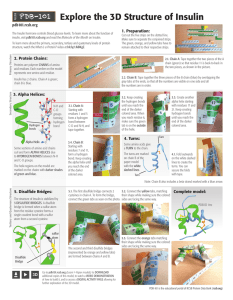
Lecture: Fasting and gene expression, Part 1
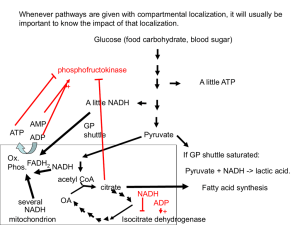
... If your blood sugar is 80 (or higher) after 6 hours of sleep, and no food intake, where it that coming from? The brain and kidneys use about 10 grams/hour. There is about 20 grams in blood and extracellular fluid, that would be used up over 2 hours. ...
... If your blood sugar is 80 (or higher) after 6 hours of sleep, and no food intake, where it that coming from? The brain and kidneys use about 10 grams/hour. There is about 20 grams in blood and extracellular fluid, that would be used up over 2 hours. ...
Enzymes - Dr. Hamad Ali Yaseen
... • For example, sucrase catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose • The name also describes the function of the enzyme • For example, oxidases catalyze oxidation reactions • Sometimes common names are used, particularly for the digestion enzymes such as pepsin and trypsin • Some names describe both the sub ...
... • For example, sucrase catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose • The name also describes the function of the enzyme • For example, oxidases catalyze oxidation reactions • Sometimes common names are used, particularly for the digestion enzymes such as pepsin and trypsin • Some names describe both the sub ...
Enzyme Structure
... Up to the optimum temperature the rate increases geometrically with temperature (i.e. it's a curve, not a straight line). The rate increases because the enzyme and substrate molecules both have more kinetic energy so collide more often, and also because more molecules have sufficient energy to overc ...
... Up to the optimum temperature the rate increases geometrically with temperature (i.e. it's a curve, not a straight line). The rate increases because the enzyme and substrate molecules both have more kinetic energy so collide more often, and also because more molecules have sufficient energy to overc ...
Rapid communication: Nucleotide sequence of red seabream
... Comments. From the total of 375 amino acids, the human β-actin amino acid sequences differed by 7 amino acids and 14 amino acids from gilthead seabream and red seabream β-actin amino acid sequences, respectively (Figure 1). The amino acid sequences of red seabream β-actin differed from those of β-ac ...
... Comments. From the total of 375 amino acids, the human β-actin amino acid sequences differed by 7 amino acids and 14 amino acids from gilthead seabream and red seabream β-actin amino acid sequences, respectively (Figure 1). The amino acid sequences of red seabream β-actin differed from those of β-ac ...
METABOLISM: BASIC CONSEPTS & DESIGN
... The active site is the region that binds the substrates (& cofactors if any) It contains the residues that directly participate in the making & breaking of bonds (these residues are called catalytic groups) The interaction of the enzyme and substrate at the active site promotes the formation o ...
... The active site is the region that binds the substrates (& cofactors if any) It contains the residues that directly participate in the making & breaking of bonds (these residues are called catalytic groups) The interaction of the enzyme and substrate at the active site promotes the formation o ...
Q1. Babies find it difficult to digest proteins in their food. Baby food
... they are easily broken down by high temperature or the wrong pH ...
... they are easily broken down by high temperature or the wrong pH ...
Calculation of hydrophobicities
... surface the respective molecule and, by extension, the respective atom type, presented to the solvent (the probing ball). Therefore, hydrophobicity is an atom-additive, surfaceindependent property, entirely similar to the charge of the molecule or the atom. The problem with this approach is that ass ...
... surface the respective molecule and, by extension, the respective atom type, presented to the solvent (the probing ball). Therefore, hydrophobicity is an atom-additive, surfaceindependent property, entirely similar to the charge of the molecule or the atom. The problem with this approach is that ass ...
Alpha oxidation
... acids, branched chain and aromatic amino acids and citric acid cycle. • The incidence of medium chain acyl coA dehydrogenase deficiency is about 1 in 2500 live birth, and is the second most common inborn error of metabolism. • They are all characterised by the accumulation of organic acids in body t ...
... acids, branched chain and aromatic amino acids and citric acid cycle. • The incidence of medium chain acyl coA dehydrogenase deficiency is about 1 in 2500 live birth, and is the second most common inborn error of metabolism. • They are all characterised by the accumulation of organic acids in body t ...
gil, virginia
... groups of macromolecules. Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary information. Nucleic acids are the molecules that enable living organisms to reproduce their complex equipment from one generation to the next. 15. Summarize the functions of nucleic acids. Nucleic acids store and transmit heredit ...
... groups of macromolecules. Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary information. Nucleic acids are the molecules that enable living organisms to reproduce their complex equipment from one generation to the next. 15. Summarize the functions of nucleic acids. Nucleic acids store and transmit heredit ...
Chapter 5- Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... Monosaccharides, particularly glucose, are major nutrients for cells. In the process known as cellular respiration, cells extract energy in a series of reactions starting with glucose molecules. Not only are simple-sugar molecules a major fuel for cellular work; their carbon skeletons also serve as ...
... Monosaccharides, particularly glucose, are major nutrients for cells. In the process known as cellular respiration, cells extract energy in a series of reactions starting with glucose molecules. Not only are simple-sugar molecules a major fuel for cellular work; their carbon skeletons also serve as ...
Summer 2003 Test 3
... 50) The cell cycle stage, at which the spindle proteins needed for mitosis are most likely made in, is? a) M b) S c) G1 d) G2 e) none of these 51) A photosynthetic CO2 reduction pathway in which CO2 is actually reduced twice, requires mesophyll and bundle sheath cells, and is more efficient in dry - ...
... 50) The cell cycle stage, at which the spindle proteins needed for mitosis are most likely made in, is? a) M b) S c) G1 d) G2 e) none of these 51) A photosynthetic CO2 reduction pathway in which CO2 is actually reduced twice, requires mesophyll and bundle sheath cells, and is more efficient in dry - ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 23: Phospholipid Biosynthesis
... L-glycerol-3-phosphate + acyl-CoA → 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate + HSCoA acyltransferase 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate + stearoyl-CoA → 1,2-diacylglycerol-3-phosphate + HSCoA ...
... L-glycerol-3-phosphate + acyl-CoA → 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate + HSCoA acyltransferase 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate + stearoyl-CoA → 1,2-diacylglycerol-3-phosphate + HSCoA ...
Biochemical Engineering Prof. Dr. Rintu Banerjee Department of
... cysteine, glycine, asparagines, glutamine are the polar amino acid, where glycine is the amino acid which is placed on the transition phase of polar and non polar amino acid. Now, this is the only amino acid where this carbon is not an asymmetric carbon atom that means here this R group is also anot ...
... cysteine, glycine, asparagines, glutamine are the polar amino acid, where glycine is the amino acid which is placed on the transition phase of polar and non polar amino acid. Now, this is the only amino acid where this carbon is not an asymmetric carbon atom that means here this R group is also anot ...
Structural Biochemistry/Enzyme
... biological reactions in the absence of enzymes may be as much as a million times slower. Virtually all enzymes are proteins, though the converse is not true and other molecules such as RNA can also catalyze reactions. The most remarkable characteristics of enzymes are their ability to accelerate che ...
... biological reactions in the absence of enzymes may be as much as a million times slower. Virtually all enzymes are proteins, though the converse is not true and other molecules such as RNA can also catalyze reactions. The most remarkable characteristics of enzymes are their ability to accelerate che ...
Document
... Reversible and Irreversible Irreversible inhibition: The irreversible inhibitors bind covalently with or destroy a functional group on an enzyme that is essential for the enzyme’s activity, or form a particularly stable noncovalent association (e.g.: heavy metals). An irreversible inhibitor decrease ...
... Reversible and Irreversible Irreversible inhibition: The irreversible inhibitors bind covalently with or destroy a functional group on an enzyme that is essential for the enzyme’s activity, or form a particularly stable noncovalent association (e.g.: heavy metals). An irreversible inhibitor decrease ...
Practice Exam III answers
... 11). Some enzymes require a necessary metal ion cofactor for catalysis. Which of the following is not a potential property that a metal ion may impart to an enzymatically catalyzed reaction? a). May act as a super acid. b). May shield and stabilize charges. c). May facilitate redox reactions. d). Ma ...
... 11). Some enzymes require a necessary metal ion cofactor for catalysis. Which of the following is not a potential property that a metal ion may impart to an enzymatically catalyzed reaction? a). May act as a super acid. b). May shield and stabilize charges. c). May facilitate redox reactions. d). Ma ...
Enzyme Kinetics
... • Nerve gas inhibits cholinesterase. • Iodoacetamide, heavy metal ions (Hg++), oxidising agents. ii. Reversible inhibitors E+I ...
... • Nerve gas inhibits cholinesterase. • Iodoacetamide, heavy metal ions (Hg++), oxidising agents. ii. Reversible inhibitors E+I ...
Enzyme Activity
... Inhibitors are chemicals that reduce the rate of enzymic reactions. The are usually specific and they work at low concentrations. They block the enzyme but they do not usually destroy it. ...
... Inhibitors are chemicals that reduce the rate of enzymic reactions. The are usually specific and they work at low concentrations. They block the enzyme but they do not usually destroy it. ...
Slide 1
... Liver cells have a responsibility to support blood glucose levels by first releasing glucose from their internal glycogen stores, and if necessary synthesizing glucose from amino acids. They will shut down glycolysis and rely on other energy sources for their own needs under these conditions. Liver ...
... Liver cells have a responsibility to support blood glucose levels by first releasing glucose from their internal glycogen stores, and if necessary synthesizing glucose from amino acids. They will shut down glycolysis and rely on other energy sources for their own needs under these conditions. Liver ...
Protein Structure and Function
... -Specific complex is necessary for productive collision; correct orientation Which induces atomic orbitals can overlap to allow the appropriate bonds to be formed or broken. -enzyme offer the time and place for second substrate to bind to enzyme. Negative substrate ...
... -Specific complex is necessary for productive collision; correct orientation Which induces atomic orbitals can overlap to allow the appropriate bonds to be formed or broken. -enzyme offer the time and place for second substrate to bind to enzyme. Negative substrate ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.