Bacterial Metabolism and Growth
... perfringens, and others) – Obligate aerobes (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) – Facultative anaerobes (most bacteria) ...
... perfringens, and others) – Obligate aerobes (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) – Facultative anaerobes (most bacteria) ...
Significance of Intestinal Digestion of Dietary Protein
... be readily available, an alternative method could be to determine cost of intestinally absorbable dietary protein (IADP) or amino acids. Intestinal Protein Digestion Methods for Measuring Intestinal Protein Digestion The total amount of protein available for absorption from the small intestine depen ...
... be readily available, an alternative method could be to determine cost of intestinally absorbable dietary protein (IADP) or amino acids. Intestinal Protein Digestion Methods for Measuring Intestinal Protein Digestion The total amount of protein available for absorption from the small intestine depen ...
Document
... Question 4. Since proteins make up most of your body, what might happen to the growth of high school students if protein is with held from their diet? ...
... Question 4. Since proteins make up most of your body, what might happen to the growth of high school students if protein is with held from their diet? ...
Quiz 7 Name: 1. After ATP fuels the Na+/K+ pump at the cell
... A) Glycolysis continues to produce ATP irrespective of what happens to NADH. B) Glycolysis stops unless NADH is used for something else. 6. During intense exercise, as muscles go into anaerobiosis (O2-deprived energy creation), the body will increase its consumption of A) fats. B) proteins. C) carbo ...
... A) Glycolysis continues to produce ATP irrespective of what happens to NADH. B) Glycolysis stops unless NADH is used for something else. 6. During intense exercise, as muscles go into anaerobiosis (O2-deprived energy creation), the body will increase its consumption of A) fats. B) proteins. C) carbo ...
POWERPOINT VERSION () - Arkansas State University
... Most are globular proteins that act as biological catalysts Enzymes are chemically specific Frequently named for the type of reaction they catalyze Enzyme names usually end in –ase (e.g., amylase, protease, nuclease, triose phosphate isomerase, hexokinase) Lower activation energy ...
... Most are globular proteins that act as biological catalysts Enzymes are chemically specific Frequently named for the type of reaction they catalyze Enzyme names usually end in –ase (e.g., amylase, protease, nuclease, triose phosphate isomerase, hexokinase) Lower activation energy ...
Unit three: - Life Science Academy
... nitrogenous organic compounds that consist of large molecules composed of one or more long chains of amino acids Are an essential part of all living organisms Structure dictates function! One primary function- to act as enzymes! ...
... nitrogenous organic compounds that consist of large molecules composed of one or more long chains of amino acids Are an essential part of all living organisms Structure dictates function! One primary function- to act as enzymes! ...
Information Sheet
... Although the final step of fermentation (conversion of pyruvate to fermentation endproducts) does not produce energy, it is critical for an anaerobic cell since it regenerates nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), which is required for glycolysis. This is important for normal cellular function, ...
... Although the final step of fermentation (conversion of pyruvate to fermentation endproducts) does not produce energy, it is critical for an anaerobic cell since it regenerates nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), which is required for glycolysis. This is important for normal cellular function, ...
Ch. 7 Cellular Respiration
... own food. heterotroph 3. ____________ an organism that gets its food from another source cellular respiration 4. ____________ the process by which cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds. ...
... own food. heterotroph 3. ____________ an organism that gets its food from another source cellular respiration 4. ____________ the process by which cells make ATP by breaking down organic compounds. ...
Microbial physiology. Microbial metabolism. Enzymes. Nutrition
... Many of the amino acids are used in building bacterial proteins, but some may also be broken down for energy. If this is the way amino acids are used, they are broken down to some form that can enter the Kreb’s cycle. These reactions include: ...
... Many of the amino acids are used in building bacterial proteins, but some may also be broken down for energy. If this is the way amino acids are used, they are broken down to some form that can enter the Kreb’s cycle. These reactions include: ...
BIOL 1322 - Victoria College
... What are the health consequences of ingesting inadequate protein and energy? Describe marasmus and kwashiorkor. How can the two conditions be distinguished, and in what ways do they overlap? ...
... What are the health consequences of ingesting inadequate protein and energy? Describe marasmus and kwashiorkor. How can the two conditions be distinguished, and in what ways do they overlap? ...
Molecules of Life
... consist of two fatty acids and one glycerol molecule. • Waxes – A wax is made of one long fatty acid chain joined to one long alcohol. • Steroids – A steroid is composed of four fused carbon rings. ...
... consist of two fatty acids and one glycerol molecule. • Waxes – A wax is made of one long fatty acid chain joined to one long alcohol. • Steroids – A steroid is composed of four fused carbon rings. ...
CP-Bio Ch 3(Chemistry of Life)
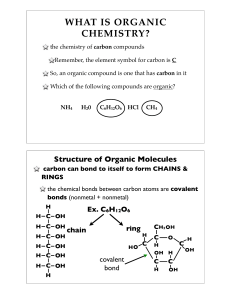
... • Molecular formulas show the kind and # of atoms in a molecule – H2O = 2 hydrogen atoms + 1 oxygen atom – CO2 = 1 carbon atom + 2 oxygen atoms – C6H12O6 = 6 carbon atoms + 12 hydrogen atoms + 6 oxygen atoms ...
... • Molecular formulas show the kind and # of atoms in a molecule – H2O = 2 hydrogen atoms + 1 oxygen atom – CO2 = 1 carbon atom + 2 oxygen atoms – C6H12O6 = 6 carbon atoms + 12 hydrogen atoms + 6 oxygen atoms ...
Document
... needed to get glucose to enter the body cells, consequently the animal breaks down fat for energy. Excessive amounts of acetyl-Coa (product A) starts to accumulate in the blood. Accumulated product A is converted to Ketone Bodies, large amounts of ketone bodies cause a condition called ketoacidosis. ...
... needed to get glucose to enter the body cells, consequently the animal breaks down fat for energy. Excessive amounts of acetyl-Coa (product A) starts to accumulate in the blood. Accumulated product A is converted to Ketone Bodies, large amounts of ketone bodies cause a condition called ketoacidosis. ...
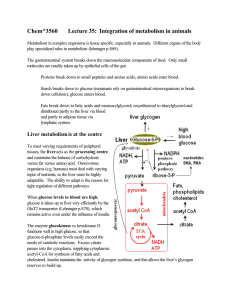
Chem*3560 Lecture 35: Integration of metabolism in animals
... from amino acid oxidation Amino acids in blood may be derived from dietary protein. If this source is insufficient, breakdown of tissue proteins occurs, mostly from body muscle mass (which is why starvation dieting is ill-advised). The liver has very active protein synthesis and degradation, and als ...
... from amino acid oxidation Amino acids in blood may be derived from dietary protein. If this source is insufficient, breakdown of tissue proteins occurs, mostly from body muscle mass (which is why starvation dieting is ill-advised). The liver has very active protein synthesis and degradation, and als ...
Molecules of Life Note Taking Guide
... 12. Name three common disaccharides and describe where they are commonly found. A. sucrose—glucose + fructose—sugar that is transported by plants—sugar cane B. maltose—glucose + glucose—sugar found in corn syrup, malt & germinating seeds C. lactose—glucose + galactose—sugar found in milk 13. Draw th ...
... 12. Name three common disaccharides and describe where they are commonly found. A. sucrose—glucose + fructose—sugar that is transported by plants—sugar cane B. maltose—glucose + glucose—sugar found in corn syrup, malt & germinating seeds C. lactose—glucose + galactose—sugar found in milk 13. Draw th ...
Structure and Function of Salivary Proteins Outline Basic salivary
... • However, single or even multiple biomarkers often do not produce unequivocal answer – Sensitivity- they may not be present in a detectable amount in all patients esp. early-stage – Specificity- they may also express in non-cancerous tissues ...
... • However, single or even multiple biomarkers often do not produce unequivocal answer – Sensitivity- they may not be present in a detectable amount in all patients esp. early-stage – Specificity- they may also express in non-cancerous tissues ...
study-guide-solutions-biochemistry
... nuclear arms and promoted high doses of vitamins to allow a long, healthy life. 2. Pauling developed the electronegativity scale of elements, which helps identify and predict the polarity of bonds. Polarity of bonds is an integral part of understanding the function of weak van der Waals forces, solu ...
... nuclear arms and promoted high doses of vitamins to allow a long, healthy life. 2. Pauling developed the electronegativity scale of elements, which helps identify and predict the polarity of bonds. Polarity of bonds is an integral part of understanding the function of weak van der Waals forces, solu ...
Nutritional biochemistry
... constitutes about 99.7% of all the essential minerals of the body. It includes calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, chlorine, sulphur. Ca, P, Mg represents 80% of total mineral content. They are mainly concentrated in bones. Microminerals: Are those that are required in very small quan ...
... constitutes about 99.7% of all the essential minerals of the body. It includes calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, chlorine, sulphur. Ca, P, Mg represents 80% of total mineral content. They are mainly concentrated in bones. Microminerals: Are those that are required in very small quan ...
Microorganisms_Background_Info
... cell divides and becomes two. (See BINARY FISSION overhead transparency.) Some bacteria can reproduce at a very rapid rate under proper conditions. If food and moisture are adequate and the temperature is right, certain bacteria can reproduce in as little as 20 minutes. Within 20 minutes, one cell b ...
... cell divides and becomes two. (See BINARY FISSION overhead transparency.) Some bacteria can reproduce at a very rapid rate under proper conditions. If food and moisture are adequate and the temperature is right, certain bacteria can reproduce in as little as 20 minutes. Within 20 minutes, one cell b ...
bio cleaning solutions - Green Worx Cleaning Solutions
... range of degradation capabilities needed for a multi-purpose product efficacious in the cleaning and deodorising and maintenance of artificial grass, waste degradation and cleaning and odour control. In their natural environment, bacteria produce hundreds of enzymes in response to the organics prese ...
... range of degradation capabilities needed for a multi-purpose product efficacious in the cleaning and deodorising and maintenance of artificial grass, waste degradation and cleaning and odour control. In their natural environment, bacteria produce hundreds of enzymes in response to the organics prese ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.