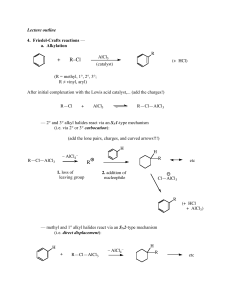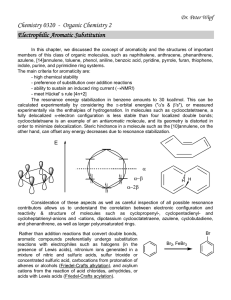
In this chapter, alkanes, alkenes, alkynes
... azulene, [14]annulene, toluene, phenol, aniline, benzoic acid, pyridine, pyrrole, furan, thiophene, indole, purine, and pyrimidine ring systems. The main criteria for aromaticity are: - high chemical stability - preference of substitution over addition reactions - ability to sustain an induced ring ...
... azulene, [14]annulene, toluene, phenol, aniline, benzoic acid, pyridine, pyrrole, furan, thiophene, indole, purine, and pyrimidine ring systems. The main criteria for aromaticity are: - high chemical stability - preference of substitution over addition reactions - ability to sustain an induced ring ...
Chemical Bonding
... » Ionic Bonding – Metal with non-metal » Covalent Bonding – Non-metal with non-metal Weak Bonds » Dipole-dipole » Hydrogen bonding » Dispersion forces ...
... » Ionic Bonding – Metal with non-metal » Covalent Bonding – Non-metal with non-metal Weak Bonds » Dipole-dipole » Hydrogen bonding » Dispersion forces ...
Chemical Bonding
... » Ionic Bonding – Metal with non-metal » Covalent Bonding – Non-metal with non-metal Weak Bonds » Dipole-dipole » Hydrogen bonding » Dispersion forces ...
... » Ionic Bonding – Metal with non-metal » Covalent Bonding – Non-metal with non-metal Weak Bonds » Dipole-dipole » Hydrogen bonding » Dispersion forces ...
Mon Feb 15 lecture
... — this pathway avoids the intermediacy of a high-E 1° cation. (This is frequently observed in carbocation chemistry; we've already seen a similar concerted rearrangement and leaving group (water) departure in the reaction of some 1° alcohols with strong acid.) ...
... — this pathway avoids the intermediacy of a high-E 1° cation. (This is frequently observed in carbocation chemistry; we've already seen a similar concerted rearrangement and leaving group (water) departure in the reaction of some 1° alcohols with strong acid.) ...
the original file
... 1. how to draw resonance structures 2. meaning of conjugated vs isolated pi bonds 3. what an orbital is 4. be able to draw MO diagrams for allyl radical and cation and benzene, such as the one in Fig. 10.2 but you dont need to know how the MOs look, just the relative energy levels and how to put in ...
... 1. how to draw resonance structures 2. meaning of conjugated vs isolated pi bonds 3. what an orbital is 4. be able to draw MO diagrams for allyl radical and cation and benzene, such as the one in Fig. 10.2 but you dont need to know how the MOs look, just the relative energy levels and how to put in ...
Ion Exchange
... Ion-exchange chromatography retains analyte molecules on the column based on coulombic (ionic) interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is an insoluble matrix no ...
... Ion-exchange chromatography retains analyte molecules on the column based on coulombic (ionic) interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is an insoluble matrix no ...
2-Norbornyl cation

In organic chemistry, the term 2-norbornyl cation (equivalent with 2-bicyclo-[2.2.1]heptyl cation) describes one of the three carbocations formed from derivatives of norbornane. Though 1-norbornyl and 7-norbornyl cations have been studied, the most extensive studies and vigorous debates have been centered on the exact structure of the 2-norbornyl cation.The 2-norbornyl cation has been formed from a variety of norbornane derivatives and reagents. First reports of its formation and reactivity published by Saul Winstein sparked controversy over the nature of its bonding, as he invoked a three-center two-electron bond to explain the stereoselectivity of the resulting product. Herbert C. Brown challenged this assertion on the grounds that classical resonance structures could explain the stereospecificity without needing to adapt a new perspective of bonding.Evidence of the non-classical nature of the 2-norbornyl cation grew over the course of several decades, mainly through spectroscopic data gathered using methods such as Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Crystallographic confirmation of its non-classical nature did not come until quite recently.The nature of bonding in the 2-norbornyl cation incorporated many new ideas into the field’s understanding of chemical bonds. Similarities can be seen between this cation and others, such as boranes.