Enzymes Lab
... 5- Prewarm starch solution in the water bath for 5min at 38C˚. 6- Add 5ml of starch solution to each of the three test tubes; stir the content with glass rode. 7- Record the time of addition of starch and at the end of each minute remove two drops reaction mixture using a test pipette, and add to on ...
... 5- Prewarm starch solution in the water bath for 5min at 38C˚. 6- Add 5ml of starch solution to each of the three test tubes; stir the content with glass rode. 7- Record the time of addition of starch and at the end of each minute remove two drops reaction mixture using a test pipette, and add to on ...
Increasing the thermostability of sucrose
... thus the screening effort, an extension of the B-FIT procedure has recently been proposed, in which the randomisation at each site is limited to amino acids that are frequently present in an alignment of related sequences (Jochens et al., 2010). These residues are assumed to be more favourable for t ...
... thus the screening effort, an extension of the B-FIT procedure has recently been proposed, in which the randomisation at each site is limited to amino acids that are frequently present in an alignment of related sequences (Jochens et al., 2010). These residues are assumed to be more favourable for t ...
What is Ketosis
... Main Characteristics Failure to transport glucose into muscle and adipose tissue Failure to catabolize glucose at a normal rate in liver Excessive oxidation of fatty acids leading to ketosis ...
... Main Characteristics Failure to transport glucose into muscle and adipose tissue Failure to catabolize glucose at a normal rate in liver Excessive oxidation of fatty acids leading to ketosis ...
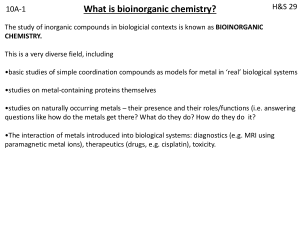
bioinorganic 1
... In virtually all nitrogen-containing biomolecules the nitrogen is in its fully reduced form i.e. in the same oxidation state as ammonia (NH3) or ammonium cation (NH4+). The source of the nitrogen (and the principle form of the element on Earth) is dinitrogen, N2. So living systems need to convert di ...
... In virtually all nitrogen-containing biomolecules the nitrogen is in its fully reduced form i.e. in the same oxidation state as ammonia (NH3) or ammonium cation (NH4+). The source of the nitrogen (and the principle form of the element on Earth) is dinitrogen, N2. So living systems need to convert di ...
Individual Part
... Hemoglobin Geneva (Hb Geneva) is an unstable hemologin with abnormal elongation. This hemoglobinopathy is known for its high instability. Concerning the pathogenesis of Hb Geneva, the data indicate a change in codon 114 from CTG (Leu) to -GG that results in a frame shift and the presumed synthesis o ...
... Hemoglobin Geneva (Hb Geneva) is an unstable hemologin with abnormal elongation. This hemoglobinopathy is known for its high instability. Concerning the pathogenesis of Hb Geneva, the data indicate a change in codon 114 from CTG (Leu) to -GG that results in a frame shift and the presumed synthesis o ...
Chapter 17 Fatty Acid Catabolism
... 1. The process takes place in the cytosol of mammalian cells. 2. Carbon atoms are removed from the acyl chain one at a time. 3. Before oxidation, fatty acids must be converted to their CoA derivatives. ...
... 1. The process takes place in the cytosol of mammalian cells. 2. Carbon atoms are removed from the acyl chain one at a time. 3. Before oxidation, fatty acids must be converted to their CoA derivatives. ...
4. Liver and Gall Bladder
... Cholesterol and Lipoproteins • Cholesterol is synthesized by the liver • Cholesterol synthesis is inversely regulated by dietary intake i.e. increased dietary intake reduces synthesis and reduced intake increases synthesis by the liver • Cholesterol is transported in the plasma as lipoproteins – com ...
... Cholesterol and Lipoproteins • Cholesterol is synthesized by the liver • Cholesterol synthesis is inversely regulated by dietary intake i.e. increased dietary intake reduces synthesis and reduced intake increases synthesis by the liver • Cholesterol is transported in the plasma as lipoproteins – com ...
Presentation
... the ligand construction process is docking One way to test the inhibitory effectiveness would be to introduce our ligands into a vascular system that contains both DUSP5 and ERK This was done in zebrafish before, so it could be repeated with our ligand as a mutation inhibitor ...
... the ligand construction process is docking One way to test the inhibitory effectiveness would be to introduce our ligands into a vascular system that contains both DUSP5 and ERK This was done in zebrafish before, so it could be repeated with our ligand as a mutation inhibitor ...
Respiration
... The outermembrane of the mitochondrial envelop is to establish an isolated environment for the mitochondrion. This membrane also adjusts the metabolites entering and leaving the mitochondrion. The inner membrane is folded up a lot to increase the surface area for attachment of ETC. These infolds are ...
... The outermembrane of the mitochondrial envelop is to establish an isolated environment for the mitochondrion. This membrane also adjusts the metabolites entering and leaving the mitochondrion. The inner membrane is folded up a lot to increase the surface area for attachment of ETC. These infolds are ...
Building 3D models of proteins Why make a structural model for your
... alignments and no direct use of known structures The basic idea is to build empirical function that simulates real physical forces and potentials of chemical contacts If we will have perfect function and we will be able to scan all the possible conformations, then we will be able to detect the corre ...
... alignments and no direct use of known structures The basic idea is to build empirical function that simulates real physical forces and potentials of chemical contacts If we will have perfect function and we will be able to scan all the possible conformations, then we will be able to detect the corre ...
Cloning and characterization of the
... tRNA biogenesis, such as nuclear export. INTRODUCTION The modified nucleoside pseudouridine (Ψ) is present in rRNAs and tRNAs in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae it is found in at least 15 different locations of tRNA. Uridines at positions 13, 27, 28, 31, 32, 38 ...
... tRNA biogenesis, such as nuclear export. INTRODUCTION The modified nucleoside pseudouridine (Ψ) is present in rRNAs and tRNAs in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae it is found in at least 15 different locations of tRNA. Uridines at positions 13, 27, 28, 31, 32, 38 ...
Both DRIs and RDAs refer to long-term average daily nutrient intake
... revision : Dietary carbohydrate : • The main carbohydrate in our diet is starch • Obesity has been more directly related to increasingly inactive lifestyle and to calorie-dense foods served in expanded portion size • Cellulose is the non digestible part of carbohydrate ( IMP) • Dietary fiber : incre ...
... revision : Dietary carbohydrate : • The main carbohydrate in our diet is starch • Obesity has been more directly related to increasingly inactive lifestyle and to calorie-dense foods served in expanded portion size • Cellulose is the non digestible part of carbohydrate ( IMP) • Dietary fiber : incre ...
Model Description Sheet
... to drastically reduce appetite, increase metabolism, and ultimately lead to weight loss. Conversely, knockout of BDNF has been shown to lead to overeating and obesity. BDNF has a high affinity for the receptor Trk-B due to neurotrophins having variable binding domains. The Westosha Central SMART (St ...
... to drastically reduce appetite, increase metabolism, and ultimately lead to weight loss. Conversely, knockout of BDNF has been shown to lead to overeating and obesity. BDNF has a high affinity for the receptor Trk-B due to neurotrophins having variable binding domains. The Westosha Central SMART (St ...
AIBSTCT Nucleic Acids Research - Walter Lab
... containing only the N-terminal 68 amino acids (SRP19N, lanes 7-11). In vitro translation products were synthesized in the absence (lane 1) or in the presence (lanes 2 and 7) of added SRP19 mRNA. Lanes 3-4 and 8-9: products immunoprecipitated with rabbit anti SRP19 antiserum under native (lanes 3 and ...
... containing only the N-terminal 68 amino acids (SRP19N, lanes 7-11). In vitro translation products were synthesized in the absence (lane 1) or in the presence (lanes 2 and 7) of added SRP19 mRNA. Lanes 3-4 and 8-9: products immunoprecipitated with rabbit anti SRP19 antiserum under native (lanes 3 and ...
Carbohydrates
... 1) Monosaccharides: Simple sugar with one saccharide molecule. They are represented by general formula Cn H2n On. The number of carbon atoms in monosaccharides varies from 3 to 7. The carbon atoms form an unbranched straight chain, joined together by single covalent bonds. A monosaccharide molecule ...
... 1) Monosaccharides: Simple sugar with one saccharide molecule. They are represented by general formula Cn H2n On. The number of carbon atoms in monosaccharides varies from 3 to 7. The carbon atoms form an unbranched straight chain, joined together by single covalent bonds. A monosaccharide molecule ...
I LEARN AT HOME ASSIGNMENT 4 Macromolecule Review
... Organic molecules have four common characteristics. First, they are all carbon based, meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all orga ...
... Organic molecules have four common characteristics. First, they are all carbon based, meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all orga ...
I LEARN AT HOME ASSIGNMENT 4 Macromolecule Review
... Organic molecules have four common characteristics. First, they are all carbon based, meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all orga ...
... Organic molecules have four common characteristics. First, they are all carbon based, meaning they all contain carbon. They are formed from just a few elements which join together to form small molecules which join together, or bond, to form large molecules. The third characteristic of all orga ...
THE EFFECT OF ISOELECTRIC AMINO ACIDS ON THE pH + OF A
... also to be the same. Similar observations have been made by Walden and Werner (11) with alanine and betaine, by Ftirth (12) with glycine, and by Bliih (13) with leucine. Aqueous solutions of alcohol, acetone, acetonitrile and glucose have markedly lower, and of urea slightly higher dielectric consta ...
... also to be the same. Similar observations have been made by Walden and Werner (11) with alanine and betaine, by Ftirth (12) with glycine, and by Bliih (13) with leucine. Aqueous solutions of alcohol, acetone, acetonitrile and glucose have markedly lower, and of urea slightly higher dielectric consta ...
Semmelweis University Department of Medical Biochemistry
... The test consists of 60 questions of multiple choice type. The questions are based on the recommended textbook, the lectures and the seminars. The questions are divided in two blocks and further points are added to the score from each block on the basis of the midterms performed during the fall seme ...
... The test consists of 60 questions of multiple choice type. The questions are based on the recommended textbook, the lectures and the seminars. The questions are divided in two blocks and further points are added to the score from each block on the basis of the midterms performed during the fall seme ...
Get - Wiley Online Library
... Each somatic cell in an organism has the same amount (and sequence) of DNA, but these vary dramatically between species. The genome of each organism or virus is organized into a unique number of DNA–protein complexes, called chromosomes. The smallest genomes are carried by viruses and may be fewer t ...
... Each somatic cell in an organism has the same amount (and sequence) of DNA, but these vary dramatically between species. The genome of each organism or virus is organized into a unique number of DNA–protein complexes, called chromosomes. The smallest genomes are carried by viruses and may be fewer t ...
Macronutrients
... Embedded in the membrane is an enzyme called ATP synthase H+ ions flow through the ATP synthase to “even out” the charges on both sides of the membrane As H+ ions flow through, their energy is used to make ATP from ADP and a ...
... Embedded in the membrane is an enzyme called ATP synthase H+ ions flow through the ATP synthase to “even out” the charges on both sides of the membrane As H+ ions flow through, their energy is used to make ATP from ADP and a ...
Practice Test Chapter 9
... A) energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase B) energy released as electrons flow through the electron transport system C) No external source of energy is required because the reaction is exergonic. D) energy released from substrate-level phosphorylation E) energy released from A ...
... A) energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase B) energy released as electrons flow through the electron transport system C) No external source of energy is required because the reaction is exergonic. D) energy released from substrate-level phosphorylation E) energy released from A ...
"thinking acids" handout
... phenolphthalein will be mostly deprotonated (In-) and appear pink. This can be confirmed with calculations, the HendersonHasselbach equation, and/or conceptual reasoning through Le Chatelier's Principle. If we can reason quickly that if pH < pKa then the protonated or unionized form is dominant, the ...
... phenolphthalein will be mostly deprotonated (In-) and appear pink. This can be confirmed with calculations, the HendersonHasselbach equation, and/or conceptual reasoning through Le Chatelier's Principle. If we can reason quickly that if pH < pKa then the protonated or unionized form is dominant, the ...
Gesheng - China
... stem cell of an animal, an animal at the various stages of its formation and development, such as a germ cell, an oosperm, an embryo and so on” ...
... stem cell of an animal, an animal at the various stages of its formation and development, such as a germ cell, an oosperm, an embryo and so on” ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.