzymes, which transduce energy substrates into a usable form of energy, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and heat. Mitochondrion literally ...
... The mitochondrion is an intracellular organelle that plays a central role in the metabolism. Here are the Krebs cycle enzymes and the electron transfer chain (ETC) enzymes, which transduce energy substrates into a usable form of energy, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and heat. Mitochondrion literally ...
get fit for sport - The Irish Sports Council
... Specific training can affect the strength, power, or endurance of muscles: i. Muscle strength is the amount of force a muscle can produce. Strength can be improved in two ways. Firstly you can train a muscle to exert more force (or lift a heavier weight) by practicing the movement (or lift) so that ...
... Specific training can affect the strength, power, or endurance of muscles: i. Muscle strength is the amount of force a muscle can produce. Strength can be improved in two ways. Firstly you can train a muscle to exert more force (or lift a heavier weight) by practicing the movement (or lift) so that ...
Self Assessment Chapter 2, part 2 - CM
... Energy is found in 3 forms in the human body; chemical, electrical, and mechanical, each of which may be potential or kinetic depending on location or process • Chemical energy – found in bonds between atoms; drives nearly all chemical processes • Electrical energy – generated by movement of charged ...
... Energy is found in 3 forms in the human body; chemical, electrical, and mechanical, each of which may be potential or kinetic depending on location or process • Chemical energy – found in bonds between atoms; drives nearly all chemical processes • Electrical energy – generated by movement of charged ...
Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
... It is to make and break bonds to generate ATP and electrons. You end up with ATP, H ions and electrons. The electrons are sent to the Electron Transport Chain where they help to make ATP through ATP synthase. ****Hydrogen ions are bonded with oxygen to make water which is used in photosynthesis. ...
... It is to make and break bonds to generate ATP and electrons. You end up with ATP, H ions and electrons. The electrons are sent to the Electron Transport Chain where they help to make ATP through ATP synthase. ****Hydrogen ions are bonded with oxygen to make water which is used in photosynthesis. ...
Molecules of the Cell: The Building Blocks of Life
... A single polysaccharide molecule may contain hundreds or thousands of monosaccharide subunits bonded together through dehydration synthesis reactions. One example of an “energy polysaccharide” is starch, which is composed exclusively of glucose molecules ( Figure 3.3b ). Starch is typically found i ...
... A single polysaccharide molecule may contain hundreds or thousands of monosaccharide subunits bonded together through dehydration synthesis reactions. One example of an “energy polysaccharide” is starch, which is composed exclusively of glucose molecules ( Figure 3.3b ). Starch is typically found i ...
free energy
... Substrate Specificity of Enzymes • The reactant that an enzyme acts on is called the enzyme’s substrate • The enzyme binds to its substrate, forming an enzyme-substrate complex • The active site is the region on the enzyme where the substrate binds • Induced fit of a substrate brings chemical group ...
... Substrate Specificity of Enzymes • The reactant that an enzyme acts on is called the enzyme’s substrate • The enzyme binds to its substrate, forming an enzyme-substrate complex • The active site is the region on the enzyme where the substrate binds • Induced fit of a substrate brings chemical group ...
Phase-I metabolism
... Oxidative Phase-I involving cytochrome P-450 enzymes: • N-oxidation: – Mostly for primary and secondary amines as well as aromatic amines: – This gives N-oxide that will be rapidly converted to hydroxylamines. ...
... Oxidative Phase-I involving cytochrome P-450 enzymes: • N-oxidation: – Mostly for primary and secondary amines as well as aromatic amines: – This gives N-oxide that will be rapidly converted to hydroxylamines. ...
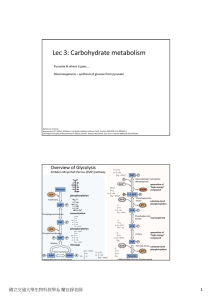
Lec 3: Carbohydrate metabolism
... Lots of heme‐containing mitochondria, used in aerobic metabolism ...
... Lots of heme‐containing mitochondria, used in aerobic metabolism ...
File
... • Necessary reaction for the metabolism of sulfurcontaining amino acids (methionine and cysteine) • Xanthine oxidase: • catalyzes the breakdown of nucleotides (precursors to DNA and RNA) to form uric acid • Uric acid contributes to the plasma antioxidant capacity of the blood Shariq AIKC/SYB/2014 ...
... • Necessary reaction for the metabolism of sulfurcontaining amino acids (methionine and cysteine) • Xanthine oxidase: • catalyzes the breakdown of nucleotides (precursors to DNA and RNA) to form uric acid • Uric acid contributes to the plasma antioxidant capacity of the blood Shariq AIKC/SYB/2014 ...
Unfinished business from April 4!
... b, Part of a expanded to indicate carbon skeletons and to define relationships between V PDH (flux through PDH complex); V X (additional CO2 production by the OPPP, the TCA, and so on); V Rub (refixation by Rubisco). Metabolites: Ac-CoA, acetyl coenzymeA; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone-3-phosphate; E4P, ery ...
... b, Part of a expanded to indicate carbon skeletons and to define relationships between V PDH (flux through PDH complex); V X (additional CO2 production by the OPPP, the TCA, and so on); V Rub (refixation by Rubisco). Metabolites: Ac-CoA, acetyl coenzymeA; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone-3-phosphate; E4P, ery ...
Mixotrophic and photoheterotrophic metabolism in
... derivatives and organic acids from central metabolic pathways, respectively) on Cyanothece 51142 growth and metabolism. Two nitrogen sources other than N2, ammonia and nitrate, were also examined. Precise readouts of metabolic state and activity were based on 13C-assisted metabolite analysis integra ...
... derivatives and organic acids from central metabolic pathways, respectively) on Cyanothece 51142 growth and metabolism. Two nitrogen sources other than N2, ammonia and nitrate, were also examined. Precise readouts of metabolic state and activity were based on 13C-assisted metabolite analysis integra ...
Respiration: ATP - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... of a cell. After many steps, the 6-carbon (hexose) glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, each with three carbon atoms. Energy from ATP is needed in the first two steps, called phosphorylation, but energy that can be used to make ATP is released in the later stages. Glycolysis is summa ...
... of a cell. After many steps, the 6-carbon (hexose) glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, each with three carbon atoms. Energy from ATP is needed in the first two steps, called phosphorylation, but energy that can be used to make ATP is released in the later stages. Glycolysis is summa ...
f212 biological molecules
... • Carbon is able to make 4 covalent bonds • Carbon can bond to form chains or rings with other atoms bonded to the chain • Carbon can also form double bonds – E.g. C=C or C=O ...
... • Carbon is able to make 4 covalent bonds • Carbon can bond to form chains or rings with other atoms bonded to the chain • Carbon can also form double bonds – E.g. C=C or C=O ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.