Comparison of Rumen Amino Acid Protection Technologies
... Glutamic acid Glutamine Glycine Proline Serine Tyrosine ...
... Glutamic acid Glutamine Glycine Proline Serine Tyrosine ...
Document
... It is thought that the enzyme Tyr1, which adds the hydroxyl group to the aromatic ring, may be a key regulated component of this biosynthetic pathway. Significant Tyr1 enzymatic activity is only seen in cells grown in media without added tyrosine. After identifying the Tyr1 gene promoter, you fuse i ...
... It is thought that the enzyme Tyr1, which adds the hydroxyl group to the aromatic ring, may be a key regulated component of this biosynthetic pathway. Significant Tyr1 enzymatic activity is only seen in cells grown in media without added tyrosine. After identifying the Tyr1 gene promoter, you fuse i ...
Cellular Metabolism and Cancer: A Review
... would seem to be little doubt of its reality (18, 140). Somatic inconstancy has been observed in at least eleven major organ or tissue systems in man, and it occurs in various other species. In the Chinese hamster, Cricetulus grÃ-seas (2« = 22), there are eleven pairs of chromosomes. Of these, nine ...
... would seem to be little doubt of its reality (18, 140). Somatic inconstancy has been observed in at least eleven major organ or tissue systems in man, and it occurs in various other species. In the Chinese hamster, Cricetulus grÃ-seas (2« = 22), there are eleven pairs of chromosomes. Of these, nine ...
- Wiley Online Library
... capability to adapt to anaerobiosis by shifting down to a drug resistant dormant state. Here, we report the identification of the first enzyme, L-alanine dehydrogenase, whose specific activity is increased during dormancy development in M. smegmatis. This mycobacterial enzyme activity was previously ...
... capability to adapt to anaerobiosis by shifting down to a drug resistant dormant state. Here, we report the identification of the first enzyme, L-alanine dehydrogenase, whose specific activity is increased during dormancy development in M. smegmatis. This mycobacterial enzyme activity was previously ...
Towards Controlling the Glycoform: A Model Framework Linking
... 19% of the pharmaceutical market with a total sales value of $142bn as of 2011 and substantial anticipated growth [1]. Glycoproteins represent the largest group of biologically-derived medicines, constituting 78 out of 212 approved products by the EMA as of May 2012 [2]. N-linked glycans exert major ...
... 19% of the pharmaceutical market with a total sales value of $142bn as of 2011 and substantial anticipated growth [1]. Glycoproteins represent the largest group of biologically-derived medicines, constituting 78 out of 212 approved products by the EMA as of May 2012 [2]. N-linked glycans exert major ...
CHAPTER 15 ACIDS AND BASES
... If Ka1 >> Ka2, we can assume that the equilibrium concentration of hydrogen ion results only from the first stage of ionization. In the second stage this always leads to an expression of the type: (c + y )( y ) = K a2 (c − y ) where c represents the equilibrium hydrogen ion concentration found in th ...
... If Ka1 >> Ka2, we can assume that the equilibrium concentration of hydrogen ion results only from the first stage of ionization. In the second stage this always leads to an expression of the type: (c + y )( y ) = K a2 (c − y ) where c represents the equilibrium hydrogen ion concentration found in th ...
Absence of Antibody against Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E6 and
... key role in HPV-induced carcinogenesis [2]. Antibodies against HPV-16 E6 and E7 are strongly associated with HPV-16– induced cervical cancer [3]. Serological assays, such as radioimmunoprecipitation assays (RIPAs) or ELISAs, performed by using the entire E6- or E7-prototype protein under native cond ...
... key role in HPV-induced carcinogenesis [2]. Antibodies against HPV-16 E6 and E7 are strongly associated with HPV-16– induced cervical cancer [3]. Serological assays, such as radioimmunoprecipitation assays (RIPAs) or ELISAs, performed by using the entire E6- or E7-prototype protein under native cond ...
Chapter 6 Powerpoint
... The Activation Energy Barrier Every chemical reaction between molecules involves bond breaking and bond forming The initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called the free energy of activation, or activation energy (EA) Activation energy is often supplied in the form of thermal ...
... The Activation Energy Barrier Every chemical reaction between molecules involves bond breaking and bond forming The initial energy needed to start a chemical reaction is called the free energy of activation, or activation energy (EA) Activation energy is often supplied in the form of thermal ...
FEBS Letters
... E. coli, Mentha and Arabidopsis [7^10]. Recently, it was found that in the subsequent steps, a cytidyl group is transferred to MEP catalyzed by the ygbP-encoded gene product of E. coli [11]. The resulting 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylerythritol is phosphorylated by the product of the E. coli ychB ge ...
... E. coli, Mentha and Arabidopsis [7^10]. Recently, it was found that in the subsequent steps, a cytidyl group is transferred to MEP catalyzed by the ygbP-encoded gene product of E. coli [11]. The resulting 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylerythritol is phosphorylated by the product of the E. coli ychB ge ...
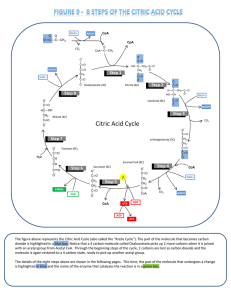
Citric Acid Cycle - BYU
... GDP to make GTP. Later the high energy phosphate on GTP can be used to phosphorylate ADP to make ATP. ...
... GDP to make GTP. Later the high energy phosphate on GTP can be used to phosphorylate ADP to make ATP. ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... • Muscles lack pyruvate dehydrogenase and cannot produce ethanol from pyruvate • Muscle lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to lactate • This reaction regenerates NAD+ for use by glyceraldehyde 3phosphate dehydrogenase in glycolysis • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transpo ...
... • Muscles lack pyruvate dehydrogenase and cannot produce ethanol from pyruvate • Muscle lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to lactate • This reaction regenerates NAD+ for use by glyceraldehyde 3phosphate dehydrogenase in glycolysis • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transpo ...
Couchioplanes caeruleus - International Journal of Systematic and
... of these strains fragmented during the growth cycle and produced motile spores arranged in chains within the mycelia. Sporangia were not observed. The strains contained menaquinone 9(H4), had guanine-plus-cytosine contents of 69.9 to 72.1 mol%, and had D-glutamic acid, D- and L-serine, glycine, L-al ...
... of these strains fragmented during the growth cycle and produced motile spores arranged in chains within the mycelia. Sporangia were not observed. The strains contained menaquinone 9(H4), had guanine-plus-cytosine contents of 69.9 to 72.1 mol%, and had D-glutamic acid, D- and L-serine, glycine, L-al ...
Text S1
... claimed that the high number of NADPH molecules required to synthesize palmitate (compared to the very few ATP molecules required) would lead to a high uptake of glucose (7 molecules of glucose per one molecule of palmitate), whose complete oxidation would generate ATP in excess in the proliferating ...
... claimed that the high number of NADPH molecules required to synthesize palmitate (compared to the very few ATP molecules required) would lead to a high uptake of glucose (7 molecules of glucose per one molecule of palmitate), whose complete oxidation would generate ATP in excess in the proliferating ...
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... Glycolysis: oxidation and cleavage of glucose ATP generation (with and without oxygen) all cells in the cytosol (the reducing equivalents are transferred to the electron-transport chain by the shuttle) ...
... Glycolysis: oxidation and cleavage of glucose ATP generation (with and without oxygen) all cells in the cytosol (the reducing equivalents are transferred to the electron-transport chain by the shuttle) ...
Maritimibacter alkaliphilus gen. nov., sp. nov., a genome
... Morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics of strain HTCC2654T are listed in the genus and species descriptions and in Table 1. The strain was found to be Gram-negative, chemoheterotrophic, strictly aerobic, slightly alkaliphilic, to require NaCl for growth and to consist of non-m ...
... Morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics of strain HTCC2654T are listed in the genus and species descriptions and in Table 1. The strain was found to be Gram-negative, chemoheterotrophic, strictly aerobic, slightly alkaliphilic, to require NaCl for growth and to consist of non-m ...
Russell, MJ, Hall, AJ, and Mellersh, AR, 2003
... those obtaining on young planets such as Earth or Mars (Shock 1996; Russell and Hall 1997; 1999). The emergence of oxygenic photosynthesis is a biochemical rather than a geochemical issue. Even so, we speculate that a pre-existing inorganic CaMn4 complex may have been sequestered by proteins to enab ...
... those obtaining on young planets such as Earth or Mars (Shock 1996; Russell and Hall 1997; 1999). The emergence of oxygenic photosynthesis is a biochemical rather than a geochemical issue. Even so, we speculate that a pre-existing inorganic CaMn4 complex may have been sequestered by proteins to enab ...
BIO 16l EXAM2 SUMMER6WKKey
... 15. For the process of diffusion to occur, molecules must A. move from areas of high concentration to areas of lesser concentration until an equilibrium is reached. b. move from areas of low concentration to areas of higher concentration until an equilibrium is reached. c. remain stationary until th ...
... 15. For the process of diffusion to occur, molecules must A. move from areas of high concentration to areas of lesser concentration until an equilibrium is reached. b. move from areas of low concentration to areas of higher concentration until an equilibrium is reached. c. remain stationary until th ...
Gram Negative Coliforms
... Reduce nitrate (NO3; an inorganic substrate in the API tube. Reduction = positive) • Facultative anaerobes • If they are motile, they have peritrichous flagella, so they can run and tumble. ...
... Reduce nitrate (NO3; an inorganic substrate in the API tube. Reduction = positive) • Facultative anaerobes • If they are motile, they have peritrichous flagella, so they can run and tumble. ...
Module 3 Metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids
... D. All of the above E. None of the above 17. ATP is a cosubstrate of the enzyme PFK-1. In most species ATP is also an inhibitor of PFK-1 at higher concentrations. This seems to violate Le Chatelier's Principle. Which statement below would provide a suitable explanation? A. PFK-1 must be phosphorylat ...
... D. All of the above E. None of the above 17. ATP is a cosubstrate of the enzyme PFK-1. In most species ATP is also an inhibitor of PFK-1 at higher concentrations. This seems to violate Le Chatelier's Principle. Which statement below would provide a suitable explanation? A. PFK-1 must be phosphorylat ...
Stored Triglycerides (Fat)
... When the albumin-FFA complex reaches muscle tissue, the FFAs are released and are transported into a muscle cell. Once in the muscle cell, the FFAs can reesterfy (rebind) with glycerol to form triglycerides or bind with intramuscular proteins to be used for energy production in the mitochondria. In ...
... When the albumin-FFA complex reaches muscle tissue, the FFAs are released and are transported into a muscle cell. Once in the muscle cell, the FFAs can reesterfy (rebind) with glycerol to form triglycerides or bind with intramuscular proteins to be used for energy production in the mitochondria. In ...
A novel sensitive method for the detection of user
... in proteins involved in neurological disorders (Karlin and Burge, 1996). Unlike proteins, DNA sequences are composed only of four residue types and can be quite long. As a result, compositional bias in DNA is considerably harder to deal with than that in proteins. There are two types of compositiona ...
... in proteins involved in neurological disorders (Karlin and Burge, 1996). Unlike proteins, DNA sequences are composed only of four residue types and can be quite long. As a result, compositional bias in DNA is considerably harder to deal with than that in proteins. There are two types of compositiona ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.