Caspaar Bijleveld and Math JH Geelen
... [lO,ll]. These difficulties can be circumvented by coupling the carboxylation reaction with the fatty acid synthase reaction. In this coupled system the rate of formation of labelled malonyl-CoA from radioactive acetyl-CoA is measured by determining the incorporation of 14C into long-chain fatty aci ...
... [lO,ll]. These difficulties can be circumvented by coupling the carboxylation reaction with the fatty acid synthase reaction. In this coupled system the rate of formation of labelled malonyl-CoA from radioactive acetyl-CoA is measured by determining the incorporation of 14C into long-chain fatty aci ...
E. Diuretics
... carboxyl group provides optimal diuretic activity, but other groups, as tetrazole, may have respectable diuretic activity. 2) A sulfamoyl group in the 5-position is essential for optimal high-ceiling diuretic activity. 3) The activating group (x-) in the 4-position can be Cl- or CF3-, a phenoxy-, al ...
... carboxyl group provides optimal diuretic activity, but other groups, as tetrazole, may have respectable diuretic activity. 2) A sulfamoyl group in the 5-position is essential for optimal high-ceiling diuretic activity. 3) The activating group (x-) in the 4-position can be Cl- or CF3-, a phenoxy-, al ...
Interaction of Urea with Amino Acids: Implications for Urea
... Hydrogen Bonding. Hydrogen bonds between water, urea, and the amino acids were analyzed, and their strength was estimated via the Espinosa formula.37 The average hydrogen bond energies are given in Figure 2 for all side-chain donors and acceptors. As can be seen, all hydrogen bonds to water (blue nu ...
... Hydrogen Bonding. Hydrogen bonds between water, urea, and the amino acids were analyzed, and their strength was estimated via the Espinosa formula.37 The average hydrogen bond energies are given in Figure 2 for all side-chain donors and acceptors. As can be seen, all hydrogen bonds to water (blue nu ...
Chemical Composition and antibacterial activity of
... EEP and H-Fr chemical compositions were analyzed by HRGC-FID and GC-MS, and high and similar concentrations of fatty acids were observed, which is corroborated by previous findings (Table 2) [12,13]. We identified the following fatty acids: oleic (18:1), palmitic (16:0), linoleic (18:2), and stearic ...
... EEP and H-Fr chemical compositions were analyzed by HRGC-FID and GC-MS, and high and similar concentrations of fatty acids were observed, which is corroborated by previous findings (Table 2) [12,13]. We identified the following fatty acids: oleic (18:1), palmitic (16:0), linoleic (18:2), and stearic ...
Directing Effects of Substituents in Conjugation with the
... Modifying the amino and hydroxy substituents provides better control of non-substitution. The substituents in N-phenylacetamide and methoxybenzene are ortho- and para-directing but less strongly activating than benzenamine and phenol. ...
... Modifying the amino and hydroxy substituents provides better control of non-substitution. The substituents in N-phenylacetamide and methoxybenzene are ortho- and para-directing but less strongly activating than benzenamine and phenol. ...
Pyruvate Glucose - School of Medicine
... an acceptor. Hexokinase has a more general specificity in that it can transfer phosphate to other sugars such as mannose. ...
... an acceptor. Hexokinase has a more general specificity in that it can transfer phosphate to other sugars such as mannose. ...
Multiple Manner Transposons in Flatworms and Hydras Are Related
... PCR, visualization of products, band purification, cloning, and sequencing were performed as described in Robertson and MacLeod (1993). Sequences were aligned with those previously obtained and those published by others, and a representative set of the closest relatives and representatives of the kn ...
... PCR, visualization of products, band purification, cloning, and sequencing were performed as described in Robertson and MacLeod (1993). Sequences were aligned with those previously obtained and those published by others, and a representative set of the closest relatives and representatives of the kn ...
Nutrition acquisition strategies during fungal infection of plants
... penetration process (Table 1). Mobilization of lipid stores occurs through lipolysis and b-oxidation cycles to form acetyl-CoA, which is further assimilated into the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) via the glyoxylate cycle. The glyoxisomal enzyme isocitrate lyase (ICL), a marker for lipolytic a ...
... penetration process (Table 1). Mobilization of lipid stores occurs through lipolysis and b-oxidation cycles to form acetyl-CoA, which is further assimilated into the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) via the glyoxylate cycle. The glyoxisomal enzyme isocitrate lyase (ICL), a marker for lipolytic a ...
work № 1. colour reactions of amino acids and proteins
... Hydrolysis of protein is a process of biopolymer’s degradation with cleavage of peptide bonds through the assistance of water molecules under the action of acids, alkalis or proteases. In laboratory conditions hydrolysis of protein is used for determination of primary structure and amino acid compos ...
... Hydrolysis of protein is a process of biopolymer’s degradation with cleavage of peptide bonds through the assistance of water molecules under the action of acids, alkalis or proteases. In laboratory conditions hydrolysis of protein is used for determination of primary structure and amino acid compos ...
Hyaluronic Acid in Dermatology and Dermocosmetics
... defence mechanisms to minimize this damage and possibly repair it, thanks to endogenous anti-oxidant substances, or substances which are synthesized by the body itself: these include catalasys, superoxide dismutases and glutathione. Other types of antioxidant can be consumed in the diet, in order to ...
... defence mechanisms to minimize this damage and possibly repair it, thanks to endogenous anti-oxidant substances, or substances which are synthesized by the body itself: these include catalasys, superoxide dismutases and glutathione. Other types of antioxidant can be consumed in the diet, in order to ...
Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of another variant of the
... Bacteriophage induction. Induction of bacteriophages was accomplished by: (1) exposure of cultures to ultraviolet light as described by O'Brien e f al. (1984); and (2) addition of mitomycin C (Sigma) to midexponential-phase cultures (ODbo00.5) to a final concentration of 1 pg ml-I (Karch & Bitzman, ...
... Bacteriophage induction. Induction of bacteriophages was accomplished by: (1) exposure of cultures to ultraviolet light as described by O'Brien e f al. (1984); and (2) addition of mitomycin C (Sigma) to midexponential-phase cultures (ODbo00.5) to a final concentration of 1 pg ml-I (Karch & Bitzman, ...
$doc.title
... the flavonoid pigmentation pathways that exist in flowers (Elomaa and Holton, 1994; Forkmann and Martens, 2001). To create black flowers, for example, researchers tried to increase the concentrations of flavonoid pigments to very high levels. Few of these attempts gave any encouraging results, and m ...
... the flavonoid pigmentation pathways that exist in flowers (Elomaa and Holton, 1994; Forkmann and Martens, 2001). To create black flowers, for example, researchers tried to increase the concentrations of flavonoid pigments to very high levels. Few of these attempts gave any encouraging results, and m ...
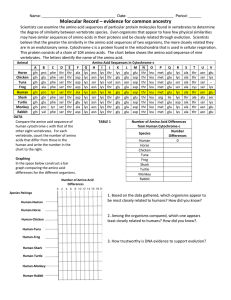
Molecular Record – evidence for common ancestry
... Scientists can examine the amino acid sequences of particular protein molecules found in vertebrates to determine the degree of similarity between vertebrate species. Even organisms that appear to have few physical similarities may have similar sequences of amino acids in their proteins and be close ...
... Scientists can examine the amino acid sequences of particular protein molecules found in vertebrates to determine the degree of similarity between vertebrate species. Even organisms that appear to have few physical similarities may have similar sequences of amino acids in their proteins and be close ...
Principles of transcriptional control in the metabolic
... Figure 1 Correlation between genes of the same metabolic pathway. (a) Distribution of the average more systematically. Isozymes could provide correlation between genes assigned to the same metabolic pathway in the KEGG database. The redundancy, which may be important for distribution corresponding t ...
... Figure 1 Correlation between genes of the same metabolic pathway. (a) Distribution of the average more systematically. Isozymes could provide correlation between genes assigned to the same metabolic pathway in the KEGG database. The redundancy, which may be important for distribution corresponding t ...
Sept18 - Staff Web Pages
... Inside cells, fatty acids (FA) are usually connected to a molecule of the tri-hydroxy (tri-alcohol) compound glycerol. Once again water is removed, this time producing an ester bond (acid + alcohol, draw, see top right corner of lipids handout). If all 3 OH 's on the glycerol are substituted with FA ...
... Inside cells, fatty acids (FA) are usually connected to a molecule of the tri-hydroxy (tri-alcohol) compound glycerol. Once again water is removed, this time producing an ester bond (acid + alcohol, draw, see top right corner of lipids handout). If all 3 OH 's on the glycerol are substituted with FA ...
©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies
... biochemistry, sugars play another role besides being the main energy source for metabolism via the process of glycolysis – they can also combine with proteins to create glycoprotein hormones that are essential for all mammal reproduction or combine with lipids to create glycolipids which make up par ...
... biochemistry, sugars play another role besides being the main energy source for metabolism via the process of glycolysis – they can also combine with proteins to create glycoprotein hormones that are essential for all mammal reproduction or combine with lipids to create glycolipids which make up par ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.