
Slide 1
... broken down during digestion and absorption into smaller units: AA’s monosaccharides and fatty acids. 2. These smaller compounds are further broken down into 2-carbon compounds. 3. Compounds are degraded into CO2 and H20. Metabolism: FON 241; L. Zienkewicz ...
... broken down during digestion and absorption into smaller units: AA’s monosaccharides and fatty acids. 2. These smaller compounds are further broken down into 2-carbon compounds. 3. Compounds are degraded into CO2 and H20. Metabolism: FON 241; L. Zienkewicz ...
Glycolysis Lecture
... III- True / False a. Electrostatic interactions occur between atoms have the same charge b. In water molecule, Oxygen is highly electrophilic. c. Water molecules are bound together through Ionic bonds. d. Buffers are made up of a mixture of a weak acid with its conjugate base or a weak base with its ...
... III- True / False a. Electrostatic interactions occur between atoms have the same charge b. In water molecule, Oxygen is highly electrophilic. c. Water molecules are bound together through Ionic bonds. d. Buffers are made up of a mixture of a weak acid with its conjugate base or a weak base with its ...
A Support Vector Machine Approach for LTP Using Amino Acid
... (Zea mays), barley (Hordeum vulgare), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and soybean (Glycine max), including a total of 174 data in the training set. In the case of newly developed All-plant model, we have used the simple amino acid approach, which was having an accuracy of 100 % for rice-specific classi ...
... (Zea mays), barley (Hordeum vulgare), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and soybean (Glycine max), including a total of 174 data in the training set. In the case of newly developed All-plant model, we have used the simple amino acid approach, which was having an accuracy of 100 % for rice-specific classi ...
Fatty acids: Review
... catalyzing a series of reactions that sequentially adds C2 units to a growing fatty acid chain covalently attached to the enzyme complex. The mechanism involves the linking malonyl-CoA to an acyl carrier protein, followed by a decarboxylation and condensation reaction that extends the hydrocarbon ch ...
... catalyzing a series of reactions that sequentially adds C2 units to a growing fatty acid chain covalently attached to the enzyme complex. The mechanism involves the linking malonyl-CoA to an acyl carrier protein, followed by a decarboxylation and condensation reaction that extends the hydrocarbon ch ...
Nutrient production by symbiotic bacteria
... of these nutrients (Douglas, 1998). The Buchnera are located in specialised insect cells, known as mycetocytes or bacteriocytes, in the aphid body cavity and they are transmitted to aphid offspring via the ovary (Buchner, 1966). The evidence that Buchnera contributes amino acids to aphids comes prin ...
... of these nutrients (Douglas, 1998). The Buchnera are located in specialised insect cells, known as mycetocytes or bacteriocytes, in the aphid body cavity and they are transmitted to aphid offspring via the ovary (Buchner, 1966). The evidence that Buchnera contributes amino acids to aphids comes prin ...
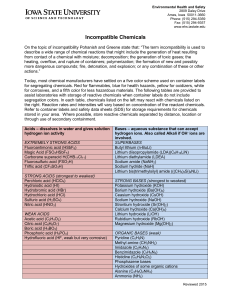
Incompatible Chemicals
... On the topic of incompatibility Pohanish and Greene state that: “The term incompatibility is used to describe a wide range of chemical reactions that might include the generation of heat resulting from contact of a chemical with moisture; decomposition; the generation of toxic gases; the heating, ov ...
... On the topic of incompatibility Pohanish and Greene state that: “The term incompatibility is used to describe a wide range of chemical reactions that might include the generation of heat resulting from contact of a chemical with moisture; decomposition; the generation of toxic gases; the heating, ov ...
Determination of Protein Concentrations Using AAA
... hindrance. Proteins with an exceptionally low composition of dye-binding amino acids (e.g., collagen) produce lower color development and thus underestimate the protein content when calibrated against a dissimilar protein (e.g., BSA). Under conditions where the accuracy of protein determination is a ...
... hindrance. Proteins with an exceptionally low composition of dye-binding amino acids (e.g., collagen) produce lower color development and thus underestimate the protein content when calibrated against a dissimilar protein (e.g., BSA). Under conditions where the accuracy of protein determination is a ...
Chapter 8 Metabolism APc8metabolismme (1)
... Mechanical work: ATP phosphorylates motor proteins Membrane protein ADP ...
... Mechanical work: ATP phosphorylates motor proteins Membrane protein ADP ...
birkbeck college - Principles of Protein Structure
... The amino acid tyrosine can undertake four types of interaction with neighbouring atoms or groups within a protein molecule. Describe these interactions in detail. [10 Marks] ...
... The amino acid tyrosine can undertake four types of interaction with neighbouring atoms or groups within a protein molecule. Describe these interactions in detail. [10 Marks] ...
S13DobrzanskiPoland
... Bakery yeasts (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) were incubated in the laboratory and pilot-plant-scale, in the presence of salts of Cr, Se and Zn according to the method described by Ryszka et al. (2002). The proposed method of yeasts production was characterized with the lack (or low amount) of liquid and ...
... Bakery yeasts (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) were incubated in the laboratory and pilot-plant-scale, in the presence of salts of Cr, Se and Zn according to the method described by Ryszka et al. (2002). The proposed method of yeasts production was characterized with the lack (or low amount) of liquid and ...
File - Manthey AP Biology
... Mechanical work: ATP phosphorylates motor proteins Membrane protein ADP ...
... Mechanical work: ATP phosphorylates motor proteins Membrane protein ADP ...
A MODEL FOR THE PROTEOLYTIC REGULATION OF
... enzymes such as creatine kinase which solve the energtics by either coupling the reaction to an energetically favourable one or by interacting directly with subsequent proteins (Shih and Whitesides, 1977). There is no evidence of either of these mechanisms occurring for this enzyme and to date there ...
... enzymes such as creatine kinase which solve the energtics by either coupling the reaction to an energetically favourable one or by interacting directly with subsequent proteins (Shih and Whitesides, 1977). There is no evidence of either of these mechanisms occurring for this enzyme and to date there ...
Pymol Tutorial
... This is because both are composed of multiple domains and the orientation of these is not equal in both proteins. To get a proper structural alignment we must align only some domains. To do this, we will select the 1ZVN B chain protein (green). Click on the the bottom right on "Selecting" on "Resid ...
... This is because both are composed of multiple domains and the orientation of these is not equal in both proteins. To get a proper structural alignment we must align only some domains. To do this, we will select the 1ZVN B chain protein (green). Click on the the bottom right on "Selecting" on "Resid ...
Protein Structure and Function
... Folding, modification, and degradation of proteins The life of a protein can briefly be described as: synthesis, folding, modification, function, degradation. a A newly synthesized polypeptide chain must undergo folding and often chemical modification to generate the final protein a All molecules o ...
... Folding, modification, and degradation of proteins The life of a protein can briefly be described as: synthesis, folding, modification, function, degradation. a A newly synthesized polypeptide chain must undergo folding and often chemical modification to generate the final protein a All molecules o ...
LEU - TCAPS Moodle
... A technique used to determine evolutionary relationships is to study the biochemical similarity of organisms. Though molds, aardvarks, and humans appear to have little in common physically, a study of their proteins reveals certain similarities. Biologists have perfected techniques for determining t ...
... A technique used to determine evolutionary relationships is to study the biochemical similarity of organisms. Though molds, aardvarks, and humans appear to have little in common physically, a study of their proteins reveals certain similarities. Biologists have perfected techniques for determining t ...
Appendix B HISS Codes for Metabolic Investigations
... Suitable samples for more wide ranging investigations MUST be collected in the acute phase, if the diagnostic window is not to be missed. When further samples, e.g. hypoglycaemia investigations, are collected during the acute presentation, it is essential that any necessary acute pre-analytical hand ...
... Suitable samples for more wide ranging investigations MUST be collected in the acute phase, if the diagnostic window is not to be missed. When further samples, e.g. hypoglycaemia investigations, are collected during the acute presentation, it is essential that any necessary acute pre-analytical hand ...
[S], K m
... (c) An enzyme complementary to the reaction transition state will help to destabilize the stick, resulting in catalysis of the reaction. The magnetic interactions provide energy that compensates for the increase in free energy required to bend the stick. Reaction coordinate diagrams show the energe ...
... (c) An enzyme complementary to the reaction transition state will help to destabilize the stick, resulting in catalysis of the reaction. The magnetic interactions provide energy that compensates for the increase in free energy required to bend the stick. Reaction coordinate diagrams show the energe ...
In vivo analysis of straight-chain and branched
... very high level of intact butyrate incorporation is, however, more consistent with the direct utilization of butyryl-CoA for fatty acid biosynthesis using either a Type I or Type II fatty acid synthase (Fig. 1). In contrast, a low level of intact hexanoate incorporation into the straight-chain fatty ...
... very high level of intact butyrate incorporation is, however, more consistent with the direct utilization of butyryl-CoA for fatty acid biosynthesis using either a Type I or Type II fatty acid synthase (Fig. 1). In contrast, a low level of intact hexanoate incorporation into the straight-chain fatty ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.





















![[S], K m](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008275352_1-bf2876422b91ee7fa9eb4fe4480083af-300x300.png)
