Curriculum Vitae
... Jansonius), and genetic engineering techniques. Also, the structure and function of a new DNA binding protein, the DgdR repressor, which has been cloned and expressed in E. coli in our lab, is under study. DNA binding by the DgdR protein is regulated by certain dialkylglycine amino acids. These stud ...
... Jansonius), and genetic engineering techniques. Also, the structure and function of a new DNA binding protein, the DgdR repressor, which has been cloned and expressed in E. coli in our lab, is under study. DNA binding by the DgdR protein is regulated by certain dialkylglycine amino acids. These stud ...
Document
... Once the amide nitrogen in compounds 1 or 4 gets deprotonated (Scheme 2) its nucleophilicity seems to be high and the formed five-membered ring is energetically favoured. As the chlorine in acyl chlorides 4 represents a good leaving group the reaction demands conditions only slightly above room temp ...
... Once the amide nitrogen in compounds 1 or 4 gets deprotonated (Scheme 2) its nucleophilicity seems to be high and the formed five-membered ring is energetically favoured. As the chlorine in acyl chlorides 4 represents a good leaving group the reaction demands conditions only slightly above room temp ...
chapter 9 cellular respiration: harvesting chemical energy
... Several steps in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are redox reactions in which dehydrogenase enzymes transfer electrons from substrates to NAD +, forming NADH. ...
... Several steps in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are redox reactions in which dehydrogenase enzymes transfer electrons from substrates to NAD +, forming NADH. ...
11-Electrophoretic method for the separation of LDH
... reaction is efficient and large amounts of lactate can be formed. In tissues that preferentially oxidize glucose aerobically to CO2 and water, such as cardiac muscle, the reaction is not efficient and pyruvate is preferentially converted to acetyl CoA which enters the citric acid cycle. In order to ...
... reaction is efficient and large amounts of lactate can be formed. In tissues that preferentially oxidize glucose aerobically to CO2 and water, such as cardiac muscle, the reaction is not efficient and pyruvate is preferentially converted to acetyl CoA which enters the citric acid cycle. In order to ...
Cell Respiration
... Several steps in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are redox reactions in which dehydrogenase enzymes transfer electrons from substrates to NAD +, forming NADH. ...
... Several steps in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are redox reactions in which dehydrogenase enzymes transfer electrons from substrates to NAD +, forming NADH. ...
KRAS activity Teachers` notes
... Discussion: How does information like this influence our approach to cancer? Use the information below to stimulate discussion on how genomic information can be used to further our understanding of cancer. Discussion points for students: • What experiments or approaches could be used to establish wh ...
... Discussion: How does information like this influence our approach to cancer? Use the information below to stimulate discussion on how genomic information can be used to further our understanding of cancer. Discussion points for students: • What experiments or approaches could be used to establish wh ...
PHOTOTROPHS
... 2) !-ketoglutarate-synthase instead of "ketoglutaratedehydrogenase 3) Fumarate synthase instead of succinate dehydrogenase ...
... 2) !-ketoglutarate-synthase instead of "ketoglutaratedehydrogenase 3) Fumarate synthase instead of succinate dehydrogenase ...
Density functional theory and FTIR spectroscopic study of carboxyl
... science: such as surface science1-2, ...
... science: such as surface science1-2, ...
Chapter 05
... • Three of the four classes of macromolecules form chainlike molecules called polymers. – Polymers consist of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ...
... • Three of the four classes of macromolecules form chainlike molecules called polymers. – Polymers consist of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ...
Sequence and transcription analysis of the Petunia mitochondrial
... extension analysis indicates that these two shorter transcripts are not due to splioing. The two shorter transcripts originate at sequences homologous to sites at 5' termini of two pea and maize genes. These consensus sequences may signal processing events other than splicing. ...
... extension analysis indicates that these two shorter transcripts are not due to splioing. The two shorter transcripts originate at sequences homologous to sites at 5' termini of two pea and maize genes. These consensus sequences may signal processing events other than splicing. ...
Key area 2 * Cellular respiration
... • To start the process off, energy from two ATP molecules is needed. • This can be thought of as an energy investment phase where ATP is used to phosphorylate intermediates in glycolysis. ...
... • To start the process off, energy from two ATP molecules is needed. • This can be thought of as an energy investment phase where ATP is used to phosphorylate intermediates in glycolysis. ...
Tangping Li, Ke Fan, Jun Wang and Wei Wang Reduction of protein
... viewpoint, this may imply that a 20 letter alphabet can be reduced into an N letter alphabet by clustering the similar amino acids into N groups, and then N letters can be chosen as the representative residues of these N groups (Chan, 1999; Wang and Wang, 1999). Obviously, the simplest reduction is ...
... viewpoint, this may imply that a 20 letter alphabet can be reduced into an N letter alphabet by clustering the similar amino acids into N groups, and then N letters can be chosen as the representative residues of these N groups (Chan, 1999; Wang and Wang, 1999). Obviously, the simplest reduction is ...
Citric acid cycle ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN AND
... 6.12 Chemiosmosis powers most ATP production • The electrons from NADH and FADH2 travel down the electron transport chain to oxygen • Energy released by the electrons is used to pump H+ into the space between the ...
... 6.12 Chemiosmosis powers most ATP production • The electrons from NADH and FADH2 travel down the electron transport chain to oxygen • Energy released by the electrons is used to pump H+ into the space between the ...
lecture notes
... Secondary structure can be defined as the local conformation adopted by a polypeptide backbone, purposefully excluding more global issues of three-dimensional shape that can be found in a 300+ residue protein. As seen in Figure S.7, the polypeptide backbone is constrained to adopt only a limited ran ...
... Secondary structure can be defined as the local conformation adopted by a polypeptide backbone, purposefully excluding more global issues of three-dimensional shape that can be found in a 300+ residue protein. As seen in Figure S.7, the polypeptide backbone is constrained to adopt only a limited ran ...
TQ bank Lab 4
... D: Means that most of the oxygen is at the top of the tube, and the least amount of oxygen is at the bottom of the tube. To prepare this medium, a reducing agent called Sodium thioglycolate was added. What does this do? A: REDUCING MEDIUM. It gets rid of the oxygen. B: Removes the free oxygen by che ...
... D: Means that most of the oxygen is at the top of the tube, and the least amount of oxygen is at the bottom of the tube. To prepare this medium, a reducing agent called Sodium thioglycolate was added. What does this do? A: REDUCING MEDIUM. It gets rid of the oxygen. B: Removes the free oxygen by che ...
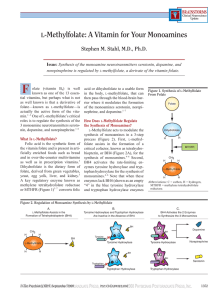
L-Methylfolate: A Vitamin for Your Monoamines
... or being from a group (Hispanic and Mediterranean populations) at high risk for decreased levels of this enzyme • Documented high homocysteine levels, which tend to rise when folate falls • Drugs that can interfere with folate conversion to L-methylfolate such as lamotrigine and valproate Preference ...
... or being from a group (Hispanic and Mediterranean populations) at high risk for decreased levels of this enzyme • Documented high homocysteine levels, which tend to rise when folate falls • Drugs that can interfere with folate conversion to L-methylfolate such as lamotrigine and valproate Preference ...
vitamine
... main groups which are fatsoluble vitamins and watersoluble vitamins. Fat-soluble vitamins are usually found in foods that contain fat. The body stores the fat soluble vitamins and because of this, people don’t usually need to make a special effort to include them in their diet. ...
... main groups which are fatsoluble vitamins and watersoluble vitamins. Fat-soluble vitamins are usually found in foods that contain fat. The body stores the fat soluble vitamins and because of this, people don’t usually need to make a special effort to include them in their diet. ...
Chapter 4 Microbial Metabolism
... Anabolism: the creation of order by the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones with the input of energy ...
... Anabolism: the creation of order by the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones with the input of energy ...
Full Text - IDOSI Publications
... species [39]. In the present study, palm pollen grains were analyzed for their contents of 17 of the most quantitatively important amino acids. Data obtained are given in Table 4 showed that palm pollen grains contained 8 essential amino acids and 9 nonessential amino acids. The major essential amin ...
... species [39]. In the present study, palm pollen grains were analyzed for their contents of 17 of the most quantitatively important amino acids. Data obtained are given in Table 4 showed that palm pollen grains contained 8 essential amino acids and 9 nonessential amino acids. The major essential amin ...
Journal of Applied Phycology
... 70% and 57% with the RecA proteins of Anabaena variabilis,Synechococcus and Escherichiacoli respectively. Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence revealed that many of the domains and residues assigned functional roles in E. coli RecA are conserved in the Spirulina RecA. Numbering of the E. col ...
... 70% and 57% with the RecA proteins of Anabaena variabilis,Synechococcus and Escherichiacoli respectively. Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence revealed that many of the domains and residues assigned functional roles in E. coli RecA are conserved in the Spirulina RecA. Numbering of the E. col ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.