Chapter 7: Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes
... Ú Alkenes are hydrocarbons with C=C in their structure. They are also known as “olefins”. Ú We have already covered the basics of alkenes nomenclature, but here are a few important groups with common names that you can use as well. ...
... Ú Alkenes are hydrocarbons with C=C in their structure. They are also known as “olefins”. Ú We have already covered the basics of alkenes nomenclature, but here are a few important groups with common names that you can use as well. ...
Topic 20 specification content - A
... I can appreciate that scientists have developed a range of analytical techniques which together enable the structures of new compounds to be confirmed ...
... I can appreciate that scientists have developed a range of analytical techniques which together enable the structures of new compounds to be confirmed ...
Unit 1
... 7. To know that ionic compounds can be formed from their elements, but most often result from combination of ions that already exist in the ionic state. 8. To know that ionic bonds result from charge attractions between individual ions throughout a crystalline lattice, without significant sharing of ...
... 7. To know that ionic compounds can be formed from their elements, but most often result from combination of ions that already exist in the ionic state. 8. To know that ionic bonds result from charge attractions between individual ions throughout a crystalline lattice, without significant sharing of ...
Slides
... A proton ( H b) can be aligned with the magnetic field or against the magnetic field, resulting in two energy states for H b The observed proton (Ha ) senses the two different magnetic moments ofH b as a slight change in the magnetic field; one magnetic moment reinforces the external field and one s ...
... A proton ( H b) can be aligned with the magnetic field or against the magnetic field, resulting in two energy states for H b The observed proton (Ha ) senses the two different magnetic moments ofH b as a slight change in the magnetic field; one magnetic moment reinforces the external field and one s ...
13C NMR Spectroscopy (#1d)
... C NMR spectra cover a wide range, from 0 to about 220 ppm, where carbonyl carbons are found. The degree of substitution on a carbon has about as much effect on its chemical shift position as does the presence of an electronegative atom. Generally, sp3-hybridized carbons appear between 8-60 ppm and s ...
... C NMR spectra cover a wide range, from 0 to about 220 ppm, where carbonyl carbons are found. The degree of substitution on a carbon has about as much effect on its chemical shift position as does the presence of an electronegative atom. Generally, sp3-hybridized carbons appear between 8-60 ppm and s ...
1 Indentifying Unknown #M20 via Infrared Spectroscopy, Mass
... value that suggests a carbonyl bond because electronegative bonds appear to the far left of the spectrum. This also confirms the functional group suggested by the IR spectrum. The peaks on the right side of the spectrum (C, D, E in Table 1) have chemical shift values that suggest a ring formation. N ...
... value that suggests a carbonyl bond because electronegative bonds appear to the far left of the spectrum. This also confirms the functional group suggested by the IR spectrum. The peaks on the right side of the spectrum (C, D, E in Table 1) have chemical shift values that suggest a ring formation. N ...
Exam 1 from 2008
... d) Although this is the structure that is usually drawn for amoxicillin (e.g., see Wikipedia), it is not accurate. Considering what you know about the acid-base properties of the functional groups in Amoxicillin, draw a more accurate representation. ...
... d) Although this is the structure that is usually drawn for amoxicillin (e.g., see Wikipedia), it is not accurate. Considering what you know about the acid-base properties of the functional groups in Amoxicillin, draw a more accurate representation. ...
Structure Determination: MS, IR, and UV
... expected to fragment by a cleavage and by dehydration. These processes would lead to fragment ions of m/z = 84, 73, and 59. Of the three expected fragments, dehydration is not observed (no m/z = 84 peak), but both a cleavages take place (m/z = 73, 59). ...
... expected to fragment by a cleavage and by dehydration. These processes would lead to fragment ions of m/z = 84, 73, and 59. Of the three expected fragments, dehydration is not observed (no m/z = 84 peak), but both a cleavages take place (m/z = 73, 59). ...
Introduction - URI Chemistry
... 2-Methylpentan-3-ol, an open-chain alcohol, has M+ = 102 and might be expected to fragment by α cleavage and by dehydration. These processes would lead to fragment ions of m/z = 84, 73, and 59. Of the three expected fragments, dehydration is not observed (no m/z = 84 peak), but both α cleavages take ...
... 2-Methylpentan-3-ol, an open-chain alcohol, has M+ = 102 and might be expected to fragment by α cleavage and by dehydration. These processes would lead to fragment ions of m/z = 84, 73, and 59. Of the three expected fragments, dehydration is not observed (no m/z = 84 peak), but both α cleavages take ...
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Bonding: Ionic vs
... Guidelines for Drawing Lewis Structures Underlying criteria: “Octet Rule”: Kind of like the Pirate Code General Scheme: (CH2Cl2 and CO2 as examples) 1. Determine arrangement of atoms (skeletal structure)…HOW? • Central vs peripheral (terminal) atoms 2. Determine total # of valence e-…HOW? 3. Draw s ...
... Guidelines for Drawing Lewis Structures Underlying criteria: “Octet Rule”: Kind of like the Pirate Code General Scheme: (CH2Cl2 and CO2 as examples) 1. Determine arrangement of atoms (skeletal structure)…HOW? • Central vs peripheral (terminal) atoms 2. Determine total # of valence e-…HOW? 3. Draw s ...
Enthalpy Barriers for Asymmetric SN2 Alkyl
... Arrhenius preexponential factors (A). To estimate the intrinsic structural effects of these reactions, free from solvent effects, it is required that these reactions be studied in the gas phase. Relatively recently, the thermochemistry and kinetics of these reactions have been studied extensively in ...
... Arrhenius preexponential factors (A). To estimate the intrinsic structural effects of these reactions, free from solvent effects, it is required that these reactions be studied in the gas phase. Relatively recently, the thermochemistry and kinetics of these reactions have been studied extensively in ...
polar covalent bonds.
... bonds (complete transfer of electrons) are two extreme types of bonding. •Most bonds lie somewhere between these extremes and are called polar covalent bonds. •Each element can be assigned an electronegativity value which represents its electron accepting ability when participating in a chemical bon ...
... bonds (complete transfer of electrons) are two extreme types of bonding. •Most bonds lie somewhere between these extremes and are called polar covalent bonds. •Each element can be assigned an electronegativity value which represents its electron accepting ability when participating in a chemical bon ...
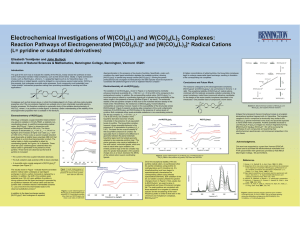
Electrochemical Investigations of W(CO) (L) and W(CO) (L) Complexes:
... pyridine. Three trends are observed as the level of pyridine is increased: • The current of the two coupled reductions decrease. ...
... pyridine. Three trends are observed as the level of pyridine is increased: • The current of the two coupled reductions decrease. ...
Chapter 14
... • Molecular ion (M): a radical cation formed by removal of a single electron from a parent molecule in a mass spectrometer • For our purposes, it does not matter which electron is lost; radical cation character is delocalized throughout the molecule; therefore, we write the molecular formula of the ...
... • Molecular ion (M): a radical cation formed by removal of a single electron from a parent molecule in a mass spectrometer • For our purposes, it does not matter which electron is lost; radical cation character is delocalized throughout the molecule; therefore, we write the molecular formula of the ...
Organic Chemistry - City University of New York
... transformed into a CH+ group in which carbon is sp2 hybridized and has a vacant 2p orbital, the overlap of orbitals is continuous and the cation is aromatic. H ...
... transformed into a CH+ group in which carbon is sp2 hybridized and has a vacant 2p orbital, the overlap of orbitals is continuous and the cation is aromatic. H ...
Show all work – Homework 5 –
... 1. Transition metal oxides containing a metal ion with multiple oxidation states may be non-stoichiometric. The non-stoichiometric compound may accommodate this by a variety of ways, including cation vacancies, oxide ion (anion) vacancies, interstitial cations, or interstitial anions. Soft chemistry ...
... 1. Transition metal oxides containing a metal ion with multiple oxidation states may be non-stoichiometric. The non-stoichiometric compound may accommodate this by a variety of ways, including cation vacancies, oxide ion (anion) vacancies, interstitial cations, or interstitial anions. Soft chemistry ...
1 12.1 Mass Spectrometry (MS) Mass Spectrometry (MS) Pentane
... intensity of the signal (roughly corresponding to the number of ions) (y-axis) ...
... intensity of the signal (roughly corresponding to the number of ions) (y-axis) ...
Terroir_geo_W8T-post
... • The CEC of soil clays are generally independent of pH, but CEC of organics are very pH-dependent (higher pH higher CEC of soil organic matter) ...
... • The CEC of soil clays are generally independent of pH, but CEC of organics are very pH-dependent (higher pH higher CEC of soil organic matter) ...
Chapter 9, Part 1
... Orbitals arrange around central atom to avoid each other. Two types of bonds: sigma () and pi (). Qualitative, visual- good for many atom systems in ground state Molecular Orbital Theory: Uses MO Diagrams Orbitals on atoms “mix” to make molecular orbitals, which go over 2 or more atoms. ...
... Orbitals arrange around central atom to avoid each other. Two types of bonds: sigma () and pi (). Qualitative, visual- good for many atom systems in ground state Molecular Orbital Theory: Uses MO Diagrams Orbitals on atoms “mix” to make molecular orbitals, which go over 2 or more atoms. ...
Test 1
... Structures that differ only in the placement of electrons. Changes in the vibrational modes of the bonds of the sample. Nuclei flipping from an aligned to nonaligned orientation when the energy difference between those states is matched in a magnetic field. Protons in the sample with excess energy t ...
... Structures that differ only in the placement of electrons. Changes in the vibrational modes of the bonds of the sample. Nuclei flipping from an aligned to nonaligned orientation when the energy difference between those states is matched in a magnetic field. Protons in the sample with excess energy t ...
DOC
... Structures that differ only in the placement of electrons. Changes in the vibrational modes of the bonds of the sample. Nuclei flipping from an aligned to nonaligned orientation when the energy difference between those states is matched in a magnetic field. Protons in the sample with excess energy t ...
... Structures that differ only in the placement of electrons. Changes in the vibrational modes of the bonds of the sample. Nuclei flipping from an aligned to nonaligned orientation when the energy difference between those states is matched in a magnetic field. Protons in the sample with excess energy t ...
Mass Spec - Fragmentation
... Fragmentation Notes - Most fragments are even-electron cations. These split to make more even-electron cations. - The probability of cleaving a given bond is related to the bond strength, and to the stability of the fragments formed. In particular, cations like to rearrange or decay into more stabl ...
... Fragmentation Notes - Most fragments are even-electron cations. These split to make more even-electron cations. - The probability of cleaving a given bond is related to the bond strength, and to the stability of the fragments formed. In particular, cations like to rearrange or decay into more stabl ...
Level 3 Distance Learning
... [Isotopomers: Note that the common usage (which you should adopt both in this question and in question 5) involves any isotopic substitution (e.g. 10BH4- and 11BH4-), but that a more restrictive definition is used by Brisdon (that isotopomeric molecules/ions must have the same relative mass)] (b) Wh ...
... [Isotopomers: Note that the common usage (which you should adopt both in this question and in question 5) involves any isotopic substitution (e.g. 10BH4- and 11BH4-), but that a more restrictive definition is used by Brisdon (that isotopomeric molecules/ions must have the same relative mass)] (b) Wh ...
Hints on Column Chromatography
... Note: O-H stretches are broader than N-H stretches N-H Stretches: 1° Amines (RNH2) has two peaks 2° Amines (RNHR) has one peak 3° Amines (NR3) has no peaks ...
... Note: O-H stretches are broader than N-H stretches N-H Stretches: 1° Amines (RNH2) has two peaks 2° Amines (RNHR) has one peak 3° Amines (NR3) has no peaks ...
2-Norbornyl cation

In organic chemistry, the term 2-norbornyl cation (equivalent with 2-bicyclo-[2.2.1]heptyl cation) describes one of the three carbocations formed from derivatives of norbornane. Though 1-norbornyl and 7-norbornyl cations have been studied, the most extensive studies and vigorous debates have been centered on the exact structure of the 2-norbornyl cation.The 2-norbornyl cation has been formed from a variety of norbornane derivatives and reagents. First reports of its formation and reactivity published by Saul Winstein sparked controversy over the nature of its bonding, as he invoked a three-center two-electron bond to explain the stereoselectivity of the resulting product. Herbert C. Brown challenged this assertion on the grounds that classical resonance structures could explain the stereospecificity without needing to adapt a new perspective of bonding.Evidence of the non-classical nature of the 2-norbornyl cation grew over the course of several decades, mainly through spectroscopic data gathered using methods such as Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Crystallographic confirmation of its non-classical nature did not come until quite recently.The nature of bonding in the 2-norbornyl cation incorporated many new ideas into the field’s understanding of chemical bonds. Similarities can be seen between this cation and others, such as boranes.