03-232 Exam III 2013 Name:__________________________
... and the TCA cycle because these pathways generate energy and none is needed. These pathways are turned on when the cell needs energy, as indicated by high AMP and ADP levels. Example, PFK in glycolysis is activated by AMP and ADP but inhibited by ATP. Pyruvate dehydrogenase and citrate synthase are ...
... and the TCA cycle because these pathways generate energy and none is needed. These pathways are turned on when the cell needs energy, as indicated by high AMP and ADP levels. Example, PFK in glycolysis is activated by AMP and ADP but inhibited by ATP. Pyruvate dehydrogenase and citrate synthase are ...
information on this product
... (GH) secretagogues, arginine and ornithine. These specific amino acids have been found to promote natural GH release from the pituitary gland. GH promotes an anabolic metabolism throughout the body, helping to maintain protein synthesis within cells. In a controlled trial, when arginine and ornithin ...
... (GH) secretagogues, arginine and ornithine. These specific amino acids have been found to promote natural GH release from the pituitary gland. GH promotes an anabolic metabolism throughout the body, helping to maintain protein synthesis within cells. In a controlled trial, when arginine and ornithin ...
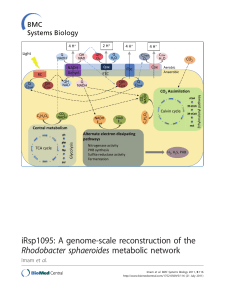
iRsp1095: A genome-scale reconstruction of the Rhodobacter
... hydrocarbons, as well as its ability to utilize atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) as a carbon source under defined conditions, make it an excellent candidate for use in a wide variety of biotechnological applications. A genomelevel understanding of its metabolic capabilities should help realize this ...
... hydrocarbons, as well as its ability to utilize atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) as a carbon source under defined conditions, make it an excellent candidate for use in a wide variety of biotechnological applications. A genomelevel understanding of its metabolic capabilities should help realize this ...
energy and enzymes - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... An animal’s use of the sun’s radiant energy begins with photosynthetic plants (and certain microorganisms) “capturing” that energy and converting it to chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates. Because plants capture the sun’s energy, they are primary producers. A primary consumer is a plant-eat ...
... An animal’s use of the sun’s radiant energy begins with photosynthetic plants (and certain microorganisms) “capturing” that energy and converting it to chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates. Because plants capture the sun’s energy, they are primary producers. A primary consumer is a plant-eat ...
SUPERCRITICAL CO EXTRACTION OF HEMP (Cannabis sativa L
... Supercritical extraction and fractionation of natural compounds is one of the early and most studied applications in the field of supercritical fluids. Fractionation of the oil is very important for producing products with physical or nutritional properties of interest to the food industry. Supercri ...
... Supercritical extraction and fractionation of natural compounds is one of the early and most studied applications in the field of supercritical fluids. Fractionation of the oil is very important for producing products with physical or nutritional properties of interest to the food industry. Supercri ...
Stryer An overview of the citric acid cycle
... 1. 26/104 amino acids residues have been invariant for > 1.5 x 109 years. 2. Met 80 and His 18 - coordinate Fe. 3. 11 residues from number 70 - 80 lining a hydrophobic crevice have remained virtually unchanged throughout all cytochrome c regardless of species or even kingdom. 4. A number of invarian ...
... 1. 26/104 amino acids residues have been invariant for > 1.5 x 109 years. 2. Met 80 and His 18 - coordinate Fe. 3. 11 residues from number 70 - 80 lining a hydrophobic crevice have remained virtually unchanged throughout all cytochrome c regardless of species or even kingdom. 4. A number of invarian ...
Student notes in ppt
... Compounds that accept electrons are called oxidants and are reduced in the reaction, whereas compounds that donate electrons are called reductants and are oxidized by loss of electrons. Each half reaction consists of a conjugate redox pair represented by a molecule with and without an electron (e-). ...
... Compounds that accept electrons are called oxidants and are reduced in the reaction, whereas compounds that donate electrons are called reductants and are oxidized by loss of electrons. Each half reaction consists of a conjugate redox pair represented by a molecule with and without an electron (e-). ...
Triacylglycerol Metabolism Gone Bad: A major cause of disease
... • Other components are added to the VLDL in the blood. ...
... • Other components are added to the VLDL in the blood. ...
Fundamentals of Biochemistry. Life at the Molecular Level. 3rd Edition Brochure
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2242601/ ...
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/2242601/ ...
Bil 255 – CMB
... 1. oxidation of COOH end of free fatty acid 2. transport of fatty acyl-coA into mitoplasm 3. oxidation of 2 carbon fragments as AcoA ...
... 1. oxidation of COOH end of free fatty acid 2. transport of fatty acyl-coA into mitoplasm 3. oxidation of 2 carbon fragments as AcoA ...
Chapter 16
... 15. Although the oxaloacetate formation form L-malate is relatively high endergonic reaction, this reaction occurs, because: 1. The [oxaloacetate] is very low at equilibrium. 2. The subsequent reaction is highly exergonic hydrolysis of the “high energy” S~C bond of acetyl-CoA. This is a reason why a ...
... 15. Although the oxaloacetate formation form L-malate is relatively high endergonic reaction, this reaction occurs, because: 1. The [oxaloacetate] is very low at equilibrium. 2. The subsequent reaction is highly exergonic hydrolysis of the “high energy” S~C bond of acetyl-CoA. This is a reason why a ...
Slide 1
... Cellular respiration is an exergonic process that transfers energy from the bonds in glucose to form ATP. Cellular respiration – produces up to 32 ATP molecules from each glucose molecule and – captures only about 34% of the energy originally stored in glucose. ...
... Cellular respiration is an exergonic process that transfers energy from the bonds in glucose to form ATP. Cellular respiration – produces up to 32 ATP molecules from each glucose molecule and – captures only about 34% of the energy originally stored in glucose. ...
Sequence Specific Modeling of E. coli Cell-Free Protein
... of RNA polymerase, ribosomes, transcription and translation elongation rates, as well as the upper bounds on oxygen and glucose consumption rates (modeled as being normally distributed around the parameter values shown in Table 2), did not qualitatively alter the performance of the model (blue regio ...
... of RNA polymerase, ribosomes, transcription and translation elongation rates, as well as the upper bounds on oxygen and glucose consumption rates (modeled as being normally distributed around the parameter values shown in Table 2), did not qualitatively alter the performance of the model (blue regio ...
FREE Sample Here
... unsaturated fatty acids. In comparison with the original oil, the new fatty acids have additional double carbon–carbon bonds, replacing what were once single bonds. This process could also be described as _____________. (a) isomerization. (b) oxidation. (c) reduction. (d) protonation. ...
... unsaturated fatty acids. In comparison with the original oil, the new fatty acids have additional double carbon–carbon bonds, replacing what were once single bonds. This process could also be described as _____________. (a) isomerization. (b) oxidation. (c) reduction. (d) protonation. ...
Citric acid cycle ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN AND
... 6.12 Chemiosmosis powers most ATP production • The electrons from NADH and FADH2 travel down the electron transport chain to oxygen • Energy released by the electrons is used to pump H+ into the space between the ...
... 6.12 Chemiosmosis powers most ATP production • The electrons from NADH and FADH2 travel down the electron transport chain to oxygen • Energy released by the electrons is used to pump H+ into the space between the ...
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Pathways in Methylomicrobium buryatense
... homologous to typical Type II fatty acid biosynthesis pathways could be annotated by bioinformatics analyses, with the exception of fatty acid transport and regulatory elements. Different approaches for improving fatty acid accumulation were investigated. These studies indicated that both fatty acid ...
... homologous to typical Type II fatty acid biosynthesis pathways could be annotated by bioinformatics analyses, with the exception of fatty acid transport and regulatory elements. Different approaches for improving fatty acid accumulation were investigated. These studies indicated that both fatty acid ...
Bioenergetics and Metabolism
... 4. What are examples of glycolysis in real life? Glycolysis is the sole source of ATP under anaerobic conditions which can occur in animal muscle tissue during intense exercise. Fermentation also relies on glycolysis which is a process that is used to make alcoholic beverages when yeast cells are pr ...
... 4. What are examples of glycolysis in real life? Glycolysis is the sole source of ATP under anaerobic conditions which can occur in animal muscle tissue during intense exercise. Fermentation also relies on glycolysis which is a process that is used to make alcoholic beverages when yeast cells are pr ...
of Glycolysis
... CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Clinical importance of Glucose Glucose‐preferred source of energy for most tissues. Brain cells derive energy mainly from glucose. Normal fasting glucose levels‐‐‐70‐ 110mg/dL ...
... CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Clinical importance of Glucose Glucose‐preferred source of energy for most tissues. Brain cells derive energy mainly from glucose. Normal fasting glucose levels‐‐‐70‐ 110mg/dL ...
Mary Jones Jennifer Gregory - Assets
... In the past, the bonds attaching the two outer phosphate groups have been called ‘high-energy bonds’, because more energy is released when they are broken than when the last phosphate is removed. This is misleading and should be The structure of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is avoided since the ener ...
... In the past, the bonds attaching the two outer phosphate groups have been called ‘high-energy bonds’, because more energy is released when they are broken than when the last phosphate is removed. This is misleading and should be The structure of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is avoided since the ener ...
Lipid Metabolism: Power Point presentation
... RCH2CH2CH2C SCoA Cycle repeats, removing two carbons each time and ...
... RCH2CH2CH2C SCoA Cycle repeats, removing two carbons each time and ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.