Protein synthesis and metabolism
... Most of the body’s fat is stored in adipocytes which form tissues called adipose tissue. Some is stored in hepatocytes. ...
... Most of the body’s fat is stored in adipocytes which form tissues called adipose tissue. Some is stored in hepatocytes. ...
Part I - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... • It is the inlet for the digestive system involved with the initial processing of food, which is aided by secretions from salivary glands. It is in the oral cavity that food and drinks are tasted and where mastication and lingual manipulation of food occur. • It manipulates sounds produced by the l ...
... • It is the inlet for the digestive system involved with the initial processing of food, which is aided by secretions from salivary glands. It is in the oral cavity that food and drinks are tasted and where mastication and lingual manipulation of food occur. • It manipulates sounds produced by the l ...
0495116572_102921
... Absorption, Transport, & Distribution – Specificity of GLUTs • GLUT1 - basic supply of glucose to cells • GLUT2 - low infinity transporter; glucose from enterocyte to blood • GLUT3 - high-affinity for brain & other glucose-dependent tissues • GLUT4 - insulin sensitive, in muscle & ...
... Absorption, Transport, & Distribution – Specificity of GLUTs • GLUT1 - basic supply of glucose to cells • GLUT2 - low infinity transporter; glucose from enterocyte to blood • GLUT3 - high-affinity for brain & other glucose-dependent tissues • GLUT4 - insulin sensitive, in muscle & ...
Polymers and Amino Acids
... A peptide bond can be split by refluxing with hydrochloric acid. During hydrolysis, the water molecule adds across the peptide bond, forming a mixture of the two amino acids. ...
... A peptide bond can be split by refluxing with hydrochloric acid. During hydrolysis, the water molecule adds across the peptide bond, forming a mixture of the two amino acids. ...
dıgestıve System - yeditepe anatomy fhs 121
... m. in adults. It absorbs fluids and salts from the gut contents, thus forming feces, and consists of the cecum, appendix, colon, rectum, and anal canal. ...
... m. in adults. It absorbs fluids and salts from the gut contents, thus forming feces, and consists of the cecum, appendix, colon, rectum, and anal canal. ...
Respiration Notes (chapter 8)
... Several Types of Fermentation: -Prokaryotic (Bacteria) fermentation -Sulfer Bacteria (Coal Mines) -Iron Bacteria (TITANIC Rusticles) -Decomposing Bacteria -indicated by a black color & aromatic methane smell. -found in: ...
... Several Types of Fermentation: -Prokaryotic (Bacteria) fermentation -Sulfer Bacteria (Coal Mines) -Iron Bacteria (TITANIC Rusticles) -Decomposing Bacteria -indicated by a black color & aromatic methane smell. -found in: ...
Protein Structure - E-Learning
... Some proteins cannot be dispersed in pure water but are readily dispersed in dilute salt solutions. When a salt solution increases the dispersibility of a protein, this is termed “salting-in.” It occurs because charged groups on a protein bind the anions and cations of the salt solution more strongl ...
... Some proteins cannot be dispersed in pure water but are readily dispersed in dilute salt solutions. When a salt solution increases the dispersibility of a protein, this is termed “salting-in.” It occurs because charged groups on a protein bind the anions and cations of the salt solution more strongl ...
Swot up of antimicrobial protein produced bacteria from ruminant
... producing from the goat raw milk sample and it is described by physiological and the biochemical tests. Three sequesters of bacteriocin creating LAB were isolated from goat milk. The culture supernatants of the three segregates were surveyed for their antimicrobial activity against food destroying o ...
... producing from the goat raw milk sample and it is described by physiological and the biochemical tests. Three sequesters of bacteriocin creating LAB were isolated from goat milk. The culture supernatants of the three segregates were surveyed for their antimicrobial activity against food destroying o ...
1050. All of the following increase gastric secretion
... Encephalopathy is associated with liver failure and increased nitrogenous products being absorbed into the circulation. There is no relationship between pancreatic ascites and encephalopathy. d. Painless abdominal enlargement Pancreatic ascites is almost always associated with a disruption of the pa ...
... Encephalopathy is associated with liver failure and increased nitrogenous products being absorbed into the circulation. There is no relationship between pancreatic ascites and encephalopathy. d. Painless abdominal enlargement Pancreatic ascites is almost always associated with a disruption of the pa ...
5. CH 5 PPT The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... between —OH groups (not shown) attached to ...
... between —OH groups (not shown) attached to ...
Chapter 26
... • Water is removed -- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C5 compound-- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C4 compound – decarboxylation reactions produce CO2 in your breath ...
... • Water is removed -- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C5 compound-- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C4 compound – decarboxylation reactions produce CO2 in your breath ...
Chapter 26
... • Water is removed -- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C5 compound-- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C4 compound – decarboxylation reactions produce CO2 in your breath ...
... • Water is removed -- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C5 compound-- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C4 compound – decarboxylation reactions produce CO2 in your breath ...
H &
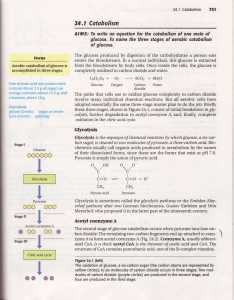
... dioxide the acetyl carbons of acetyl CoAformed in the breakdown of sugars, fats, and amino acids. Prodrtction of two molecules of carbon dioxide and two ofwater for eachmolecule of acetylCoAentering the cyclecompletesthe third stageof glucosecatabolism.The citric acid cycle is also called the Krebs ...
... dioxide the acetyl carbons of acetyl CoAformed in the breakdown of sugars, fats, and amino acids. Prodrtction of two molecules of carbon dioxide and two ofwater for eachmolecule of acetylCoAentering the cyclecompletesthe third stageof glucosecatabolism.The citric acid cycle is also called the Krebs ...
UG Curriculum
... 1. Need not know the structure of cholesterol. Should know why it cannot be carried free in plasma. 2. Mutarotation should not be taught. Student should know why amylase will not hydrolyse cellulose. 3. Need not know the details of alpha - helix and beta – pleats in proteins. 4. Need not know mechan ...
... 1. Need not know the structure of cholesterol. Should know why it cannot be carried free in plasma. 2. Mutarotation should not be taught. Student should know why amylase will not hydrolyse cellulose. 3. Need not know the details of alpha - helix and beta – pleats in proteins. 4. Need not know mechan ...
Macromolecule WebQuest
... 24. Each hemoglobin is made of four separate globin strands, and each contains a flat disk, a _____ carrying ______. The iron attracts oxygen, holds on to it, and releases it where it is needed. 25. Amino acids can link together in a _____fashion, and make various shapes, including folds. a. what do ...
... 24. Each hemoglobin is made of four separate globin strands, and each contains a flat disk, a _____ carrying ______. The iron attracts oxygen, holds on to it, and releases it where it is needed. 25. Amino acids can link together in a _____fashion, and make various shapes, including folds. a. what do ...
Biomolecule PPT
... living things as a source of energy. Examples: Cellulose - plants make it for cell walls Starch - (long chain of glucose) ...
... living things as a source of energy. Examples: Cellulose - plants make it for cell walls Starch - (long chain of glucose) ...
Chapter 26
... • Water is removed -- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C5 compound-- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C4 compound – decarboxylation reactions produce CO2 in your breath ...
... • Water is removed -- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C5 compound-- NAD+ is reduced to NADH -- CO2 is removed to form a C4 compound – decarboxylation reactions produce CO2 in your breath ...
protein
... requires ~ 30–50 % more than RMR highly active individual may require 100% or more calories above RMR ...
... requires ~ 30–50 % more than RMR highly active individual may require 100% or more calories above RMR ...
Organic Compounds
... Almost all organisms use carbohydrates as sources of energy. In addition, some carbohydrates serve as structural materials. Carbohydrates are molecules composed of Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H) and Oxygen (O). The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms is 2:1. In few words for every two H there is an at ...
... Almost all organisms use carbohydrates as sources of energy. In addition, some carbohydrates serve as structural materials. Carbohydrates are molecules composed of Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H) and Oxygen (O). The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms is 2:1. In few words for every two H there is an at ...
Course Name:
... The Faculty of Pharmacy offers two biochemistry courses to satisfy the needs of the Pharmacy students in this area. The first course covers the area of metabolism and biosynthesis of the biological molecules. The two courses have common aims and objectives. ...
... The Faculty of Pharmacy offers two biochemistry courses to satisfy the needs of the Pharmacy students in this area. The first course covers the area of metabolism and biosynthesis of the biological molecules. The two courses have common aims and objectives. ...
CH 3: The Molecules of Life
... In the small intestines the enzyme sucrase catalyzes the hydrolysis of the bond between glucose and fructose • In the lab this bond can be broken by…..? ...
... In the small intestines the enzyme sucrase catalyzes the hydrolysis of the bond between glucose and fructose • In the lab this bond can be broken by…..? ...
SECTION 2 - CELL FUNCTION AND BIOCHEMICAL MEASUREMENT
... 11. Plasma proteins contribute to the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood, which is needed for fluid balance. Plasma proteins also serve as circulating enzymes, hormones, transport molecules, and antibodies. Although the liver is a major source of plasma proteins, these molecules can originate fro ...
... 11. Plasma proteins contribute to the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood, which is needed for fluid balance. Plasma proteins also serve as circulating enzymes, hormones, transport molecules, and antibodies. Although the liver is a major source of plasma proteins, these molecules can originate fro ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.