File
... All six essential elements may be used in the production of small subunits called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids, each with a specific side chain of chemicals. Amino acids bond to other amino acids to form a long chain called a protein. These chains of amino acids fold into a partic ...
... All six essential elements may be used in the production of small subunits called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids, each with a specific side chain of chemicals. Amino acids bond to other amino acids to form a long chain called a protein. These chains of amino acids fold into a partic ...
3 - Milan Area Schools
... Answer: unsaturated (or carbon double) 2. Many monosaccharides like fructose, mannose, and galactose have the same chemical formula as glucose (C6H12O6), but the atoms are combined differently to yield different structural arrangements. These varying forms of the same chemical formula are called ___ ...
... Answer: unsaturated (or carbon double) 2. Many monosaccharides like fructose, mannose, and galactose have the same chemical formula as glucose (C6H12O6), but the atoms are combined differently to yield different structural arrangements. These varying forms of the same chemical formula are called ___ ...
Model Description Sheet
... Primary Citation: Babu, Y.S., Buggs, C.E., & Cook, W.J. (1998) Structure of Calmodulin refined at 2.2 A resolution. J.Mol. Biology. 204. 191-204. ...
... Primary Citation: Babu, Y.S., Buggs, C.E., & Cook, W.J. (1998) Structure of Calmodulin refined at 2.2 A resolution. J.Mol. Biology. 204. 191-204. ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... two stages: transcription of DNA into mRNA translation of the mRNA into protein mRNA is transcribed from one strand of DNA and is complementary to this (noncoding) strand and identical with the other (coding) strand. The sequence of mRNA, in triplet codons 5′ 3′, is related to the amino acid sequenc ...
... two stages: transcription of DNA into mRNA translation of the mRNA into protein mRNA is transcribed from one strand of DNA and is complementary to this (noncoding) strand and identical with the other (coding) strand. The sequence of mRNA, in triplet codons 5′ 3′, is related to the amino acid sequenc ...
SN1 Question Paper Sum 2007
... (iv) Some triglycerides have several double bonds (C=C), others have none. Describe one way in which the physical property of triglycerides which include several double bonds will differ from triglycerides which have no double bonds. ...
... (iv) Some triglycerides have several double bonds (C=C), others have none. Describe one way in which the physical property of triglycerides which include several double bonds will differ from triglycerides which have no double bonds. ...
Lipids
... the plasma, where they bind to serum albumin and are transported to tissue for oxidation ...
... the plasma, where they bind to serum albumin and are transported to tissue for oxidation ...
S.G. Key Final - USC Upstate: Faculty
... The acidic form of hemoglobin (H·Hb+) is the form of hemoglobin that has lower affinity for O2. This shift is known as the Bohr effect, and it is among a number of factors that act to shift Hb to the lower affinity form to increase its release of O2 in the tissues. 28. Given a chiral molecule, be ab ...
... The acidic form of hemoglobin (H·Hb+) is the form of hemoglobin that has lower affinity for O2. This shift is known as the Bohr effect, and it is among a number of factors that act to shift Hb to the lower affinity form to increase its release of O2 in the tissues. 28. Given a chiral molecule, be ab ...
Separation of Racemic Mixtures of Amino Acids Using Chiral Eluents
... exception of glycin, are chiral substances; however, only the single enantiomeric forms are used. Modern technologies for production of amino acids single enantiomers are based on chemical or biochemical synthesis and fermentation methods.3-7 The asymmetric synthesis is associated with high costs, c ...
... exception of glycin, are chiral substances; however, only the single enantiomeric forms are used. Modern technologies for production of amino acids single enantiomers are based on chemical or biochemical synthesis and fermentation methods.3-7 The asymmetric synthesis is associated with high costs, c ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... The citric acid enters the Krebs cycle and is converted into carbon dioxide (a waste product), ATP, NADH, and FADH2 The NADH and FADH2 can now enter the electron transport chain These reactions take place in the mitochondria ...
... The citric acid enters the Krebs cycle and is converted into carbon dioxide (a waste product), ATP, NADH, and FADH2 The NADH and FADH2 can now enter the electron transport chain These reactions take place in the mitochondria ...
migdy
... Explain the induced fit model of enzyme function and describe the catalytic cycle of an enzyme. Induced fit brings chemical groups of the active site into positions that enhance their ability to work on the substrate and catalyze the chemical reaction. The catalytic cycle of an enzyme starts by the ...
... Explain the induced fit model of enzyme function and describe the catalytic cycle of an enzyme. Induced fit brings chemical groups of the active site into positions that enhance their ability to work on the substrate and catalyze the chemical reaction. The catalytic cycle of an enzyme starts by the ...
Document
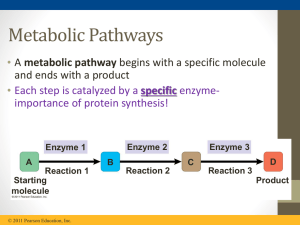
... • Catabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds (Cellular respiration, the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen) • Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones (synthesis of protein from amino acids) ...
... • Catabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds (Cellular respiration, the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen) • Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones (synthesis of protein from amino acids) ...
Document
... amino acids, diacids) and bacterial DNA damages (ELISA protocols) at 4 depths (5, 80, 200, and 1000 m) 3-Irradiation experiments of freshly collected seawater: sunlight exposure of DOM (photoproduction of sugars, amino acids, diacids) and bacteria (photoproduction of bacterial DNA damages) followed ...
... amino acids, diacids) and bacterial DNA damages (ELISA protocols) at 4 depths (5, 80, 200, and 1000 m) 3-Irradiation experiments of freshly collected seawater: sunlight exposure of DOM (photoproduction of sugars, amino acids, diacids) and bacteria (photoproduction of bacterial DNA damages) followed ...
1 acetyl CoA - WordPress.com
... Oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to a-ketoglutarate (a-kg) (a metabolically irreversible reaction) One of four oxidation-reduction reactions of the cycle Hydride ion from the C-2 of isocitrate is transferred to NAD+ to form NADH Oxalosuccinate is decarboxylated to a-kg ...
... Oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to a-ketoglutarate (a-kg) (a metabolically irreversible reaction) One of four oxidation-reduction reactions of the cycle Hydride ion from the C-2 of isocitrate is transferred to NAD+ to form NADH Oxalosuccinate is decarboxylated to a-kg ...
in Graminaceous Plants
... vulgare) is the most tolerant to Fe deficiency and secretes the largest amount of MAs, while rice is the most susceptible to Fe deficiency and secretes very little MAs (Sugiura et al., 1981; Takagi et al., 1984). MAs are synthesized from l-Met (Mori and Nishizawa, 1987). Nicotianamine synthase (NAS) ...
... vulgare) is the most tolerant to Fe deficiency and secretes the largest amount of MAs, while rice is the most susceptible to Fe deficiency and secretes very little MAs (Sugiura et al., 1981; Takagi et al., 1984). MAs are synthesized from l-Met (Mori and Nishizawa, 1987). Nicotianamine synthase (NAS) ...
unit 1: introduction to biology
... Q. 6: Which of the following metabolic pathways is common to both aerobic and anaerobic processes of sugar breakdown? A) Krebs cycle B) electron transport chain C) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid D) conversion of glucose to pyruvate E) none of the above Q. 7: Which of the following is NOT true ...
... Q. 6: Which of the following metabolic pathways is common to both aerobic and anaerobic processes of sugar breakdown? A) Krebs cycle B) electron transport chain C) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid D) conversion of glucose to pyruvate E) none of the above Q. 7: Which of the following is NOT true ...
Transcription
... strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. ...
... strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.