Pentose Phosphate Pathway
... PPP is a shunt • The pathway begins with the glycolytic intermediate glucose 6-P. • It reconnects with glycolysis because two of the end products of the PPP are glyceraldehyde 3-P and fructose 6-P; two intermediates further down in the glycolytic pathway. • It is for this reason that the PPP is oft ...
... PPP is a shunt • The pathway begins with the glycolytic intermediate glucose 6-P. • It reconnects with glycolysis because two of the end products of the PPP are glyceraldehyde 3-P and fructose 6-P; two intermediates further down in the glycolytic pathway. • It is for this reason that the PPP is oft ...
Link to Unit 2.1
... All living things are composed of four basic categories of macromolecules and share the same basic needs for life. Students need to relate the primary function of the carbohydrates to providing and storing energy. Also, students will relate the primary function of lipids to insulating, energy storag ...
... All living things are composed of four basic categories of macromolecules and share the same basic needs for life. Students need to relate the primary function of the carbohydrates to providing and storing energy. Also, students will relate the primary function of lipids to insulating, energy storag ...
Protein Malnutrition - MSUD Family Support Group
... nutritional problems usually involve proteins and their component parts, the amino acids. For that reason, this discussion will be limited to protein and amino acid malnutrition. Proteins are associated with all forms of life and have many different functions in the body. Proteins act as catalysts f ...
... nutritional problems usually involve proteins and their component parts, the amino acids. For that reason, this discussion will be limited to protein and amino acid malnutrition. Proteins are associated with all forms of life and have many different functions in the body. Proteins act as catalysts f ...
RNA Transcription
... feature of the CAP that you need not learn is the presence of a methyl group at the 7 position of the guanine, which was removed from the figure for simplicity.) The CAP will become important when we consider the translation of eukaryotic mRNAs. ...
... feature of the CAP that you need not learn is the presence of a methyl group at the 7 position of the guanine, which was removed from the figure for simplicity.) The CAP will become important when we consider the translation of eukaryotic mRNAs. ...
Broomfield High School
... have on protein structure. Concept: Most macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. Polymers are longs chain molecules made of repeating subunits called monomers. Examples: Starch is a polymer composed of glucose monomers. Proteins are polymers composed of amino acid monomers. 2. Condensati ...
... have on protein structure. Concept: Most macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers 1. Polymers are longs chain molecules made of repeating subunits called monomers. Examples: Starch is a polymer composed of glucose monomers. Proteins are polymers composed of amino acid monomers. 2. Condensati ...
3.2 Carbohydrates, lipids and proteins – summary of previous mark
... lipids are insoluble in water less osmotic effect; lipids have more / twice the energy content per unit mass of carbohydrates; lipids / triglycerides used for long-term energy storage; triglycerides converted to fatty acids and glycerol (when energy is required); triglycerides broken down to yield a ...
... lipids are insoluble in water less osmotic effect; lipids have more / twice the energy content per unit mass of carbohydrates; lipids / triglycerides used for long-term energy storage; triglycerides converted to fatty acids and glycerol (when energy is required); triglycerides broken down to yield a ...
Nucleotide
... - Hypoxanthine (I) is commonly found in transfer RNA (tRNA) as an essential modification but in DNA as a mismatch due to its preferential base-pairing with cytosine (C) - In both DNA and tRNA, hypoxanthine (I) results from the deamination of adenine (A) ...
... - Hypoxanthine (I) is commonly found in transfer RNA (tRNA) as an essential modification but in DNA as a mismatch due to its preferential base-pairing with cytosine (C) - In both DNA and tRNA, hypoxanthine (I) results from the deamination of adenine (A) ...
Design of a novel globularprotein with atommic
... Makes hemoglobin sticky and red blood cells will clump together and cause all sorts of problems ...
... Makes hemoglobin sticky and red blood cells will clump together and cause all sorts of problems ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... Protein Synthesis Cartoon In groups of three or four, you will make a six-step cartoon of protein synthesis on the dry-erase board provided. All of the bold terms must be labeled on your cartoon. You may use analogies to represent the structures rather than the structure themselves. Once it is appr ...
... Protein Synthesis Cartoon In groups of three or four, you will make a six-step cartoon of protein synthesis on the dry-erase board provided. All of the bold terms must be labeled on your cartoon. You may use analogies to represent the structures rather than the structure themselves. Once it is appr ...
Instructor Supplement: Ideas for Workshop Extension Activities Core
... RNA nucleotides contain ribose while DNA nucleotides contain deoxyribose. RNA contains G, C, A, and U bases, while DNA contains G, C, A, and T. Both RNA and DNA nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds to form polymers. RNA is a more stable molecule than DNA. ...
... RNA nucleotides contain ribose while DNA nucleotides contain deoxyribose. RNA contains G, C, A, and U bases, while DNA contains G, C, A, and T. Both RNA and DNA nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds to form polymers. RNA is a more stable molecule than DNA. ...
document
... phosphate. • Calcium phosphate is more soluble when the pH decreases (especially below 5.5): Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 + 8H+ → 10Ca2+ + 6HPO42- + 2H2O ...
... phosphate. • Calcium phosphate is more soluble when the pH decreases (especially below 5.5): Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 + 8H+ → 10Ca2+ + 6HPO42- + 2H2O ...
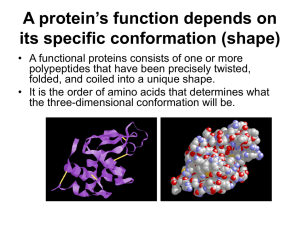
A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation
... • A functional proteins consists of one or more polypeptides that have been precisely twisted, folded, and coiled into a unique shape. • It is the order of amino acids that determines what the three-dimensional conformation will be. ...
... • A functional proteins consists of one or more polypeptides that have been precisely twisted, folded, and coiled into a unique shape. • It is the order of amino acids that determines what the three-dimensional conformation will be. ...
Chapter 4 The Importance of High
... -CO 2 Æ glucose in plant: need input of light energy Æ results in the formation of ATP -even a weak covalent bond is very strong Æ need energy supply to break Æ achieve (달성하다) activation state -activation energy is usually less than the original bond energy, because molecular rearrangements do not i ...
... -CO 2 Æ glucose in plant: need input of light energy Æ results in the formation of ATP -even a weak covalent bond is very strong Æ need energy supply to break Æ achieve (달성하다) activation state -activation energy is usually less than the original bond energy, because molecular rearrangements do not i ...
Chapter 4 The Importance of High
... -CO 2 Æ glucose in plant: need input of light energy Æ results in the formation of ATP -even a weak covalent bond is very strong Æ need energy supply to break Æ achieve (달성하다) activation state -activation energy is usually less than the original bond energy, because molecular rearrangements do not i ...
... -CO 2 Æ glucose in plant: need input of light energy Æ results in the formation of ATP -even a weak covalent bond is very strong Æ need energy supply to break Æ achieve (달성하다) activation state -activation energy is usually less than the original bond energy, because molecular rearrangements do not i ...
Sect3DNAReplication - Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
... Many enzymes are required for DNA replication. We will only consider enzyme activities, not specific enzymes. Enzymes with these activities are also used for DNA manipulation in the lab. ...
... Many enzymes are required for DNA replication. We will only consider enzyme activities, not specific enzymes. Enzymes with these activities are also used for DNA manipulation in the lab. ...
SECTION 2 - CELL FUNCTION AND BIOCHEMICAL MEASUREMENT
... represent a subcategory of lipids; “not all lipids are fats” because the term lipids includes other subcategories such as phospholipids and steroids, that are not triglycerides. 11. Plasma proteins contribute to the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood, which is needed for fluid balance. Plasma pro ...
... represent a subcategory of lipids; “not all lipids are fats” because the term lipids includes other subcategories such as phospholipids and steroids, that are not triglycerides. 11. Plasma proteins contribute to the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood, which is needed for fluid balance. Plasma pro ...
SECTION 2 - CELL FUNCTION AND BIOCHEMICAL MEASUREMENT
... represent a subcategory of lipids; “not all lipids are fats” because the term lipids includes other subcategories such as phospholipids and steroids, that are not triglycerides. 11. Plasma proteins contribute to the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood, which is needed for fluid balance. Plasma pro ...
... represent a subcategory of lipids; “not all lipids are fats” because the term lipids includes other subcategories such as phospholipids and steroids, that are not triglycerides. 11. Plasma proteins contribute to the colloid osmotic pressure of the blood, which is needed for fluid balance. Plasma pro ...
Chapter 17 Presentation
... mRNA is the “messenger” or vehicle that carries the genetic information from the DNA to the protein synthesizing machinery. RNA polymerase pries apart the DNA and joins RNA nucleotides together in the 5’-->3’ direction (adding, again, to the free 3’ end). RNA polymerase is just like DNA polymerase, ...
... mRNA is the “messenger” or vehicle that carries the genetic information from the DNA to the protein synthesizing machinery. RNA polymerase pries apart the DNA and joins RNA nucleotides together in the 5’-->3’ direction (adding, again, to the free 3’ end). RNA polymerase is just like DNA polymerase, ...
05. Amino acids, Protein
... producing 9 of these 20 acids, these 9 amino acids, called essential amino acids, must be obtained from food. The human body can synthesize small amounts of some of the essential amino acids, but not enough to meet its needs, especially in the case of growing children. The 9 essential amino acids ...
... producing 9 of these 20 acids, these 9 amino acids, called essential amino acids, must be obtained from food. The human body can synthesize small amounts of some of the essential amino acids, but not enough to meet its needs, especially in the case of growing children. The 9 essential amino acids ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.