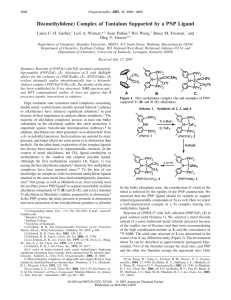
Hybridization of atomic orbitals In general VSEPR predicts the
... In general VSEPR predicts the shape of molecules and ions accurately CH4 : tetrahedral Four equal bonds with equal HCH angles A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons by two atoms Imagine an orbital (containing 1 electron) from one atom overlaps with an orbital from the other atom to form ...
... In general VSEPR predicts the shape of molecules and ions accurately CH4 : tetrahedral Four equal bonds with equal HCH angles A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons by two atoms Imagine an orbital (containing 1 electron) from one atom overlaps with an orbital from the other atom to form ...
3 center 4 electron bond article
... can be extended to the study of bonding in SF6 and PF6–. Unlike the pentacoordinated AB5-type molecules (D3h symmetry), in the hexacoordinated AB6-type molecules such as SF6 and PF6– (Oh symmetry), the six fluorine ligands approach to the central sulfur or phosphorus atom along the x, y, and z axes ...
... can be extended to the study of bonding in SF6 and PF6–. Unlike the pentacoordinated AB5-type molecules (D3h symmetry), in the hexacoordinated AB6-type molecules such as SF6 and PF6– (Oh symmetry), the six fluorine ligands approach to the central sulfur or phosphorus atom along the x, y, and z axes ...
Suggested Problems for Chapter 1
... Please write your name above and on the back of the last page. ...
... Please write your name above and on the back of the last page. ...
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II
... of the starting material reacts in such a way that it gives a specific stereoisomeric form of the product l Example: cis- and trans-2-butene give stereoisomeric products ...
... of the starting material reacts in such a way that it gives a specific stereoisomeric form of the product l Example: cis- and trans-2-butene give stereoisomeric products ...
Covalent Bonding 5 Practice Problems
... Caffeine has the formula C8H10N4O2. A model of caffeine is shown below. Atoms without symbols are hydrogen atoms. ...
... Caffeine has the formula C8H10N4O2. A model of caffeine is shown below. Atoms without symbols are hydrogen atoms. ...
Mechanism of the oxymercuration of substituted cyclohexenes
... and other reactions32led us to investigate the stereochemical aspects of the oxymercuration of a series of substituted cyclohexenes, and to compare the stereochemical course of the oxymercuration reaction with other electrophilic addition reactions known to proceed via onium ion-type intermediates a ...
... and other reactions32led us to investigate the stereochemical aspects of the oxymercuration of a series of substituted cyclohexenes, and to compare the stereochemical course of the oxymercuration reaction with other electrophilic addition reactions known to proceed via onium ion-type intermediates a ...
Ionization Potential and Structure Relaxation of Adenine, Thymine
... magnitude and the nature of the interactions of the biomolecules and is consequently responsible for the important unique properties of nucleic acids [12]. The stability of DNA and RNA structure is not only due to the H-bond base pairing, but also the base stacking, which is actually an interaction ...
... magnitude and the nature of the interactions of the biomolecules and is consequently responsible for the important unique properties of nucleic acids [12]. The stability of DNA and RNA structure is not only due to the H-bond base pairing, but also the base stacking, which is actually an interaction ...
Nickel(II) cis- and trans-Dimethyl Complexes of
... monitoring the decrease of the Me resonance in the 1H NMR spectrum relative to an internal reference of maleic anhydride flame-sealed in a glass capillary. Decomposition of 2 displayed first-order kinetics and was independent of the concentration of 2 and the addition of excess tBuCCeth, as shown in ...
... monitoring the decrease of the Me resonance in the 1H NMR spectrum relative to an internal reference of maleic anhydride flame-sealed in a glass capillary. Decomposition of 2 displayed first-order kinetics and was independent of the concentration of 2 and the addition of excess tBuCCeth, as shown in ...
The Chemistry of Alkyl Halides - Welcome to people.pharmacy
... The SN1 product A, derived from the Lewis acid–base association reaction of solvent with the first-formed carbocation, should have largely inverted configuration at carbon-2, because the carbocation will be a backside-solvated ion pair; this carbocation will react faster with the solvent molecule th ...
... The SN1 product A, derived from the Lewis acid–base association reaction of solvent with the first-formed carbocation, should have largely inverted configuration at carbon-2, because the carbocation will be a backside-solvated ion pair; this carbocation will react faster with the solvent molecule th ...
Naming Compounds
... Solubilized – meaning dissolved in water, and therefore, usually represented with an (aq) phase symbol Hydrates – ionic salts with water molecules weakly attached Organic – carbon based in which C is covalently bonded, mainly with hydrogen (H). However, organic compounds may at times contain some ni ...
... Solubilized – meaning dissolved in water, and therefore, usually represented with an (aq) phase symbol Hydrates – ionic salts with water molecules weakly attached Organic – carbon based in which C is covalently bonded, mainly with hydrogen (H). However, organic compounds may at times contain some ni ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... Alkyl halides are defined as primary if the carbon that the halogen is attached to is directly attached to one other carbon. Similarly if the carbon that the halogen is attached to is directly attached to two carbons then it is a secondary alkyl halide. In tertiary alkyl halides the carbon with the ...
... Alkyl halides are defined as primary if the carbon that the halogen is attached to is directly attached to one other carbon. Similarly if the carbon that the halogen is attached to is directly attached to two carbons then it is a secondary alkyl halide. In tertiary alkyl halides the carbon with the ...
RESONANCE AND INDUCTION TUTORIAL Jack DeRuiter The
... Resonance differs from the two examples above in that it involves the sharing of electrons between more than two atoms via delocalization. The classical example of resonance is provided by the pi-bonding system of benzene. Benzene is a six membered ring composed of six sp2 hybridized carbon atoms in ...
... Resonance differs from the two examples above in that it involves the sharing of electrons between more than two atoms via delocalization. The classical example of resonance is provided by the pi-bonding system of benzene. Benzene is a six membered ring composed of six sp2 hybridized carbon atoms in ...
On the Chromophore of the Ninhydrin
... The aim o f this paper is to attach the Chromo phore to the dye structure. We propose that the conjugated five-membered rings having partial anti-aromatic character cause the unusual longwavelength absorption. In former papers [7 -1 0 ] we have presented our investigations on colored com pounds wit ...
... The aim o f this paper is to attach the Chromo phore to the dye structure. We propose that the conjugated five-membered rings having partial anti-aromatic character cause the unusual longwavelength absorption. In former papers [7 -1 0 ] we have presented our investigations on colored com pounds wit ...
Organometallics - X-Ray - University of Kentucky
... this distance is similar to the TadC distances in the range 1.932.00 Å for (mesityl)(Me3P)2Ta(dCHCMe3)2 and (Me3SiCH2)(Me3P)2Ta(dCHSiMe3),15 the other crystallographically characterized approximately trigonal-bipyramidal tantalum bis(alkylidenes). Crystallographic evidence for a T-shaped arrangement ...
... this distance is similar to the TadC distances in the range 1.932.00 Å for (mesityl)(Me3P)2Ta(dCHCMe3)2 and (Me3SiCH2)(Me3P)2Ta(dCHSiMe3),15 the other crystallographically characterized approximately trigonal-bipyramidal tantalum bis(alkylidenes). Crystallographic evidence for a T-shaped arrangement ...
Aromatic compounds
... • 3 isomers are produced by further addition of Br2 • Same will occur with chlorobenzene • Must be explained by structure of benzene ...
... • 3 isomers are produced by further addition of Br2 • Same will occur with chlorobenzene • Must be explained by structure of benzene ...
test 1 key 2325, s13
... must have alcohol (due to peak disappearing with D2O at 3.8 ppm and symmetry of other three singlets proves structure 7.(28) A combustion analysis was performed on an unknown compound A and it was determined that it contained nine carbons and eleven hydrogens in its molecular formula. Any other elem ...
... must have alcohol (due to peak disappearing with D2O at 3.8 ppm and symmetry of other three singlets proves structure 7.(28) A combustion analysis was performed on an unknown compound A and it was determined that it contained nine carbons and eleven hydrogens in its molecular formula. Any other elem ...
13C -NMR - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Protons, neutrons, and electrons all have something called “spin.” This doesn’t mean that they’re actually spinning around in tight circles like Olympian ice skaters, but they’re moving nonetheless and this movement creates a magnetic field around each particle. But for simplicity (and because Chem ...
... Protons, neutrons, and electrons all have something called “spin.” This doesn’t mean that they’re actually spinning around in tight circles like Olympian ice skaters, but they’re moving nonetheless and this movement creates a magnetic field around each particle. But for simplicity (and because Chem ...
4.9 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen Halides
... at faster rates than those proceeding via secondary carbocations. Reactions involving primary carbocations or CH3+ are rare. ...
... at faster rates than those proceeding via secondary carbocations. Reactions involving primary carbocations or CH3+ are rare. ...
Role of Amine–Cavity Interactions in Determining the Structure and
... mechanical properties. In such materials, interactions between the protonated amine and the metal−formate cavity have a large impact on the mechanical properties. We use complementary single-crystal X-ray diffraction and 1H solid state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to investigate amine−cavi ...
... mechanical properties. In such materials, interactions between the protonated amine and the metal−formate cavity have a large impact on the mechanical properties. We use complementary single-crystal X-ray diffraction and 1H solid state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to investigate amine−cavi ...
CH 908: Mass Spectrometry Lecture 3
... fluorine. The m/z=51 ion represents half the molecule. A hydrogen shift is necessary to explain the m/z=33 ion. 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane. Important differences from isomer 1 are that the m/z=51 ion is much smaller, m/z=33 is much larger, and a new strong ion at m/z=69 has appeared. Since fluorine i ...
... fluorine. The m/z=51 ion represents half the molecule. A hydrogen shift is necessary to explain the m/z=33 ion. 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane. Important differences from isomer 1 are that the m/z=51 ion is much smaller, m/z=33 is much larger, and a new strong ion at m/z=69 has appeared. Since fluorine i ...
Document
... offers to nucleophilic attack. The nucleophile must approach the alkyl halide from the side opposite the bond to the leaving group, and this approach is hindered by alkyl substituents on the carbon that is being attacked. The three hydrogens of methyl bromide offer little resistance to approach of t ...
... offers to nucleophilic attack. The nucleophile must approach the alkyl halide from the side opposite the bond to the leaving group, and this approach is hindered by alkyl substituents on the carbon that is being attacked. The three hydrogens of methyl bromide offer little resistance to approach of t ...
Small Dopant Effect on Static Grain Growth and Flow Stress in
... of 0.3–0.5 mm as summarized in Table 1. Fairly uniform and equiaxed grain structure was obtained for the present materials. As shown in our previous reports, it has been revealed with high-resolution transmission electron microscopy technique that there is no second phase such as second phase partic ...
... of 0.3–0.5 mm as summarized in Table 1. Fairly uniform and equiaxed grain structure was obtained for the present materials. As shown in our previous reports, it has been revealed with high-resolution transmission electron microscopy technique that there is no second phase such as second phase partic ...
4.5: Bonding in Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
... a. Inductive Effects: shifting of electrons in a -bond in response to the electronegativity of a nearby atom (or group). Carbon is a good electron donor. Substitution can also stabilize carbocations by donating electron density through the -bond. R ...
... a. Inductive Effects: shifting of electrons in a -bond in response to the electronegativity of a nearby atom (or group). Carbon is a good electron donor. Substitution can also stabilize carbocations by donating electron density through the -bond. R ...
Nucleophilic substitution at saturated carbon
... polarizability of the atom. Because the electrons are farther away in the larger atom, they are not held as tightly and can, therefore, move more freely toward a positive charge. As a result, the electrons are able to overlap from farther away with the orbital of carbon, as shown in Figure 10.5. Thi ...
... polarizability of the atom. Because the electrons are farther away in the larger atom, they are not held as tightly and can, therefore, move more freely toward a positive charge. As a result, the electrons are able to overlap from farther away with the orbital of carbon, as shown in Figure 10.5. Thi ...
Shielding vs. Deshielding
... When a chemical bond is placed in a external magnetic field, it will generate a local field ...
... When a chemical bond is placed in a external magnetic field, it will generate a local field ...
2-Norbornyl cation

In organic chemistry, the term 2-norbornyl cation (equivalent with 2-bicyclo-[2.2.1]heptyl cation) describes one of the three carbocations formed from derivatives of norbornane. Though 1-norbornyl and 7-norbornyl cations have been studied, the most extensive studies and vigorous debates have been centered on the exact structure of the 2-norbornyl cation.The 2-norbornyl cation has been formed from a variety of norbornane derivatives and reagents. First reports of its formation and reactivity published by Saul Winstein sparked controversy over the nature of its bonding, as he invoked a three-center two-electron bond to explain the stereoselectivity of the resulting product. Herbert C. Brown challenged this assertion on the grounds that classical resonance structures could explain the stereospecificity without needing to adapt a new perspective of bonding.Evidence of the non-classical nature of the 2-norbornyl cation grew over the course of several decades, mainly through spectroscopic data gathered using methods such as Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Crystallographic confirmation of its non-classical nature did not come until quite recently.The nature of bonding in the 2-norbornyl cation incorporated many new ideas into the field’s understanding of chemical bonds. Similarities can be seen between this cation and others, such as boranes.