Document
... combining substrates to create a larger molecule For example, the enzyme could be building up a sucrose molecule from glucose and fructose The next sequence shows how an enzyme can help to break a large molecule into smaller molecules ...
... combining substrates to create a larger molecule For example, the enzyme could be building up a sucrose molecule from glucose and fructose The next sequence shows how an enzyme can help to break a large molecule into smaller molecules ...
Uncoupling Proteins Cellular Metabolism Cellular Metabolism
... • ↑insulin faster from ingested glucose than from intravenous glucose! ...
... • ↑insulin faster from ingested glucose than from intravenous glucose! ...
Bioenergetics
... Chemical energy enters the body as carbohydrates, fats and proteins, which are comprised of glucose molecules, fatty acids and amino acids, respectively o The body uses these substrates to produce ATP ...
... Chemical energy enters the body as carbohydrates, fats and proteins, which are comprised of glucose molecules, fatty acids and amino acids, respectively o The body uses these substrates to produce ATP ...
Chapter 7 Ans
... immune response : A coordinated set of steps, including production of antibodies, that the immune system takes in response to an antigen. ...
... immune response : A coordinated set of steps, including production of antibodies, that the immune system takes in response to an antigen. ...
File
... Use flavorful rubs—dry or wet. The larger the protein is, the longer the rub can stay on. The rub flavors the exterior. Marinades build flavor profiles naturally so you don’t need as much fat, cream, or sauces. To give marinated foods flavor, try minced fruits and veggies, low-sodium soy sauce, ...
... Use flavorful rubs—dry or wet. The larger the protein is, the longer the rub can stay on. The rub flavors the exterior. Marinades build flavor profiles naturally so you don’t need as much fat, cream, or sauces. To give marinated foods flavor, try minced fruits and veggies, low-sodium soy sauce, ...
Biology - Perry Beeches IV
... B2 – Diet and Health Explain several good sources of each food group Explain why some people need more energy than others. Explain the functions of each part of the digestive system Explain the importance of bacteria in the human digestive system. Identify enzymes as proteins which aid digestion of ...
... B2 – Diet and Health Explain several good sources of each food group Explain why some people need more energy than others. Explain the functions of each part of the digestive system Explain the importance of bacteria in the human digestive system. Identify enzymes as proteins which aid digestion of ...
BMS Appetite handout
... • sensitive to glucose, free fatty acids, some amino acids; • mutations in metabolic enzymes (e.g. fatty acid synthase) cause obesity; • AMP kinase is important cellular regulator of appetite and metabolic rate; • appetite/feeding behaviour and metabolic rate/activity are always linked. ...
... • sensitive to glucose, free fatty acids, some amino acids; • mutations in metabolic enzymes (e.g. fatty acid synthase) cause obesity; • AMP kinase is important cellular regulator of appetite and metabolic rate; • appetite/feeding behaviour and metabolic rate/activity are always linked. ...
Homeostasis: Functions of the liver - mf011
... used for energy for cellular functions (more energy than glucose) Liver responsible for proper lipid concentrations in the blood. Lipids removed from blood by liver cells or transported to fat storage areas in the form of adipose tissue or lipoproteins for brain and nerve tissue synthesis Chol ...
... used for energy for cellular functions (more energy than glucose) Liver responsible for proper lipid concentrations in the blood. Lipids removed from blood by liver cells or transported to fat storage areas in the form of adipose tissue or lipoproteins for brain and nerve tissue synthesis Chol ...
File
... • Selenium is a trace element that is essential in small amounts, but like all essential elements, it is toxic at high levels • Humans require selenium for the function of a number of seleniumdependent enzymes, also known as selenoproteins ...
... • Selenium is a trace element that is essential in small amounts, but like all essential elements, it is toxic at high levels • Humans require selenium for the function of a number of seleniumdependent enzymes, also known as selenoproteins ...
Chapter 1
... site of N-linked glycosylation • Domain 3 - immediately outside plasma membrane, site of O-linked glycosylation • Domain 4 - made of 22 hydrophobic amino acids • Domain 5 - COOH terminal end of protein that projects into the cytoplast ...
... site of N-linked glycosylation • Domain 3 - immediately outside plasma membrane, site of O-linked glycosylation • Domain 4 - made of 22 hydrophobic amino acids • Domain 5 - COOH terminal end of protein that projects into the cytoplast ...
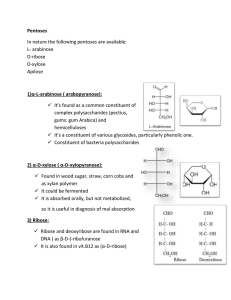
2) α-D-xylose
... It has a sweet flavor that’s cool because of negative heat of solution, thus used in: -chewing gums -tooth pastes In Iron Sorbitex inj. It is cholagogue: increases biliary flow and increases volume of biliary secretions, thus it’s used for treatment of biliary stones ...
... It has a sweet flavor that’s cool because of negative heat of solution, thus used in: -chewing gums -tooth pastes In Iron Sorbitex inj. It is cholagogue: increases biliary flow and increases volume of biliary secretions, thus it’s used for treatment of biliary stones ...
Breath Hydrogen Test Price Quote
... The hydrogen breath test uses a measurement of hydrogen in the breath to test for a number of conditions that cause gastrointestinal symptoms. It can be used to diagnose lactase deficiency, fructose intolerance, bacterial overgrowth, or oro-cecal gastrointestinal (rapid) transit. Only anaerobic bact ...
... The hydrogen breath test uses a measurement of hydrogen in the breath to test for a number of conditions that cause gastrointestinal symptoms. It can be used to diagnose lactase deficiency, fructose intolerance, bacterial overgrowth, or oro-cecal gastrointestinal (rapid) transit. Only anaerobic bact ...
3. Pharmacokinetics1 Absorption
... Lipid-soluble is the non ionized, or uncharged form….Can cross membrane Percentage of ionized drug depends on : 1.Whether the drug was an acid or a base 2. Whether it is dissolved in an acid or base medium (Stomach or intestine ?) i.e pH 3. And also the pKa of the drug As pH increases, a weak base w ...
... Lipid-soluble is the non ionized, or uncharged form….Can cross membrane Percentage of ionized drug depends on : 1.Whether the drug was an acid or a base 2. Whether it is dissolved in an acid or base medium (Stomach or intestine ?) i.e pH 3. And also the pKa of the drug As pH increases, a weak base w ...
Document
... – Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids of various chain lengths are components of phospholipids, sphingolipids, and triglycerides – fatty acids are synthesized by water-soluble enzymes and modified by elongation and desaturation in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – The finals steps in the synthesis ...
... – Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids of various chain lengths are components of phospholipids, sphingolipids, and triglycerides – fatty acids are synthesized by water-soluble enzymes and modified by elongation and desaturation in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – The finals steps in the synthesis ...
Phosphorus in industry and society
... • however only 2% of P is used in true P4 chemistry • 2% more P use efficiency can probably be achieved more easily in agricultural applciation improvements and reducing meat consumption (feed phosphate – 5 to 10% of total) • consider cradle-to-cradle design for P chemicals (e.g. recycle flame retar ...
... • however only 2% of P is used in true P4 chemistry • 2% more P use efficiency can probably be achieved more easily in agricultural applciation improvements and reducing meat consumption (feed phosphate – 5 to 10% of total) • consider cradle-to-cradle design for P chemicals (e.g. recycle flame retar ...
Tongue Scraping
... hygiene practice that removes bacteria, food debris, fungi, toxins, and dead cells from the surface of the tongue. During sleep, our digestive system continues working, removing toxins from our body and depositing some of them onto the surface of our tongue. Because there is less saliva produced at ...
... hygiene practice that removes bacteria, food debris, fungi, toxins, and dead cells from the surface of the tongue. During sleep, our digestive system continues working, removing toxins from our body and depositing some of them onto the surface of our tongue. Because there is less saliva produced at ...
Phenol Sensitivity Phenols are a group substances found in natural
... Phenols are a group substances found in natural foods which have antioxidant effects. They are also produced by gut microbes. Phenols are metabolized by PST (Phenol Sulfo Transferase enzyme) which many autistic children are deficient in. Deficiency of PST leads to problems of poor sulphation and tox ...
... Phenols are a group substances found in natural foods which have antioxidant effects. They are also produced by gut microbes. Phenols are metabolized by PST (Phenol Sulfo Transferase enzyme) which many autistic children are deficient in. Deficiency of PST leads to problems of poor sulphation and tox ...
Autism
... The structure of glutathione (GSH) is composed of the amino acids (AA) glutamic acid, glycine and once again, that sulfur containing essential amino acid, cysteine. Studies show autistic children to be deficient in glutathione.(12) When toxic metals such as mercury and cadmium enter the system, MT w ...
... The structure of glutathione (GSH) is composed of the amino acids (AA) glutamic acid, glycine and once again, that sulfur containing essential amino acid, cysteine. Studies show autistic children to be deficient in glutathione.(12) When toxic metals such as mercury and cadmium enter the system, MT w ...
1 - Wk 1-2
... 2. Explain how the lack of insulin in DKA leads to overproduction of glucagon with stimulation of gluconeogenesis and lipolysis The balance between insulin and glucagon levels in the blood is the principal control of metabolism. Both are synthesised as ‘pre-pro’ and ‘prohormones’ which are cleaved ...
... 2. Explain how the lack of insulin in DKA leads to overproduction of glucagon with stimulation of gluconeogenesis and lipolysis The balance between insulin and glucagon levels in the blood is the principal control of metabolism. Both are synthesised as ‘pre-pro’ and ‘prohormones’ which are cleaved ...
12.1 Mechanisms regulating enzyme synthesis 12.1.2.2 Enzyme
... conservation efficiency and maintenance energy when growing on different carbon sources. For the most efficient growth under given conditions, catabolism and anabolism are coordinately regulated not only through the expression of the gens but also through the control of enzyme activities ...
... conservation efficiency and maintenance energy when growing on different carbon sources. For the most efficient growth under given conditions, catabolism and anabolism are coordinately regulated not only through the expression of the gens but also through the control of enzyme activities ...
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 118, pp. 7646.
... structure and dynamics. The first chapter, by Goh, gives a useful review of experimental aspects of imaging processes and applications of force microscopy to polymers, and it deals with atomic force spectroscopy of mesoscopic scales. It emphasizes instrumental details and the interpretation of patte ...
... structure and dynamics. The first chapter, by Goh, gives a useful review of experimental aspects of imaging processes and applications of force microscopy to polymers, and it deals with atomic force spectroscopy of mesoscopic scales. It emphasizes instrumental details and the interpretation of patte ...
Slide 1 - Caldwell County Schools
... Younger children often eat small portions. Offering smaller servings and allowing them to ask for more, satisfies their hunger and does not waste food. ...
... Younger children often eat small portions. Offering smaller servings and allowing them to ask for more, satisfies their hunger and does not waste food. ...
high quality protein wrapped
... There appears to be a growing trend for people, particularly women, to self-diagnose lactose intolerance. Regardless of whether a diagnosis is correct or not, it is often wrongly assumed that sufferers cannot tolerate yogurt. Lactose is a type of sugar found in milk. Lactose intolerance occurs when ...
... There appears to be a growing trend for people, particularly women, to self-diagnose lactose intolerance. Regardless of whether a diagnosis is correct or not, it is often wrongly assumed that sufferers cannot tolerate yogurt. Lactose is a type of sugar found in milk. Lactose intolerance occurs when ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.