Problem Sets / Exams - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... a. (5 points) If a 50 amino acid polypeptide were to sample all of its possible conformations in order to fold, how long would this process take? Assume that each amino acid residue can have three different conformations and it takes one picosecond (10-12) to convert between structures. b. (5 points ...
... a. (5 points) If a 50 amino acid polypeptide were to sample all of its possible conformations in order to fold, how long would this process take? Assume that each amino acid residue can have three different conformations and it takes one picosecond (10-12) to convert between structures. b. (5 points ...
The Aerobic Fate of Pyruvate
... I could tell that some of you were not impressed by the mere 2 ATPs produced per glucose by glycolysis. The 2 ATP’s produced are only a small fraction of the potential energy available from glucose. Under anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potentia ...
... I could tell that some of you were not impressed by the mere 2 ATPs produced per glucose by glycolysis. The 2 ATP’s produced are only a small fraction of the potential energy available from glucose. Under anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potentia ...
E. coli
... Describe what is meant by invasiveness and the mechanisms and factors that affect invasiveness (adherence, penetration, avoidance of phagocytosis, ability to cause damage). ...
... Describe what is meant by invasiveness and the mechanisms and factors that affect invasiveness (adherence, penetration, avoidance of phagocytosis, ability to cause damage). ...
DNA as the Genetic Material
... 1. During DNA replication, this is carried out by DNA polymerase, which proofreads each nucleotide against its template as it is added to a strand. When mistake is found, polymerase removes it and resumes synthesis B. Genetic maintenance is also required in DNA 1. Often DNA molecules are subjected t ...
... 1. During DNA replication, this is carried out by DNA polymerase, which proofreads each nucleotide against its template as it is added to a strand. When mistake is found, polymerase removes it and resumes synthesis B. Genetic maintenance is also required in DNA 1. Often DNA molecules are subjected t ...
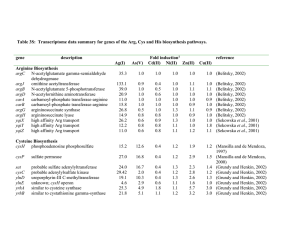
Table 3S
... The yqiXYZ operon encodes a high affinity Arg transport system (Sekowska et al., 2001).The cysH operon together with cysK encodes enzymes for the synthesis of Cys from sulfate and O-acetylserine and the yrhAB genes encode the cystathionine -synthase and lyase for conversion of homocysteine to Cys ...
... The yqiXYZ operon encodes a high affinity Arg transport system (Sekowska et al., 2001).The cysH operon together with cysK encodes enzymes for the synthesis of Cys from sulfate and O-acetylserine and the yrhAB genes encode the cystathionine -synthase and lyase for conversion of homocysteine to Cys ...
milliliters per liter. After 5-day-old cultures wvere
... greatest N15 enrichment. The amino group of glutamine and glutamic acid had the next highest N15 content while that of alanine was lower. These re- ...
... greatest N15 enrichment. The amino group of glutamine and glutamic acid had the next highest N15 content while that of alanine was lower. These re- ...
Organic Acids The basics
... Severe forms will present acutely in the neonatal period whereas other forms may present chronically over a long period of time sometimes with acute episodes. There may be multisystem involvement or the brain may be the only organ affected. Some of the more common organic acid disorders are discusse ...
... Severe forms will present acutely in the neonatal period whereas other forms may present chronically over a long period of time sometimes with acute episodes. There may be multisystem involvement or the brain may be the only organ affected. Some of the more common organic acid disorders are discusse ...
Macromolecule Lecture Notes
... The pink balls with legs are lipids. Lipids, as you can see form the majority of the cell membrane. Lipids also form what we call “fats” in our food. Notes: Macromolecules: Lipids This cell membrane is constructed largely of lipids (fats) arranged in a bi-layer, or 2 layers ("bi" means two). Each li ...
... The pink balls with legs are lipids. Lipids, as you can see form the majority of the cell membrane. Lipids also form what we call “fats” in our food. Notes: Macromolecules: Lipids This cell membrane is constructed largely of lipids (fats) arranged in a bi-layer, or 2 layers ("bi" means two). Each li ...
Lecture Notes Ch21
... add/remove atoms to/from a double bond rearrange atoms combine molecules using ATP Ch 21 | # 4 of 47 ...
... add/remove atoms to/from a double bond rearrange atoms combine molecules using ATP Ch 21 | # 4 of 47 ...
Date: Period
... o Avery, MacLeod, McCarty – tried transformation after knocking out macromolecules (RNA, DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates) transformation NOT successful if DNA knocked out 2. Structure of DNA Deoxyribose nucleic acid, Double helix (two twisted stsrands) made of nucleotides (monomers) Nucleot ...
... o Avery, MacLeod, McCarty – tried transformation after knocking out macromolecules (RNA, DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates) transformation NOT successful if DNA knocked out 2. Structure of DNA Deoxyribose nucleic acid, Double helix (two twisted stsrands) made of nucleotides (monomers) Nucleot ...
Decreased
... windshield washer fluid, etc.) is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase to formaldehyde and formic acid. Leads to metabolic acidosis and optic neuritis (from formate) that can cause blindness. • Treatment: Infuse EtOH to keep blood concentration at 100-200 mg/dL (legally intoxicated) for long enough ...
... windshield washer fluid, etc.) is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase to formaldehyde and formic acid. Leads to metabolic acidosis and optic neuritis (from formate) that can cause blindness. • Treatment: Infuse EtOH to keep blood concentration at 100-200 mg/dL (legally intoxicated) for long enough ...
Cell Respiration Flow Chart
... joins a 4 carbon molecule, called oxaloacetate, to become a 6 carbon molecule called citric acid. Seven more steps happen, each involving different enzymes. Both acetyl CoA from the two pyruvates will go through this cycle. D uring this process, two carbon atoms are removed to become CO2 while ...
... joins a 4 carbon molecule, called oxaloacetate, to become a 6 carbon molecule called citric acid. Seven more steps happen, each involving different enzymes. Both acetyl CoA from the two pyruvates will go through this cycle. D uring this process, two carbon atoms are removed to become CO2 while ...
Measuring the Electron Transport Properties of DNA Molecules
... academic, electronic behavior of DNA is very closely related to function. There are electrochemical processes which are mediated by these DNA biological molecules. For instance, radiation damage and mutation – how does the DNA deal with an extra electron or an absence of an electron located somewher ...
... academic, electronic behavior of DNA is very closely related to function. There are electrochemical processes which are mediated by these DNA biological molecules. For instance, radiation damage and mutation – how does the DNA deal with an extra electron or an absence of an electron located somewher ...
Lecture 5: Major Nutrient Groups
... primary: the sequence of AA’s forming the protein secondary: forces generated by the close proximity of one AA residue to another (e.g., helix design or pleated sheet)(i.e., certain amino acids can form bonds with others, if close enough, cysteine) tertiary: bending of one AA chain due to attrac ...
... primary: the sequence of AA’s forming the protein secondary: forces generated by the close proximity of one AA residue to another (e.g., helix design or pleated sheet)(i.e., certain amino acids can form bonds with others, if close enough, cysteine) tertiary: bending of one AA chain due to attrac ...
Presentation
... Mutations may be harmful. Mutations may be beneficial. Mutations may have no effect on the organism. ...
... Mutations may be harmful. Mutations may be beneficial. Mutations may have no effect on the organism. ...
here - Sites@PSU
... (esp. Lactobacillus, Lactococcus) – Lb. johnsonii can’t make any amino acids, for example ...
... (esp. Lactobacillus, Lactococcus) – Lb. johnsonii can’t make any amino acids, for example ...
4 Regulation Enzyme Activity GOB Structures
... In feedback control, when the end product level is high, • the end product of a series of reactions acts as a negative regulator and binds to the allosteric site. • the substrate cannot bind to the active site, and production of all of the intermediate compounds in the subsequent reaction sequence s ...
... In feedback control, when the end product level is high, • the end product of a series of reactions acts as a negative regulator and binds to the allosteric site. • the substrate cannot bind to the active site, and production of all of the intermediate compounds in the subsequent reaction sequence s ...
Full_ppt_ch21
... • An enzyme binds a substrate in a region called the active site – Only certain substrates can fit the active site – Amino acid R groups in the active site help substrate bind and align correctly ...
... • An enzyme binds a substrate in a region called the active site – Only certain substrates can fit the active site – Amino acid R groups in the active site help substrate bind and align correctly ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.