Digestive Systems
... that are used by living organisms and cells to handle nutrients after they have been absorbed from the digestive system ...
... that are used by living organisms and cells to handle nutrients after they have been absorbed from the digestive system ...
Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids
... Repetition of the Beta Oxidation Cycle The shortened fatty acyl-CoA that was the ...
... Repetition of the Beta Oxidation Cycle The shortened fatty acyl-CoA that was the ...
Week III Lecture I slides
... Oxygen molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane into the cell, then into the mitochondria ...
... Oxygen molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane into the cell, then into the mitochondria ...
Events of The Krebs Cycle
... The conversion of pyruvic acid to acetyl COA is a three step process: 1. First, each of the two pyruvic acids are decarboxylated . At this point, two carbon dioxides are produced and diffuse to the blood. This event yields two acetyl groups. 2. Next, hydrogen is removed from each acetyl group and ad ...
... The conversion of pyruvic acid to acetyl COA is a three step process: 1. First, each of the two pyruvic acids are decarboxylated . At this point, two carbon dioxides are produced and diffuse to the blood. This event yields two acetyl groups. 2. Next, hydrogen is removed from each acetyl group and ad ...
1 A Comparative, Double-blind, Triple Crossover Net Nitrogen
... N balance represents the difference between the Intake (I) and output (O) of N. The N balance could be positive (I > O), when the N intake is higher than its output (N retention), as in active growth and during pregnancy; it could be negative (I < O), when N intake is less than its output (N loss), ...
... N balance represents the difference between the Intake (I) and output (O) of N. The N balance could be positive (I > O), when the N intake is higher than its output (N retention), as in active growth and during pregnancy; it could be negative (I < O), when N intake is less than its output (N loss), ...
Chapter 9
... Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2 ...
... Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2 ...
CHAPTER 2 - PULMONARY FUNCTION, TRANSPORT OF BLOOD
... c) Explain how oxygen is exchanged between the blood and active muscle tissues. Answer • Gas molecules, such as oxygen, diffuse from high to low pressure - called a diffusion gradient. • Arriving oxygen partial pressure (pO2) in arterial blood is greater than oxygen partial presure in tissu ...
... c) Explain how oxygen is exchanged between the blood and active muscle tissues. Answer • Gas molecules, such as oxygen, diffuse from high to low pressure - called a diffusion gradient. • Arriving oxygen partial pressure (pO2) in arterial blood is greater than oxygen partial presure in tissu ...
Systems-level metabolic flux profiling identifies fatty acid synthesis as a target for anti-viral therapy.
... large changes in metabolite concentrations first appear18. A battery of five assays was used: (i) direct measurement of key cellular metabolic influxes (glucose and glutamine) and effluxes (pyruvate, lactate, alanine and glutamate), (ii) kinetic flux profiling with uniformly 13C-labeled glucose, (ii ...
... large changes in metabolite concentrations first appear18. A battery of five assays was used: (i) direct measurement of key cellular metabolic influxes (glucose and glutamine) and effluxes (pyruvate, lactate, alanine and glutamate), (ii) kinetic flux profiling with uniformly 13C-labeled glucose, (ii ...
Energetics and carbon metabolism during growth
... to quantitatively assess intracellular fluxes through the main metabolic pathways of microalgal cells [10,11]. The performance of microalgal culture systems can be evaluated and compared through the efficiency with which the supplied energy to the culture can be utilized for biomass production [12]. ...
... to quantitatively assess intracellular fluxes through the main metabolic pathways of microalgal cells [10,11]. The performance of microalgal culture systems can be evaluated and compared through the efficiency with which the supplied energy to the culture can be utilized for biomass production [12]. ...
Build a Better Body with BCAA`s(Branched Chain Amino Acids)
... Whey, casein, and even soy are typically tossed around as the protein powders of choice for people who want to pack on muscle. And, there's evidence they all work. However, BCAA's play an equally important role in maximizing muscle gains. BCAA's work primarily by preventing muscle breakdown in the r ...
... Whey, casein, and even soy are typically tossed around as the protein powders of choice for people who want to pack on muscle. And, there's evidence they all work. However, BCAA's play an equally important role in maximizing muscle gains. BCAA's work primarily by preventing muscle breakdown in the r ...
Chapter 3: Energy, Catalysis, and Biosynthesis
... Roommate 2 counters that maintaining an organized environment makes life easier in many ways, and that chaos is not inevitable. What law of thermodynamics drives the thinking of roommate 1? What thermodynamic argument can be used to support roommate 2? ...
... Roommate 2 counters that maintaining an organized environment makes life easier in many ways, and that chaos is not inevitable. What law of thermodynamics drives the thinking of roommate 1? What thermodynamic argument can be used to support roommate 2? ...
Student Study Guide
... will now examine how the oxidation of this glucose during cellular respiration is used to drive the production of ATP (the fuel source of cells). Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are key ecological concepts involved with energy flow. Photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy ( ...
... will now examine how the oxidation of this glucose during cellular respiration is used to drive the production of ATP (the fuel source of cells). Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are key ecological concepts involved with energy flow. Photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy ( ...
Chapter 4 - Jenkins Independent Schools
... other atoms. When carbon atoms form covalent bonds, they obtain the stability of a noble gas with eight electrons in their outer energy level. One of carbon’s most frequent partners in forming covalent bonds is hydrogen. Substances can be classified into two groups—those derived from living things a ...
... other atoms. When carbon atoms form covalent bonds, they obtain the stability of a noble gas with eight electrons in their outer energy level. One of carbon’s most frequent partners in forming covalent bonds is hydrogen. Substances can be classified into two groups—those derived from living things a ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway - Lectures For UG-5
... • The pathway provides a major portion of the body's NADPH, which functions as a biochemical reductant. • It also produces ribose 5-phosphate, required for the biosynthesis of nucleotides, and provides a mechanism for the metabolic use of five-carbon sugars obtained from the diet or the degradation ...
... • The pathway provides a major portion of the body's NADPH, which functions as a biochemical reductant. • It also produces ribose 5-phosphate, required for the biosynthesis of nucleotides, and provides a mechanism for the metabolic use of five-carbon sugars obtained from the diet or the degradation ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... 26. (Page 25.) List several structural features that white muscle cells have that explains why these muscle fibers mainly use glycolysis to synthesize ATP (as opposed to the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation). 27. (Page 26.) Why are white muscle fibers also called "fast-twitch glycolytic fib ...
... 26. (Page 25.) List several structural features that white muscle cells have that explains why these muscle fibers mainly use glycolysis to synthesize ATP (as opposed to the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation). 27. (Page 26.) Why are white muscle fibers also called "fast-twitch glycolytic fib ...
Biochemie jater
... The alcohol content of alcoholic beverages Ethanol is rapidly taken up from the digestive Given as percent by volume (conversion to tract by diffusion gram ethanol, density = 0,79 kg/l) The maximum blood alcohol level is reached A bottle of beer: 0,5l with 4% alcohol contains within 60-90 minute ...
... The alcohol content of alcoholic beverages Ethanol is rapidly taken up from the digestive Given as percent by volume (conversion to tract by diffusion gram ethanol, density = 0,79 kg/l) The maximum blood alcohol level is reached A bottle of beer: 0,5l with 4% alcohol contains within 60-90 minute ...
Muscle Metabolism - Interactive Physiology
... 26. (Page 25.) List several structural features that white muscle cells have that explains why these muscle fibers mainly use glycolysis to synthesize ATP (as opposed to the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation). 27. (Page 26.) Why are white muscle fibers also called "fast-twitch glycolytic fib ...
... 26. (Page 25.) List several structural features that white muscle cells have that explains why these muscle fibers mainly use glycolysis to synthesize ATP (as opposed to the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation). 27. (Page 26.) Why are white muscle fibers also called "fast-twitch glycolytic fib ...
Handout: Fatty Acid Synthesis
... 28.2 Elongation and Desaturation C16:0 to C18:n – C20:n Elongation occurs with enzymes on the cytosolic face of the ER membrane. This is done by elongases that use malonyl-CoA to add the 2-carbon subunits. Oxidase ...
... 28.2 Elongation and Desaturation C16:0 to C18:n – C20:n Elongation occurs with enzymes on the cytosolic face of the ER membrane. This is done by elongases that use malonyl-CoA to add the 2-carbon subunits. Oxidase ...
HA Convention 2016 Master course How to Handle Abnormal
... – a class of genetic disorders with defects of metabolism which are mostly due to single gene defects resulting in defective function of particular enzymes that are essential for conversion of substrates into products. ...
... – a class of genetic disorders with defects of metabolism which are mostly due to single gene defects resulting in defective function of particular enzymes that are essential for conversion of substrates into products. ...
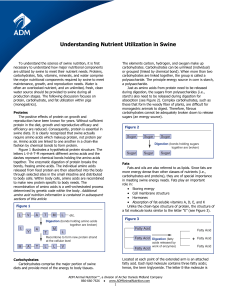
Nutrient Utilization in Swine
... the pig’s body in sufficient quantities and are referred to as non-essential amino acids. The other ten amino acids that cannot be synthesized or cannot be synthesized at a sufficient rate to enable optimal growth or reproduction must be provided in the diet for proper growth or reproduction. These ...
... the pig’s body in sufficient quantities and are referred to as non-essential amino acids. The other ten amino acids that cannot be synthesized or cannot be synthesized at a sufficient rate to enable optimal growth or reproduction must be provided in the diet for proper growth or reproduction. These ...
Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy
... 1. Describe the process of glycolysis. 2. State the reactants and products of glycolysis. ...
... 1. Describe the process of glycolysis. 2. State the reactants and products of glycolysis. ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.