Group B_reaction of alkenes
... •Therefore, the more stable transition state is the 1 achieved by adding the nucleophile to the more substituted sp2 carbon- carbon bonded to fewer H. • because, in this case the partial +ve charge is on a secondary carbon rather than on a primary carbon. • thus, this reaction too follows the gener ...
... •Therefore, the more stable transition state is the 1 achieved by adding the nucleophile to the more substituted sp2 carbon- carbon bonded to fewer H. • because, in this case the partial +ve charge is on a secondary carbon rather than on a primary carbon. • thus, this reaction too follows the gener ...
File
... Understand that the fragmentation of a molecular ion gives rise to a characteristic relative abundance spectrum that may give information about the structure of the molecule Know that the more stable X+ species give higher peaks, limited to carbocation and acylium (RCO+) ions Be able to use IR spect ...
... Understand that the fragmentation of a molecular ion gives rise to a characteristic relative abundance spectrum that may give information about the structure of the molecule Know that the more stable X+ species give higher peaks, limited to carbocation and acylium (RCO+) ions Be able to use IR spect ...
O - Clark College
... 1. Complete the following Lewis structures by filling in missing electrons (as lone pairs and bonds), computing formal charges, and indicating equivalent resonance structures, where they exist. The number of resonance structures that can be drawn is indicated next to the structure. For each set of s ...
... 1. Complete the following Lewis structures by filling in missing electrons (as lone pairs and bonds), computing formal charges, and indicating equivalent resonance structures, where they exist. The number of resonance structures that can be drawn is indicated next to the structure. For each set of s ...
Carbocation Stability
... electrons in this s bond can be shared by positively charged carbon because the sp3 orbital can overlap with the empty 2p orbital of positively charged carbon ...
... electrons in this s bond can be shared by positively charged carbon because the sp3 orbital can overlap with the empty 2p orbital of positively charged carbon ...
Formulas of Compounds
... 1. Now we can use names and formulas of cations and anions to write formulas of compounds. 2. In these formulas, the sum of the total cation and anion charges must be zero. 3. We use subscripts to balance the charges. 4. In most cases, we write the cation first and then the anion. (Positive first). ...
... 1. Now we can use names and formulas of cations and anions to write formulas of compounds. 2. In these formulas, the sum of the total cation and anion charges must be zero. 3. We use subscripts to balance the charges. 4. In most cases, we write the cation first and then the anion. (Positive first). ...
Lecture 21 – Cations, Anions and Hydrolysis in
... Natural waters usually have pH values between 6 and 9, so we can see from the diagram what form of phosphorous might be present. ...
... Natural waters usually have pH values between 6 and 9, so we can see from the diagram what form of phosphorous might be present. ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) ISSN: 2278-5736.
... accompanying functional group must be protected [1]. Hydroxyl group of primary secondary, tertiary, allylic or alicyclic alcohol may be protected by conversion into an ester [2], a silyl ether [3], an ester [4] or acetals and ketals [5]. The most important method for the protection 1.2 diols or 1,3 ...
... accompanying functional group must be protected [1]. Hydroxyl group of primary secondary, tertiary, allylic or alicyclic alcohol may be protected by conversion into an ester [2], a silyl ether [3], an ester [4] or acetals and ketals [5]. The most important method for the protection 1.2 diols or 1,3 ...
Chemistry 160 Th 13 Mar 2008 In-Class Worksheet A. Each of the
... Numbering of a substituent should be the lowest possible. If you number the molecule from the other end (probably from the right instead of from the left), you can also call this molecule 2,2-dimethylbutane, which is technically the correct answer. ...
... Numbering of a substituent should be the lowest possible. If you number the molecule from the other end (probably from the right instead of from the left), you can also call this molecule 2,2-dimethylbutane, which is technically the correct answer. ...
Exam 2-Answer Key
... two pi bonds and a sigma bond, each formed by a lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by overlap of two s orbitals and two pi bonds, each formed by lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by end-on overlap of two sp" orbitals and a pi bond formed by lateral overlap of ...
... two pi bonds and a sigma bond, each formed by a lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by overlap of two s orbitals and two pi bonds, each formed by lateral overlap of two p orbitals. a sigma bond formed by end-on overlap of two sp" orbitals and a pi bond formed by lateral overlap of ...
Analysis of Organic Mass Spectral Data
... location of the lone electron cannot be predicted and the formula is written to reflect this using brackets ...
... location of the lone electron cannot be predicted and the formula is written to reflect this using brackets ...
Chemical Bonding
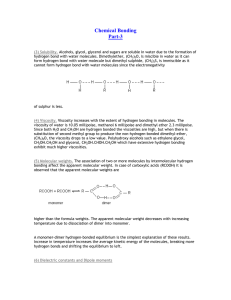
... It is generally assumed that covalent and ionic bonds are entirely distinct but this is probably not a totally valid assumption. Bonds intermediate between ionic and covalent do occur through a process of deformation or polarization. ...
... It is generally assumed that covalent and ionic bonds are entirely distinct but this is probably not a totally valid assumption. Bonds intermediate between ionic and covalent do occur through a process of deformation or polarization. ...
Chapter 12: Basic Review Worksheet
... 2. What do we mean by ionic bonding? Give an example of a substance whose particles are held together by ionic bonding. 3. What do we mean by covalent bonding and polar covalent bonding? How are these two bonding types similar, and how do they differ? 4. Define electronegativity. 5. What does it mea ...
... 2. What do we mean by ionic bonding? Give an example of a substance whose particles are held together by ionic bonding. 3. What do we mean by covalent bonding and polar covalent bonding? How are these two bonding types similar, and how do they differ? 4. Define electronegativity. 5. What does it mea ...
Guideline
... the more likely is cleavage. This is a consequence of the increased stability of a tertiary carbocation over a secondary, which in turn is more stable than a primary. Generally, the largest substituent at a branch is eliminated most readily as a radical, presumably because a long-chain radical can a ...
... the more likely is cleavage. This is a consequence of the increased stability of a tertiary carbocation over a secondary, which in turn is more stable than a primary. Generally, the largest substituent at a branch is eliminated most readily as a radical, presumably because a long-chain radical can a ...
24 Sept 08 - Seattle Central College
... – KHSO4 … K+ + HSO4- potassium hydrogen sulfate – NH4C2H3O2 … NH4+ + C2H3O2- ammonium acetate – NaH2PO3 ... Na+ + H2PO3- sodium dihydrogen phosphite ...
... – KHSO4 … K+ + HSO4- potassium hydrogen sulfate – NH4C2H3O2 … NH4+ + C2H3O2- ammonium acetate – NaH2PO3 ... Na+ + H2PO3- sodium dihydrogen phosphite ...
13c nmr questions
... QUESTION THREE There are four possible structures for an alcohol with the molecular formula C4H10O. Draw the structural formulae for all four alcohols and determine which one belongs to the following 13C NMR spectra ...
... QUESTION THREE There are four possible structures for an alcohol with the molecular formula C4H10O. Draw the structural formulae for all four alcohols and determine which one belongs to the following 13C NMR spectra ...
Unit 6 part 1 notes on Naming Compounds
... The elements are named in order they appear in the molecule. Prefixes are used to denote the number of atoms of each element. An exception is that the first element named is given a prefix only if there are more than one atom of that element in the compound. ...
... The elements are named in order they appear in the molecule. Prefixes are used to denote the number of atoms of each element. An exception is that the first element named is given a prefix only if there are more than one atom of that element in the compound. ...
CHEM 2311
... the correct answer). What is the strongest intermolecular force in the compound you circled? ...
... the correct answer). What is the strongest intermolecular force in the compound you circled? ...
CATION ANALYSIS - webhosting.au.edu
... identity of an unknown sample. Given a totally “ unknown” sample, how does one go about determining what is actually present? This process is called “ qualitative analysis”. Cations are classified into five groups on the basis of their behavior against some reagents by using group reagents; we can d ...
... identity of an unknown sample. Given a totally “ unknown” sample, how does one go about determining what is actually present? This process is called “ qualitative analysis”. Cations are classified into five groups on the basis of their behavior against some reagents by using group reagents; we can d ...
Review for Exam 1
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
... Determine how many of each ion type is needed for an overall charge of zero. When the cation and anion have different charges, use the ion charges to determine the number of ions of each needed. ...
Mass Spectrometry and Free Radicals MS recap Positive mode of
... In most cases, the radical cation will fragment. This is what generates the other peaks in the mass spectrum. This fragmentation is just free radical chemistry, like we have been previously studying. The only difference is we are starting from a radical cation. But it is the radical character that ...
... In most cases, the radical cation will fragment. This is what generates the other peaks in the mass spectrum. This fragmentation is just free radical chemistry, like we have been previously studying. The only difference is we are starting from a radical cation. But it is the radical character that ...
... these reactions to be reversible and the intermediates to be stable. We describe here the electrolytic and chemical preparation of cation radicals of various porphyrins and of ethyl chlorophyllide a as well as the formation of the dication of magnesium octaethylporphyrin. Electrolysis 3 of magnesium ...
2-Norbornyl cation

In organic chemistry, the term 2-norbornyl cation (equivalent with 2-bicyclo-[2.2.1]heptyl cation) describes one of the three carbocations formed from derivatives of norbornane. Though 1-norbornyl and 7-norbornyl cations have been studied, the most extensive studies and vigorous debates have been centered on the exact structure of the 2-norbornyl cation.The 2-norbornyl cation has been formed from a variety of norbornane derivatives and reagents. First reports of its formation and reactivity published by Saul Winstein sparked controversy over the nature of its bonding, as he invoked a three-center two-electron bond to explain the stereoselectivity of the resulting product. Herbert C. Brown challenged this assertion on the grounds that classical resonance structures could explain the stereospecificity without needing to adapt a new perspective of bonding.Evidence of the non-classical nature of the 2-norbornyl cation grew over the course of several decades, mainly through spectroscopic data gathered using methods such as Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Crystallographic confirmation of its non-classical nature did not come until quite recently.The nature of bonding in the 2-norbornyl cation incorporated many new ideas into the field’s understanding of chemical bonds. Similarities can be seen between this cation and others, such as boranes.