Genetic Transcription & Translation Lecture PowerPoint
... science-related PowerPoints, articles and images. The site is designed to be a helpful resource for students, educators, and anyone interested in learning about science. • The SPO Virtual Classrooms offer many educational resources, including practice test questions, review questions, lecture PowerP ...
... science-related PowerPoints, articles and images. The site is designed to be a helpful resource for students, educators, and anyone interested in learning about science. • The SPO Virtual Classrooms offer many educational resources, including practice test questions, review questions, lecture PowerP ...
syllabusbioch205 - OSU Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
... 5. To learn the interrelationships among the various metabolic pathways. 6. To learn the energetic relationships. 7. To learn the chemical principles of metabolism and biochemical conversions. 8. To learn the enzymes and coenzymes involved in metabolism and how they participate in the reactions. 9. ...
... 5. To learn the interrelationships among the various metabolic pathways. 6. To learn the energetic relationships. 7. To learn the chemical principles of metabolism and biochemical conversions. 8. To learn the enzymes and coenzymes involved in metabolism and how they participate in the reactions. 9. ...
Spectroscopy
... • Linear IR spectroscopy - study of the structures and interactions of small molecules. • At first, it appeared to be too ambitious to apply this technique to biological macromolecules, because of their enormous number of vibrational modes. • Biological macromolecules exhibit an intrinsic order of r ...
... • Linear IR spectroscopy - study of the structures and interactions of small molecules. • At first, it appeared to be too ambitious to apply this technique to biological macromolecules, because of their enormous number of vibrational modes. • Biological macromolecules exhibit an intrinsic order of r ...
Sources of enzyme
... Enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond Hydrolytic enzymes are normally associated with degradative reactions, (break down large molecules into small molecules) e.g., ◦ conversion of starch to sugar, ◦ proteins to polypeptides and amino acids, ◦ and lipids to their constituent glycer ...
... Enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond Hydrolytic enzymes are normally associated with degradative reactions, (break down large molecules into small molecules) e.g., ◦ conversion of starch to sugar, ◦ proteins to polypeptides and amino acids, ◦ and lipids to their constituent glycer ...
Vitamins Chart
... Phosphorylated form requires hydrolosis by phosphatases, free form goes passively into jejunum, phosphorylated, PNP/PMP are oxidized by flavin dependent oxidase to PLP, ...
... Phosphorylated form requires hydrolosis by phosphatases, free form goes passively into jejunum, phosphorylated, PNP/PMP are oxidized by flavin dependent oxidase to PLP, ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Where are electrons with the least potential energy located? The most potential energy? the inner shell; the outermost shell ...
... Where are electrons with the least potential energy located? The most potential energy? the inner shell; the outermost shell ...
do not
... How do enzymes work? 1) Enzymes act upon a substance called a substrate 2) The enzyme has an indent in it called the active site where the substrate can fit into, kind of like a lock and a key ...
... How do enzymes work? 1) Enzymes act upon a substance called a substrate 2) The enzyme has an indent in it called the active site where the substrate can fit into, kind of like a lock and a key ...
File - Wk 1-2
... 3. Outline the citric acid cycle, listing the main substrates and products of the cycle and the role of the cycle in providing reducing equivalents for the electron transport chain. The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) occurs in the mitacholdria of the cell and occurs in the presence of oxygen (aero ...
... 3. Outline the citric acid cycle, listing the main substrates and products of the cycle and the role of the cycle in providing reducing equivalents for the electron transport chain. The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) occurs in the mitacholdria of the cell and occurs in the presence of oxygen (aero ...
Metabolism
... • Stimulates mobilization of fuels • Stimulates glycogen breakdown in liver and glucose is released to the blood stream • Glucose is not taken up by muscle tissues but used primarily to fuel the brain • Glucagon stimulates release of fatty acids from adipose tissues and the shift of muscle fuel from ...
... • Stimulates mobilization of fuels • Stimulates glycogen breakdown in liver and glucose is released to the blood stream • Glucose is not taken up by muscle tissues but used primarily to fuel the brain • Glucagon stimulates release of fatty acids from adipose tissues and the shift of muscle fuel from ...
Beginning of life
... the temperature, use a different energy form from electric discharges, but the final result will always be the same: organic substance. ...
... the temperature, use a different energy form from electric discharges, but the final result will always be the same: organic substance. ...
Energy metabolism
... We have discussed various fuels which are oxidized via different catabolic pathways to generate ATP, or reducing equivalents required to carry out various functions and synthesis. Fuels sources: Starch/Glycogen ...
... We have discussed various fuels which are oxidized via different catabolic pathways to generate ATP, or reducing equivalents required to carry out various functions and synthesis. Fuels sources: Starch/Glycogen ...
BIO 101 Exam 2 practice questions Practice questions Ch 8,9 YOU
... 24. Enzymes: can bind metal ions that participate in reactions. A. have defined structures. B. bind their substrates at active sites. C. all statements are true. D. 25. A(n) _______ reaction releases energy. Energy must be added for a(n) _______ reaction to proceed. a. enzyme catalyzed, non-spontane ...
... 24. Enzymes: can bind metal ions that participate in reactions. A. have defined structures. B. bind their substrates at active sites. C. all statements are true. D. 25. A(n) _______ reaction releases energy. Energy must be added for a(n) _______ reaction to proceed. a. enzyme catalyzed, non-spontane ...
Substrate
... on the temperature and the activation energy. (1) k = Ae –Eα/RT which can be transformed to ln (k) = -Eα/R x 1/T + ln (A) where A is the Arrhenius or prefactor, and R is the gas constant (1.98 cal K-1 mol-1). The activation energy for the enzyme catalyzed reaction was estimated by plotting ln kcat v ...
... on the temperature and the activation energy. (1) k = Ae –Eα/RT which can be transformed to ln (k) = -Eα/R x 1/T + ln (A) where A is the Arrhenius or prefactor, and R is the gas constant (1.98 cal K-1 mol-1). The activation energy for the enzyme catalyzed reaction was estimated by plotting ln kcat v ...
Fatty Acid Oxidation
... pathological states. Following this lecture students should understand that ...
... pathological states. Following this lecture students should understand that ...
Decoding the Flu - National Center for Case Study Teaching in
... Jason was worried. He had landed a summer internship at the National Center for Preparedness, Detection, and Control of Infectious Diseases (NCPDCID). It didn’t pay, but it helped boost his resume before applying to medical school. His boss also let him tag along on a CDC research trip to rural Mex ...
... Jason was worried. He had landed a summer internship at the National Center for Preparedness, Detection, and Control of Infectious Diseases (NCPDCID). It didn’t pay, but it helped boost his resume before applying to medical school. His boss also let him tag along on a CDC research trip to rural Mex ...
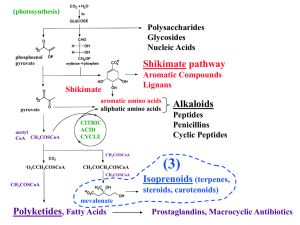
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.