DNA STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. BASICS OF DNA A
... amounts of DNA. He also observed that the proportions of the nitrogen bases varied from species to species. 1. Chargaff also observed several points that today are known as Chargaff’s Rules: a. The amount of adenine in a single DNA molecule is always equal to the amount of thymine in that same DNA m ...
... amounts of DNA. He also observed that the proportions of the nitrogen bases varied from species to species. 1. Chargaff also observed several points that today are known as Chargaff’s Rules: a. The amount of adenine in a single DNA molecule is always equal to the amount of thymine in that same DNA m ...
Chapter 1 - TeacherWeb
... Difference between cellular respiration and “breathing” respiration General cellular respiration equation, total ATP produced, % energy of glucose harvested Cellular respiration – name four phases, starting reactants/ending products of each phase, location of each process, general understanding of e ...
... Difference between cellular respiration and “breathing” respiration General cellular respiration equation, total ATP produced, % energy of glucose harvested Cellular respiration – name four phases, starting reactants/ending products of each phase, location of each process, general understanding of e ...
Chapter 2
... • Contain only carbon, hydrogen and oxygen • Most common are called fats – Made of glycerol and fatty acid • Triglyceride ...
... • Contain only carbon, hydrogen and oxygen • Most common are called fats – Made of glycerol and fatty acid • Triglyceride ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY B.Sc. Semester III
... Unit III : Replication and Transcription in Prokaryotes a. Replication- Enzymology of replication DNA polymerase I, brief account of pol II and III, helicases, topoisomerases, single strand binding proteins, primase action b. Proof for semiconservative replication, Okazaki fragments, c. Replication ...
... Unit III : Replication and Transcription in Prokaryotes a. Replication- Enzymology of replication DNA polymerase I, brief account of pol II and III, helicases, topoisomerases, single strand binding proteins, primase action b. Proof for semiconservative replication, Okazaki fragments, c. Replication ...
If you have a the following genotypes as babies, what must the
... • What cell parts or cellular activities does this incorporate? • DNA and RNA are major players. • Nucleus, ribosome, nucleolus, cytoplasm • What is a protein? • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begi n/dna/tour_protein.html ...
... • What cell parts or cellular activities does this incorporate? • DNA and RNA are major players. • Nucleus, ribosome, nucleolus, cytoplasm • What is a protein? • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begi n/dna/tour_protein.html ...
... 19. The major reason for A pairing with U is: a) complementary hydrogen bonds. b) a purine-pyrimidine pair fits well in the double helix. c) efficient stacking of this arrangement of bases in the helix. d) recognition of non-’Watson-Crick’ hydrogen bonds by DNA polymerases 20. An expression vector o ...
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
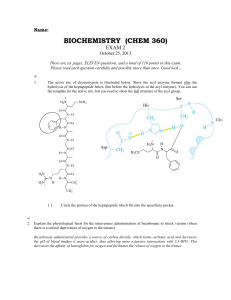
... derivatives, an example of which is given below. Describe two structural features of penicillin, to which the inhibitory activity can be attributed. (1) the structure resembles D-ala.D-ala moiety (2) nucleophilic attack by the carboxypeptidase is more likely to occur to the -lactam ring than the al ...
... derivatives, an example of which is given below. Describe two structural features of penicillin, to which the inhibitory activity can be attributed. (1) the structure resembles D-ala.D-ala moiety (2) nucleophilic attack by the carboxypeptidase is more likely to occur to the -lactam ring than the al ...
幻灯片 1
... Double membrane surrounding the chromosomes and the nucleolus. The place where almost all DNA replication and RNA synthesis occur. ...
... Double membrane surrounding the chromosomes and the nucleolus. The place where almost all DNA replication and RNA synthesis occur. ...
Quantitative amino acids analysis for the diagnosis and follow up of
... Clinical indications for amino acids analysis o Diagnosis of inborn errors of amino acid metabolism and transport o Diagnosis of inborn errors of the urea cycle o Diet monitoring in patients with known IEM o Nutritional assessment of patients with nonmetabolic conditions [e.g. short bowel ...
... Clinical indications for amino acids analysis o Diagnosis of inborn errors of amino acid metabolism and transport o Diagnosis of inborn errors of the urea cycle o Diet monitoring in patients with known IEM o Nutritional assessment of patients with nonmetabolic conditions [e.g. short bowel ...
Lecture outline handouts
... ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ○ Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. • The chemical mechanisms that cells use to make and break polymers are similar for all classes of macromolecules. • Monomers are connected by covalent bonds th ...
... ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ○ Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. • The chemical mechanisms that cells use to make and break polymers are similar for all classes of macromolecules. • Monomers are connected by covalent bonds th ...
File
... ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ○ Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. The chemical mechanisms that cells use to make and break polymers are similar for all classes of macromolecules. Monomers are connected by covalent bonds th ...
... ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ○ Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. The chemical mechanisms that cells use to make and break polymers are similar for all classes of macromolecules. Monomers are connected by covalent bonds th ...
Class Notes
... ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ○ Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. The chemical mechanisms that cells use to make and break polymers are similar for all classes of macromolecules. Monomers are connected by covalent bonds th ...
... ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ○ Some of the molecules that serve as monomers have other functions of their own. The chemical mechanisms that cells use to make and break polymers are similar for all classes of macromolecules. Monomers are connected by covalent bonds th ...
Chapter Five
... Two or more food proteins whose amino acid assortments complement each other in such a way that the essential amino acids limited in or missing from each are supplied by the others. ...
... Two or more food proteins whose amino acid assortments complement each other in such a way that the essential amino acids limited in or missing from each are supplied by the others. ...
E U F T DG Unfolded state, ensemble Native fold, one
... and some are “forbidden” (not found in natural proteins). – Name properties on which the amino acids can be grouped. – Explain the driving forces behind protein folding related to the properties of the backbone and the side chains. ...
... and some are “forbidden” (not found in natural proteins). – Name properties on which the amino acids can be grouped. – Explain the driving forces behind protein folding related to the properties of the backbone and the side chains. ...
Macromolecular Crystallography in India, IUCr, 2017
... uncovered the long sought after mechanism of D-‐amino acid rejection during protein synthesis that prevents the opposite chiral molecules from infiltrating the translational machinery. The work r ...
... uncovered the long sought after mechanism of D-‐amino acid rejection during protein synthesis that prevents the opposite chiral molecules from infiltrating the translational machinery. The work r ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.