Conjugated bilirubin
... Lobules are the functional units, consisting of clusters of hepatocytes ...
... Lobules are the functional units, consisting of clusters of hepatocytes ...
Amino acid, ammonia and urea concentrations in human pre
... ovarian follicular fluid and to compare these concentrations with those in the circulation. METHODS: Samples of pre-ovulatory follicular fluid and peripheral venous blood were obtained from 14 IVF patients. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) measurements of 25 AAs were the main outcome me ...
... ovarian follicular fluid and to compare these concentrations with those in the circulation. METHODS: Samples of pre-ovulatory follicular fluid and peripheral venous blood were obtained from 14 IVF patients. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) measurements of 25 AAs were the main outcome me ...
Survey - University of Washington
... • Instead of comparing a target sequence to the query, each target is compared to the model. • The PSI-BLAST model is called a position-specific scoring matrix (PSSM). • The PSSM can be constructed from a collection of targets aligned to the query sequence. • PSI-BLAST is more accurate than BLAST. ...
... • Instead of comparing a target sequence to the query, each target is compared to the model. • The PSI-BLAST model is called a position-specific scoring matrix (PSSM). • The PSSM can be constructed from a collection of targets aligned to the query sequence. • PSI-BLAST is more accurate than BLAST. ...
Document
... Entry of other carbohydrates into glycolysis Fructose Liver Cells They have another enzyme, fructokinase. • It has a stronger affinity for fructose. • It catalyzes phosphoryl group transfer from ATP to produce fructose-1phosphate. An aldolase-type cleavage and additional phosphorylation must also o ...
... Entry of other carbohydrates into glycolysis Fructose Liver Cells They have another enzyme, fructokinase. • It has a stronger affinity for fructose. • It catalyzes phosphoryl group transfer from ATP to produce fructose-1phosphate. An aldolase-type cleavage and additional phosphorylation must also o ...
Cellular Respiration
... 9.6: Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways • Catabolic pathways are versatile; they funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules (not just glucose!) into cellular respiration • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must first be ...
... 9.6: Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways • Catabolic pathways are versatile; they funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules (not just glucose!) into cellular respiration • Glycolysis accepts a wide range of carbohydrates • Proteins must first be ...
Chapter 9 - Slothnet
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduce ...
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduce ...
Properties of ATP - BioWiki
... Likewise we make about the same amount from the turnover products. When energy is needed, carbohydrates and lipids are oxidized and ATP is produced, which can then be immediately used for motility, biosynthesis, etc. It is very important to realize that although ATP is converted to ADP in a thermody ...
... Likewise we make about the same amount from the turnover products. When energy is needed, carbohydrates and lipids are oxidized and ATP is produced, which can then be immediately used for motility, biosynthesis, etc. It is very important to realize that although ATP is converted to ADP in a thermody ...
General Important Information to Guide You on Your
... MTHFR C677T mutations so that the long way around the cycle can function properly then the body will not need to rely as heavily on the shortcut through the BHMT enzyme. Once the methionine levels appear to be more in balance on a urine AA test, and the methylmalonic acid levels are in normal range, ...
... MTHFR C677T mutations so that the long way around the cycle can function properly then the body will not need to rely as heavily on the shortcut through the BHMT enzyme. Once the methionine levels appear to be more in balance on a urine AA test, and the methylmalonic acid levels are in normal range, ...
What is respiration?
... reactions, they are not very good at catalysing oxidation or reduction reactions. Coenzymes are needed to help them carry out the oxidation reactions of respiration. The hydrogen atoms are combined with coenzymes such as NAD. These carry the hydrogen atoms, which can later be split into hydrogen ion ...
... reactions, they are not very good at catalysing oxidation or reduction reactions. Coenzymes are needed to help them carry out the oxidation reactions of respiration. The hydrogen atoms are combined with coenzymes such as NAD. These carry the hydrogen atoms, which can later be split into hydrogen ion ...
Student Book (Unit 1 Module 4) - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... reactions, they are not very good at catalysing oxidation or reduction reactions. Coenzymes are needed to help them carry out the oxidation reactions of respiration. The hydrogen atoms are combined with coenzymes such as NAD. These carry the hydrogen atoms, which can later be split into hydrogen ion ...
... reactions, they are not very good at catalysing oxidation or reduction reactions. Coenzymes are needed to help them carry out the oxidation reactions of respiration. The hydrogen atoms are combined with coenzymes such as NAD. These carry the hydrogen atoms, which can later be split into hydrogen ion ...
Growth-limiting Intracellular Metabolites in Yeast Growing Under Diverse Nutrient Limitations.
... CTP and thereby reduced RNA biosynthesis and slower growth. Baker’s yeast, as the best-studied eukaryotic microbe, provides a valuable system for investigating the pathways linking nutrient environment to growth rate. Recent studies have examined the transcriptome (and to a limited extent, the prote ...
... CTP and thereby reduced RNA biosynthesis and slower growth. Baker’s yeast, as the best-studied eukaryotic microbe, provides a valuable system for investigating the pathways linking nutrient environment to growth rate. Recent studies have examined the transcriptome (and to a limited extent, the prote ...
The Biochemistry of Malic Acid Metabolism by Wine Yeasts
... The glyoxalate cycle in yeast peroxisomes is primarily associated with the complete degradation of fatty acids via (3-oxidation. However, it also plays an important role in the synthesis of C4 compounds from C2 carbon substrates by employing some of the TCA cycle enzymes (Fraenkel, 1982). In S. cere ...
... The glyoxalate cycle in yeast peroxisomes is primarily associated with the complete degradation of fatty acids via (3-oxidation. However, it also plays an important role in the synthesis of C4 compounds from C2 carbon substrates by employing some of the TCA cycle enzymes (Fraenkel, 1982). In S. cere ...
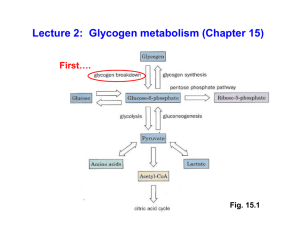
Lecture 2: Glycogen metabolism (Chapter 15)
... Glycogen synthesis can only occur by extending an already existing (1 4)-linked glucan chain. Therefore, how can it get started in the first place? Answer: The first step in glycogen synthesis is the attachment of a glucose residue to the -OH group on Tyr-194 of GLYCOGENIN. This attachment step is d ...
... Glycogen synthesis can only occur by extending an already existing (1 4)-linked glucan chain. Therefore, how can it get started in the first place? Answer: The first step in glycogen synthesis is the attachment of a glucose residue to the -OH group on Tyr-194 of GLYCOGENIN. This attachment step is d ...
Isolation and Characterization of Two Polypeptides
... ABSTRACT Cells in the stratified squamous epithelium of bovine esophagus contain abundant tonofilaments measuring 6-10 nm in diameter . Two polypeptides, extracted from esophageal epithelium with 0 .05 M Tris, pH 7 .4, containing 8 M urea and 25 mM ß-mercaptoethanol, comprise 35% of the total extrac ...
... ABSTRACT Cells in the stratified squamous epithelium of bovine esophagus contain abundant tonofilaments measuring 6-10 nm in diameter . Two polypeptides, extracted from esophageal epithelium with 0 .05 M Tris, pH 7 .4, containing 8 M urea and 25 mM ß-mercaptoethanol, comprise 35% of the total extrac ...
Supporting document 1 Safety assessment
... DNA sequences from the backbone of the transformation vector, including antibiotic resistance marker genes, were transferred during the transformation event. The csr1-2 gene expression cassette in CV127 is identical in sequence to the transforming plasmid DNA except for three point mutations, one o ...
... DNA sequences from the backbone of the transformation vector, including antibiotic resistance marker genes, were transferred during the transformation event. The csr1-2 gene expression cassette in CV127 is identical in sequence to the transforming plasmid DNA except for three point mutations, one o ...
Complete genome sequence of the rifamycin SV
... although the corresponding PKS protein does have the same domain structure as that of M. tuberculosis. Actually, with several putative transporters and regulators annotated in these two clusters, they are more likely to code for the biosynthesis of unknown secondary metabolites (Figure 1). In additi ...
... although the corresponding PKS protein does have the same domain structure as that of M. tuberculosis. Actually, with several putative transporters and regulators annotated in these two clusters, they are more likely to code for the biosynthesis of unknown secondary metabolites (Figure 1). In additi ...
Pharmaceutical Faculty 3- d course Module 1 General principles of
... Anabolic pathways _______ A. Do not depend on enzymes B. Lead to the synthesis of catabolic compounds C. Release energy as they degrade polymers to monomers D. All of the above E. Consume energy to build up polymers from monomers ANSWER: E ...
... Anabolic pathways _______ A. Do not depend on enzymes B. Lead to the synthesis of catabolic compounds C. Release energy as they degrade polymers to monomers D. All of the above E. Consume energy to build up polymers from monomers ANSWER: E ...
Purification and Physico-Chemical Analysis of Fractions from the
... charide, was essential for toxicity; but a more recent investigation of endotoxins from rough Salmonella strains led them to suggest more strongly that the lipid moiety ('lipid A') was 'the factor decisive for at least some endotoxic effects' (Liideritz & Westphal, 1966). They also believe that, wit ...
... charide, was essential for toxicity; but a more recent investigation of endotoxins from rough Salmonella strains led them to suggest more strongly that the lipid moiety ('lipid A') was 'the factor decisive for at least some endotoxic effects' (Liideritz & Westphal, 1966). They also believe that, wit ...
Kinetic models of metabolism: model construction, model
... are inadequate and instead a kinetic modelling approach is necessary. Given the large number of reactions included in the network, a pipeline has been built to automatically generate kinetic laws from reaction stoichiometries. In this context a precise description of the reactional mechanism is impo ...
... are inadequate and instead a kinetic modelling approach is necessary. Given the large number of reactions included in the network, a pipeline has been built to automatically generate kinetic laws from reaction stoichiometries. In this context a precise description of the reactional mechanism is impo ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.