proteinS
... •AA are optically active molecules due to the presence of a chiral carbon (except in the case of glycine where the R-group is hydrogen) ...
... •AA are optically active molecules due to the presence of a chiral carbon (except in the case of glycine where the R-group is hydrogen) ...
atom
... – Elements differ in the number of subatomic particles in their atoms. • The number of protons, the atomic number, determines which ...
... – Elements differ in the number of subatomic particles in their atoms. • The number of protons, the atomic number, determines which ...
Hypothesis-Driven Science Hypothesis
... – Elements differ in the number of subatomic particles in their atoms. • The number of protons, the atomic number, determines which ...
... – Elements differ in the number of subatomic particles in their atoms. • The number of protons, the atomic number, determines which ...
DNA (double helix)
... DNA is identical in all cells of an individual, almost identical among different individuals of same species (99.9%), and very similar in related species (human vs chimpanzee - 98% identity). ...
... DNA is identical in all cells of an individual, almost identical among different individuals of same species (99.9%), and very similar in related species (human vs chimpanzee - 98% identity). ...
Syllabus: Biochem 104b
... -induced diploes, Van der Waals Forces, Lennard Jones potential -hydrogen bonding -hydrophobic effect: not a force but an entropic effect ...
... -induced diploes, Van der Waals Forces, Lennard Jones potential -hydrogen bonding -hydrophobic effect: not a force but an entropic effect ...
Exam I Review - Iowa State University
... a. increasing the percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in the membrane. b. decreasing the number of hydrophobic proteins in the membrane. c. increasing the percentage of saturated phospholipids in the membrane. d. A and B are both correct. A function of mitochondria in plant cells is a. to catab ...
... a. increasing the percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in the membrane. b. decreasing the number of hydrophobic proteins in the membrane. c. increasing the percentage of saturated phospholipids in the membrane. d. A and B are both correct. A function of mitochondria in plant cells is a. to catab ...
Exam I Review - Iowa State University
... One way that winter wheat (and many other organisms) keep cell membranes fluid when environmental temperatures drop in fall and winter is by *a. increasing the percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in the membrane. b. decreasing the number of hydrophobic proteins in the membrane. c. increasing th ...
... One way that winter wheat (and many other organisms) keep cell membranes fluid when environmental temperatures drop in fall and winter is by *a. increasing the percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in the membrane. b. decreasing the number of hydrophobic proteins in the membrane. c. increasing th ...
DNA Replication
... prevents contact with enzymes, which are specialized carbohydrate molecules that help speed up chemical reactions. I’d better take you through this amazing process step by step. (5) First, an enzyme unwinds and unzips the DNA molecule. The unzipping occurs when the ionic bonds between base pairs are ...
... prevents contact with enzymes, which are specialized carbohydrate molecules that help speed up chemical reactions. I’d better take you through this amazing process step by step. (5) First, an enzyme unwinds and unzips the DNA molecule. The unzipping occurs when the ionic bonds between base pairs are ...
Nucleoside Phosphoramidate Monoesters: Potential
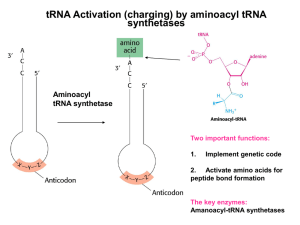
... The accuracy of protein synthesis depends on correct charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correc ...
... The accuracy of protein synthesis depends on correct charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correc ...
HD Rx of Hyperammonemia (Gregory et al, Vol. 5,abst. 55P
... Flow Diagram to Evaluate Hyperammonemia Sig incr Plasma amino acids ...
... Flow Diagram to Evaluate Hyperammonemia Sig incr Plasma amino acids ...
document
... •These enzymes make about one mistake in 10,000. For most amino acids, this level of accuracy is not too difficult to achieve. •Most of the amino acids are quite different from one another. •But in a few cases, it is difficult to choose just the right amino acids and these enzymes must resort to spe ...
... •These enzymes make about one mistake in 10,000. For most amino acids, this level of accuracy is not too difficult to achieve. •Most of the amino acids are quite different from one another. •But in a few cases, it is difficult to choose just the right amino acids and these enzymes must resort to spe ...
Proteins
... • . essential life substance of all living matter . • act as structural unit to build our bodies . • specific structural chemical units amino acids • amino [alkaline substance carbon, hydrogen ,o2& NH2. ...
... • . essential life substance of all living matter . • act as structural unit to build our bodies . • specific structural chemical units amino acids • amino [alkaline substance carbon, hydrogen ,o2& NH2. ...
Substrate Metabolism – Rest vs Stress
... - rest = basal metabolic rate + minimal exercise - major stress = 50% burn - aim = to preserve plasma glucose levels for brain metabolism. REST - least expensive form of energy production utilized: carbohydrate -> fat -> protein in decreasing ratios. Carbohydrate Sources ...
... - rest = basal metabolic rate + minimal exercise - major stress = 50% burn - aim = to preserve plasma glucose levels for brain metabolism. REST - least expensive form of energy production utilized: carbohydrate -> fat -> protein in decreasing ratios. Carbohydrate Sources ...
division - IRIS - Lake Land College
... Write chemical equation for the reactions of amines and amides. Classify proteins with three main groups and briefly explain the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins. List the six classes of enzymes, describe the theories of action of enzymes, and explain factors that af ...
... Write chemical equation for the reactions of amines and amides. Classify proteins with three main groups and briefly explain the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins. List the six classes of enzymes, describe the theories of action of enzymes, and explain factors that af ...
Protein mteabolism
... For this reason melatonin has been called "the hormone of darkness. - Melatonin is sleep-inducing molecule -So ingestion of food rich in tryptophan leads to sleepiness. It is powerful antioxidant It has important role in protecting skin from damaging effect of UV radiation: ...
... For this reason melatonin has been called "the hormone of darkness. - Melatonin is sleep-inducing molecule -So ingestion of food rich in tryptophan leads to sleepiness. It is powerful antioxidant It has important role in protecting skin from damaging effect of UV radiation: ...
Center for Structural Biology
... derivatives. E.g thyrosine and catecholamines. Amines: Some amino acids give corresponding amines by decarboxylation e.g histidine gives histamine which is vasodilator. ...
... derivatives. E.g thyrosine and catecholamines. Amines: Some amino acids give corresponding amines by decarboxylation e.g histidine gives histamine which is vasodilator. ...
Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is
... (C) carbon dioxide only (D) water only (E) carbon dioxide and water 56.The concentration of bacteria is greater around an algal filament exposed to red light than around the same filament exposed to green light because (A) green light affects enzyme action in bacteria (B) photosynthesis proceeds mor ...
... (C) carbon dioxide only (D) water only (E) carbon dioxide and water 56.The concentration of bacteria is greater around an algal filament exposed to red light than around the same filament exposed to green light because (A) green light affects enzyme action in bacteria (B) photosynthesis proceeds mor ...
Chapter 1 Review Key
... diversity in roles, including enzyme production, transport, immunity, structure, recognition, and other functions due to the large number of amino acid combinations and functional groups. 104. Answers may vary. Sample Answer: Understanding about the biological molecules and how they function in cell ...
... diversity in roles, including enzyme production, transport, immunity, structure, recognition, and other functions due to the large number of amino acid combinations and functional groups. 104. Answers may vary. Sample Answer: Understanding about the biological molecules and how they function in cell ...
Section 2.3 - Father Michael McGivney Catholic Academy
... • Catabolic pathways feed into the respiratory pathways. Polysaccharides are broken down into glucose, which enters glycolysis. Glycerol from fats also enters glycolysis, and acetyl CoA from fatty acid degradation enters the citric acid cycle. Proteins enter glycolysis and the citric acid cycle via ...
... • Catabolic pathways feed into the respiratory pathways. Polysaccharides are broken down into glucose, which enters glycolysis. Glycerol from fats also enters glycolysis, and acetyl CoA from fatty acid degradation enters the citric acid cycle. Proteins enter glycolysis and the citric acid cycle via ...
Cell Membrane
... sides of the ladder The bases are held together with hydrogen bonds to make the rungs (C=G and A=T) ...
... sides of the ladder The bases are held together with hydrogen bonds to make the rungs (C=G and A=T) ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.