Krebs Intro and CycleON
... Most CO2 from catabolism is released during the citric acid cycle or Kreb’s cycle. If anaerobic respiration is occurring, CO2 can be released from alcoholic ...
... Most CO2 from catabolism is released during the citric acid cycle or Kreb’s cycle. If anaerobic respiration is occurring, CO2 can be released from alcoholic ...
Name: __ Date: Homework: The Function of Biomolecules Answer
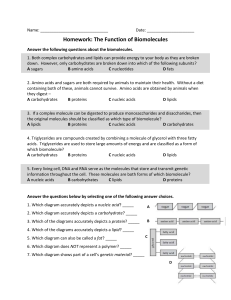
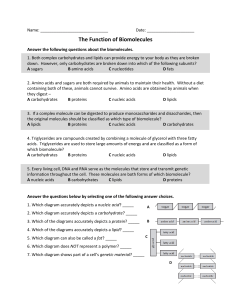
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy C be used to create cell walls B transmit information D be classified as a polymer ...
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy C be used to create cell walls B transmit information D be classified as a polymer ...
Function of Biomolecules Worksheet
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy ...
... 4. A primary difference between the two types of molecules shown above is that only the nucleic acid is able to – A store chemical energy ...
Contributions of direct incorporation from diet and microbial amino
... 4. The incorporation of dietary protein carbon was dependent on dietary protein content and on each amino acid’s biosynthesis pathway. The d13C values of glycolytic amino acids, such as glycine, serine and alanine, had roughly constant values that reflected a large contribution of dietary carbohydra ...
... 4. The incorporation of dietary protein carbon was dependent on dietary protein content and on each amino acid’s biosynthesis pathway. The d13C values of glycolytic amino acids, such as glycine, serine and alanine, had roughly constant values that reflected a large contribution of dietary carbohydra ...
Krebs and ETC
... In step 1, acetyl-CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate. NAD+ is reduced to NADH in steps 3, 4 and 8. FAD is reduced to FADH2 in step 6. ATP if formed in step 5 by substrate-level phosphorylation. The phosphate group from succinylCoA is transferred to GDP, forming GTP, which then forms ATP. ...
... In step 1, acetyl-CoA combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate. NAD+ is reduced to NADH in steps 3, 4 and 8. FAD is reduced to FADH2 in step 6. ATP if formed in step 5 by substrate-level phosphorylation. The phosphate group from succinylCoA is transferred to GDP, forming GTP, which then forms ATP. ...
NMEICT PROJECT
... Enzyme assays is used to measure the enzymatic activity. They are required to study the enzyme kinetics. It has many applications in enzyme kinetics. It helps in understanding the rates of reactions which assist in judging the kind of reaction that enzyme follows. (single- or multiple-substrate mech ...
... Enzyme assays is used to measure the enzymatic activity. They are required to study the enzyme kinetics. It has many applications in enzyme kinetics. It helps in understanding the rates of reactions which assist in judging the kind of reaction that enzyme follows. (single- or multiple-substrate mech ...
Data Sheet
... role in metabolism, healthy growth, reproductive health, and immunity. It also acts as a powerful antioxidant to prevent fatty acid oxidation which can cause tissue damage. Research has shown that Sel-Plex®, an organic form of selenium, is more readily absorbed and retained than selenium in inorgani ...
... role in metabolism, healthy growth, reproductive health, and immunity. It also acts as a powerful antioxidant to prevent fatty acid oxidation which can cause tissue damage. Research has shown that Sel-Plex®, an organic form of selenium, is more readily absorbed and retained than selenium in inorgani ...
Enzymes - Coleg y Cymoedd Moodle
... Interactions between the R groups of the enzyme and the atoms of the substrate can break or encourage formation of bonds with the substrate molecule. So 2 or more products are formed. When reaction complete, product(s) leave active site. Enzyme unchanged, so ready to be used again. Pretty quick rea ...
... Interactions between the R groups of the enzyme and the atoms of the substrate can break or encourage formation of bonds with the substrate molecule. So 2 or more products are formed. When reaction complete, product(s) leave active site. Enzyme unchanged, so ready to be used again. Pretty quick rea ...
Bacterial Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
... of the ribosomes might be in a non-dissociating, ‘active 708’ form. 308 and 5 0 8 particles had been previously shown to reassociate to 708 when the Mga+concentration was restored to 0.01 M but this procedure did not yield ‘ active 708’ribosomes. Until recently it was generally assumed that the RNAs ...
... of the ribosomes might be in a non-dissociating, ‘active 708’ form. 308 and 5 0 8 particles had been previously shown to reassociate to 708 when the Mga+concentration was restored to 0.01 M but this procedure did not yield ‘ active 708’ribosomes. Until recently it was generally assumed that the RNAs ...
The Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions
... 2. The amount of an enzyme is very small compared to the amount of substrate. Therefore, the formation of the enzyme substrate complex does not significantly deplete the substrate. 3. The product concentration is so low that product inhibition may be ...
... 2. The amount of an enzyme is very small compared to the amount of substrate. Therefore, the formation of the enzyme substrate complex does not significantly deplete the substrate. 3. The product concentration is so low that product inhibition may be ...
Discovery of Novel Phosphonate Natural Products Joel P. Cioni1
... allowing identification of organisms with the potential to produce phosphonate compounds, along with the corresponding biosynthetic genes. While this strategy has been validated by identifying and cloning previously known phosphonate gene clusters, a novel phosphonate has yet to be discovered using ...
... allowing identification of organisms with the potential to produce phosphonate compounds, along with the corresponding biosynthetic genes. While this strategy has been validated by identifying and cloning previously known phosphonate gene clusters, a novel phosphonate has yet to be discovered using ...
Bacterial Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
... of the ribosomes might be in a non-dissociating, ‘active 708’ form. 308 and 5 0 8 particles had been previously shown to reassociate to 708 when the Mga+concentration was restored to 0.01 M but this procedure did not yield ‘ active 708’ribosomes. Until recently it was generally assumed that the RNAs ...
... of the ribosomes might be in a non-dissociating, ‘active 708’ form. 308 and 5 0 8 particles had been previously shown to reassociate to 708 when the Mga+concentration was restored to 0.01 M but this procedure did not yield ‘ active 708’ribosomes. Until recently it was generally assumed that the RNAs ...
Conformation-Reactivity Relationship for Pyridoxal Schiff`s Bases
... These include transaminases, decarboxylases, synthetases, racemases, etc. (Snell & Dimari, 1970). All of these reactions are believed to proceed via cleavage of one of three bonds to C, of the amino acid. Dunathan (1966, 1971) postulated that these enzymes control the reaction specificity by control ...
... These include transaminases, decarboxylases, synthetases, racemases, etc. (Snell & Dimari, 1970). All of these reactions are believed to proceed via cleavage of one of three bonds to C, of the amino acid. Dunathan (1966, 1971) postulated that these enzymes control the reaction specificity by control ...
Our work was originally motivated my collaboration with Drs
... DNA sequence corresponding to a known peptide sequence is spliced into the phage DNA. When this spliced sequence is transcribed and translated it produces a 9-mer polypeptide of the form $CX_7C$ (here, $C$ = cysteine, $X$ = any amino acid) which is attached to one of the phage's coat proteins. Conce ...
... DNA sequence corresponding to a known peptide sequence is spliced into the phage DNA. When this spliced sequence is transcribed and translated it produces a 9-mer polypeptide of the form $CX_7C$ (here, $C$ = cysteine, $X$ = any amino acid) which is attached to one of the phage's coat proteins. Conce ...
Chapter 8- An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism
... Where does the energy for maintaining life come from, and how is it used by the cell? All cells require the constant input and expenditure of some form of usable energy. Metabolic pathways use many enzymes and coenzymes to extract chemical energy present in nutrient fuels (like the sugar glucose) an ...
... Where does the energy for maintaining life come from, and how is it used by the cell? All cells require the constant input and expenditure of some form of usable energy. Metabolic pathways use many enzymes and coenzymes to extract chemical energy present in nutrient fuels (like the sugar glucose) an ...
Chapter 6
... At this point the original 6C sugar has been converted to 2 moles of the 3C aldehyde, G3P. This conversion has consumed 2 moles of ATP and has thus been an energy drain on the cell. The glyceraldehyde-3-P is now oxidized to the corresponding acid. This reaction is one of the best understood examples ...
... At this point the original 6C sugar has been converted to 2 moles of the 3C aldehyde, G3P. This conversion has consumed 2 moles of ATP and has thus been an energy drain on the cell. The glyceraldehyde-3-P is now oxidized to the corresponding acid. This reaction is one of the best understood examples ...
SAMPLE PAPER -9 Time Allowed: 3 Hrs
... Helix – peptide chains are right handed screw due to formation of inter H bond between CO gp of one turn amino acid and NH gp of next turn amino acid . Pleated Peptide chains are arranged side by side in Zig – Zag with alternate R on same side. Two neighbouring chains are held by H bond . Sheets are ...
... Helix – peptide chains are right handed screw due to formation of inter H bond between CO gp of one turn amino acid and NH gp of next turn amino acid . Pleated Peptide chains are arranged side by side in Zig – Zag with alternate R on same side. Two neighbouring chains are held by H bond . Sheets are ...
BC 367 Experiment 4 Kinetic Properties of Acid Phosphatase
... artificial substrates for hydrolytic enzymes have been developed which liberate a chromophore (a group that absorbs light) upon hydrolysis. For example, p-Nitrophenylphosphate (PNPP) itself has no absorbance in the visible spectrum, whereas p-nitrophenolate ion, one of the products of enzymic hydrol ...
... artificial substrates for hydrolytic enzymes have been developed which liberate a chromophore (a group that absorbs light) upon hydrolysis. For example, p-Nitrophenylphosphate (PNPP) itself has no absorbance in the visible spectrum, whereas p-nitrophenolate ion, one of the products of enzymic hydrol ...
Thermodynamic considerations of carbon dioxide evolution in
... the present study are as follows: is (i) The reaction, pathway 'H + HCO; - > COzo,,close to equilibrium, since the free energy change of the overall process is only a fraction of 1 kcal mol-'. This value may be compared to the free energy change of the glycolytic pathway in human erythrocytes (-25.2 ...
... the present study are as follows: is (i) The reaction, pathway 'H + HCO; - > COzo,,close to equilibrium, since the free energy change of the overall process is only a fraction of 1 kcal mol-'. This value may be compared to the free energy change of the glycolytic pathway in human erythrocytes (-25.2 ...
Roberts, LM Dept. of Chemistry California State
... FORMAT: The final exam will be all Scantron and will involve True/False and Multiple Choice questions. Water, Acids, and Bases; Bonding; Thermodynamics • Thoroughly understand water's hydrogen-bonding properties • Be able to do a buffer problem • Know that low pKa means good acid, etc. • Be able to ...
... FORMAT: The final exam will be all Scantron and will involve True/False and Multiple Choice questions. Water, Acids, and Bases; Bonding; Thermodynamics • Thoroughly understand water's hydrogen-bonding properties • Be able to do a buffer problem • Know that low pKa means good acid, etc. • Be able to ...
DNA - smoser
... Discovery of the Structure of DNA Erwin Chargaff, 1940’s and early 50's DNA was thought to contain equal amounts of A, T, T, and C. Chargaff found that the base composition of DNA differs among species. His data showed that in each species, the percent of A equals the percent of T, and the percent ...
... Discovery of the Structure of DNA Erwin Chargaff, 1940’s and early 50's DNA was thought to contain equal amounts of A, T, T, and C. Chargaff found that the base composition of DNA differs among species. His data showed that in each species, the percent of A equals the percent of T, and the percent ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.