A General Method Applicable to the Search for Similarities in the
... of amino acid as Bi; if they are different amino acids, MATij is assigned the value, zero. The sophistication of the comparison is increased if, instead of zero or one, each cell value is made a function of the composition of the proteins, the genetic code triplets representing the amino acids, the ...
... of amino acid as Bi; if they are different amino acids, MATij is assigned the value, zero. The sophistication of the comparison is increased if, instead of zero or one, each cell value is made a function of the composition of the proteins, the genetic code triplets representing the amino acids, the ...
Chapter 1
... • Trihydroxy alcohol (glycerol) to which 3 fatty acids are attached by ester bonds • Nomenclature: stereospecific numbering (sn) • Exist as fats or oils depending on nature of fatty acid components 2009 Cengage-Wadsworth ...
... • Trihydroxy alcohol (glycerol) to which 3 fatty acids are attached by ester bonds • Nomenclature: stereospecific numbering (sn) • Exist as fats or oils depending on nature of fatty acid components 2009 Cengage-Wadsworth ...
Exam #1
... determine when it will be a a substrate cycle. What is the key control step involving F2,6P as an allosteric activator/inhibitor (pg 543). Why is this called a ‘Futile cycle’. What are the precursors for gluconeogenesis? Study the overview of glucose metabolism shown on fig 16-1 pg 518. Lipids (chap ...
... determine when it will be a a substrate cycle. What is the key control step involving F2,6P as an allosteric activator/inhibitor (pg 543). Why is this called a ‘Futile cycle’. What are the precursors for gluconeogenesis? Study the overview of glucose metabolism shown on fig 16-1 pg 518. Lipids (chap ...
Chem 204
... Which of the following is least likely to result in protein denaturation, and explain why it is the least likely? A) Altering net charge by changing pH B) Changing the salt concentration C) Disruption of weak interactions by boiling D) Exposure to detergents E) Mixing with organic solvents such as a ...
... Which of the following is least likely to result in protein denaturation, and explain why it is the least likely? A) Altering net charge by changing pH B) Changing the salt concentration C) Disruption of weak interactions by boiling D) Exposure to detergents E) Mixing with organic solvents such as a ...
COURSE DETAILS: E INTRODUCTION Metabolism can be defined
... by E1. Therefore, when sufficient G is synthesized, it blocks further synthesis of itself. This phenomenon whereby product of a reaction sequence inhibits the activity of an enzyme early in the biosynthetic pathway is referred to as feedback inhibition or feedback regulation or end-product inhibitio ...
... by E1. Therefore, when sufficient G is synthesized, it blocks further synthesis of itself. This phenomenon whereby product of a reaction sequence inhibits the activity of an enzyme early in the biosynthetic pathway is referred to as feedback inhibition or feedback regulation or end-product inhibitio ...
Unit 04 Enzymes and respiration Review
... 4. Enzymes are a type of _______________________. The characteristics of enzymes are that they can __________________________________, are a ______________________ fit to their substrate referred to as the __________________________ complex, they can be altered by ___________ or _____________, and a ...
... 4. Enzymes are a type of _______________________. The characteristics of enzymes are that they can __________________________________, are a ______________________ fit to their substrate referred to as the __________________________ complex, they can be altered by ___________ or _____________, and a ...
03-131 F 2013 Final Exam Name:_________________________
... The hydrophobic effect is a change in the order of the water molecules due to the presence of a non-polar group. The water molecules will order themselves around a non-polar group. This decreases the order of the water which is unfavorable. Therefore non-polar groups do not interact with water. Prot ...
... The hydrophobic effect is a change in the order of the water molecules due to the presence of a non-polar group. The water molecules will order themselves around a non-polar group. This decreases the order of the water which is unfavorable. Therefore non-polar groups do not interact with water. Prot ...
Brewing biochemistry
... The theoretical teaching is subdivided in two parts and supported by practicals: Biochemistry of malting and brewing: (1) barley an enzymatic reactions occurring during malting, (2) biochemical reactions during brewing. Biochemistry of fermentation: Focused on the utilization of Saccharomyces cerevi ...
... The theoretical teaching is subdivided in two parts and supported by practicals: Biochemistry of malting and brewing: (1) barley an enzymatic reactions occurring during malting, (2) biochemical reactions during brewing. Biochemistry of fermentation: Focused on the utilization of Saccharomyces cerevi ...
chapter_6_-_plus_ch_review
... 2. What is the basic building block of a protein? Make a labeled sketch of such a building block – include carboxyl group, amine group and R group. 3. The bonds between the protein’s building blocks have a specific name – what is it? 4. A simple chain of these building blocks is not a completely fun ...
... 2. What is the basic building block of a protein? Make a labeled sketch of such a building block – include carboxyl group, amine group and R group. 3. The bonds between the protein’s building blocks have a specific name – what is it? 4. A simple chain of these building blocks is not a completely fun ...
Cloning of Plastid Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase cDNA from Setaria italica
... Key words: Setaria italica; Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase; cloning; herbicide; target site Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACCase; EC 6.4.1.2) is a biotinylated enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in fatty acid biosynthesis and provides malonyl-CoA for the synthesis of a variety of important secondary m ...
... Key words: Setaria italica; Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase; cloning; herbicide; target site Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACCase; EC 6.4.1.2) is a biotinylated enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in fatty acid biosynthesis and provides malonyl-CoA for the synthesis of a variety of important secondary m ...
Sequencing genomes
... A new species of frog has been introduced into an area where it has too few natural predators. In an attempt to restore the ecological balance, a team of scientists is considering introducing a species of bird which feeds on this frog. Experimental data suggests that the population of frogs and bird ...
... A new species of frog has been introduced into an area where it has too few natural predators. In an attempt to restore the ecological balance, a team of scientists is considering introducing a species of bird which feeds on this frog. Experimental data suggests that the population of frogs and bird ...
757 (Agus Kurnia)ok
... The deduced amino acid sequence of GSX L in this study, exhibited high identity with that of E-GSX T-6, Geobacillus sp. WBI (GX WBI) and GTX (Figure 1 & Table 2). Moreover, the sequence with a signal peptide shared high identity with GSX T-6, while the mature protein without signal peptide shared th ...
... The deduced amino acid sequence of GSX L in this study, exhibited high identity with that of E-GSX T-6, Geobacillus sp. WBI (GX WBI) and GTX (Figure 1 & Table 2). Moreover, the sequence with a signal peptide shared high identity with GSX T-6, while the mature protein without signal peptide shared th ...
1a ExamI Intro-MicrGrwth
... 6. Most microbes are capable of causing human disease. 7. The bond between two separate molecules of water is a covalent bond. 8. An oxidizing agent like hydrogen peroxide causes damage by donating electrons to other molecules. ------------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
... 6. Most microbes are capable of causing human disease. 7. The bond between two separate molecules of water is a covalent bond. 8. An oxidizing agent like hydrogen peroxide causes damage by donating electrons to other molecules. ------------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
pdf - The Elf Lab
... We modeled how the charged levels of different transfer RNAs (tRNAs) that carry the same amino acid (isoacceptors) respond when this amino acid becomes growth-limiting. The charged levels will approach zero for some isoacceptors (such as tRNA2Leu) and remain high for others (such as tRNA4Leu), as de ...
... We modeled how the charged levels of different transfer RNAs (tRNAs) that carry the same amino acid (isoacceptors) respond when this amino acid becomes growth-limiting. The charged levels will approach zero for some isoacceptors (such as tRNA2Leu) and remain high for others (such as tRNA4Leu), as de ...
Notes for lecture 17: RNA Secondary Structure Prediction Adam
... proposed that RNA was the original biopolymer. RNA Structure Unlike DNA, RNA is usually single-stranded. The entropic benefits of base stacking and the enthalpic benefits of base pairing result in the formation of secondary structures. Base pairing rules are the same as for DNA, except that 'T' (thy ...
... proposed that RNA was the original biopolymer. RNA Structure Unlike DNA, RNA is usually single-stranded. The entropic benefits of base stacking and the enthalpic benefits of base pairing result in the formation of secondary structures. Base pairing rules are the same as for DNA, except that 'T' (thy ...
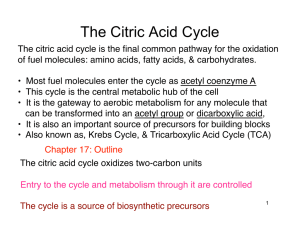
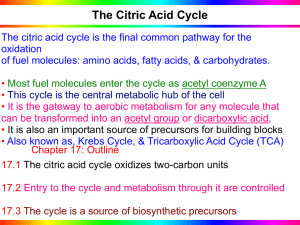
Cellular Respiration
... • The mitochondria are the engines of our cells where sugar is burned for fuel and the exhaust is CO2 and H2O. ...
... • The mitochondria are the engines of our cells where sugar is burned for fuel and the exhaust is CO2 and H2O. ...
Poster
... A particular heme-containing enzyme, known as CYP17, converts cholesterol-derived hormones into androgens including testosterone. Fe(III) is a key part as all reactions occur within this heme group. Pharmacological efforts, such as the drug abiraterone, decrease the efficiency of CYP17 catalysis and ...
... A particular heme-containing enzyme, known as CYP17, converts cholesterol-derived hormones into androgens including testosterone. Fe(III) is a key part as all reactions occur within this heme group. Pharmacological efforts, such as the drug abiraterone, decrease the efficiency of CYP17 catalysis and ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.