biology 422 - TeacherWeb
... 11. What type of molecule is NAD+ and what is its role? 12. What, if any, changes occur in the pathway of glycolysis in the absence of oxygen? 13. How does fermentation allow glycolysis to occur when oxygen is not present? ...
... 11. What type of molecule is NAD+ and what is its role? 12. What, if any, changes occur in the pathway of glycolysis in the absence of oxygen? 13. How does fermentation allow glycolysis to occur when oxygen is not present? ...
MINERALS AND TRACE ELEMENTS - Univerzita Karlova. Prague
... Food iron is predominantly in the ferric state. In the stomach, where the pH is less than 4, Fe3+ can dissociate and react with low-molecular weight compounds such fructose, ascorbic acid, citric acid, amino acids to form ferric complexes soluble in neutral pH of intestine fluid. A protein DMT1 (di ...
... Food iron is predominantly in the ferric state. In the stomach, where the pH is less than 4, Fe3+ can dissociate and react with low-molecular weight compounds such fructose, ascorbic acid, citric acid, amino acids to form ferric complexes soluble in neutral pH of intestine fluid. A protein DMT1 (di ...
The Molecules of Cells
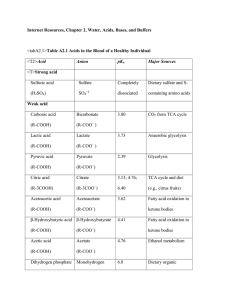
... – Functions to minimize changes in pH – Consists of a chemical or group of chemicals – Function by binding excess hydrogen ions or hydroxyl ions ...
... – Functions to minimize changes in pH – Consists of a chemical or group of chemicals – Function by binding excess hydrogen ions or hydroxyl ions ...
Name ENERGY AND LIFE 8-1 pp 201
... 3. CIRCLE ALL THE STATEMENTS THAT ARE TRUE about ATP. A. ATP consists of ribose sugar, adenine, and 3 phosphate groups B. ADP forms when ATP loses a phosphate and releases energy. C. Used ATP is discarded by the cell as waste. D. ATP provides energy for active transport in cells. ...
... 3. CIRCLE ALL THE STATEMENTS THAT ARE TRUE about ATP. A. ATP consists of ribose sugar, adenine, and 3 phosphate groups B. ADP forms when ATP loses a phosphate and releases energy. C. Used ATP is discarded by the cell as waste. D. ATP provides energy for active transport in cells. ...
Cellular Respiration Guided Reading Notes Section 7
... 6. If there is no oxygen in cells, the products of glycolysis enter ________________________ pathways that yield no additional ______________________. 7. Fermentation is __________________________ because no oxygen is used. 8. If oxygen is present in cells, the glycolysis products enter the ________ ...
... 6. If there is no oxygen in cells, the products of glycolysis enter ________________________ pathways that yield no additional ______________________. 7. Fermentation is __________________________ because no oxygen is used. 8. If oxygen is present in cells, the glycolysis products enter the ________ ...
EXAM III KEY - the Complex Carbohydrate Research Center
... __T___ 9) Most of the free energy needed to drive ATP formation in the mitochondria is the result of an electrical contribution from a charge gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. __T___ 10) Complex II participates in both the electron transport chain and the citric acid cycle. __T___ 11 ...
... __T___ 9) Most of the free energy needed to drive ATP formation in the mitochondria is the result of an electrical contribution from a charge gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. __T___ 10) Complex II participates in both the electron transport chain and the citric acid cycle. __T___ 11 ...
Nutrition Power Point
... Protein molecules consist of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen. The smallest part of a protein is called an amino acid. There are 20 different amino acids Compose blood tissue, muscle tissue, hormones and ...
... Protein molecules consist of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen. The smallest part of a protein is called an amino acid. There are 20 different amino acids Compose blood tissue, muscle tissue, hormones and ...
KREBS CYCLE Definition Krebs cycle (aka tricarboxylic acid cycle
... 2. Before the oxidation reactions can begin, the hydroxyl group of citrate must be repositioned. This is done by removing a water molecule from one carbon and the water is added to different carbon. The product is an isomer of citrate called isocitrate. ...
... 2. Before the oxidation reactions can begin, the hydroxyl group of citrate must be repositioned. This is done by removing a water molecule from one carbon and the water is added to different carbon. The product is an isomer of citrate called isocitrate. ...
Chemical Level of Organization
... 1. ----------- is sum of all chemical reactions taking place in body 2. ----------- increase the rate of reactions 3. -------- substances have large molecules with carbon and hydrogen 4. ----------- is stored energy 5. ---------- is energy of moving substances 6. ---------- release H+ 7. pH scale ha ...
... 1. ----------- is sum of all chemical reactions taking place in body 2. ----------- increase the rate of reactions 3. -------- substances have large molecules with carbon and hydrogen 4. ----------- is stored energy 5. ---------- is energy of moving substances 6. ---------- release H+ 7. pH scale ha ...
Chapter 23 - Evangel University
... Essential Amino Acids • The biosynthesis of proteins requires the presence of all the constituent amino acids • Some species, including humans, cannot produce all of the amino acids and they must come from ____________ and are called essential amino acids ...
... Essential Amino Acids • The biosynthesis of proteins requires the presence of all the constituent amino acids • Some species, including humans, cannot produce all of the amino acids and they must come from ____________ and are called essential amino acids ...
24,7 Loctic Fermentotion
... Your respiratory system supplies the mitochondria of your body cells with enough oxygen to operate their respiratory chains efficiently at normal levels of activity. If you undertake vigorous exercise,such as spdnting or longdistance running, your cells step up respiration to make AIP to megl/their ...
... Your respiratory system supplies the mitochondria of your body cells with enough oxygen to operate their respiratory chains efficiently at normal levels of activity. If you undertake vigorous exercise,such as spdnting or longdistance running, your cells step up respiration to make AIP to megl/their ...
Citrátový cyklus a dýchací řetězec
... • CAC is a set of reactions which form a metabolic pathway for aerobic oxidation of saccharides, lipids and proteins. • Reduced equivalents (NADH, FADH2) are released by sequential decarboxylations and oxidations of citric acid. These reduced equivalents are used to respiratory chain and oxidative p ...
... • CAC is a set of reactions which form a metabolic pathway for aerobic oxidation of saccharides, lipids and proteins. • Reduced equivalents (NADH, FADH2) are released by sequential decarboxylations and oxidations of citric acid. These reduced equivalents are used to respiratory chain and oxidative p ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... passed to oxygen which then picks up a pair of hydrogen ions, forming water FADH2 adds electrons to the chain starting at complex II Complexes I, III, and IV pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space resulting in a higher concentration on one side ...
... passed to oxygen which then picks up a pair of hydrogen ions, forming water FADH2 adds electrons to the chain starting at complex II Complexes I, III, and IV pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space resulting in a higher concentration on one side ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 6, Part 2 Notes – Aerobic Cellular
... 4. The last molecule to receive the electrons is oxygen gas (O 2). Oxygen gas combines with the electrons and H+ to form H2O, one of the products of aerobic cellular respiration. 5. H+ builds up in the intermembrane space and wants to flow back down its concentration gradient across the inner membra ...
... 4. The last molecule to receive the electrons is oxygen gas (O 2). Oxygen gas combines with the electrons and H+ to form H2O, one of the products of aerobic cellular respiration. 5. H+ builds up in the intermembrane space and wants to flow back down its concentration gradient across the inner membra ...
Contents
... At the outset, the senior author of the book welcomes his two sons, Dr. Sunjay Jain and Er. Nitin Jain who have joined me as coauthors of this text, a credit which would have been given earlier to them as they were helping in a latent way in the evolution of the book for the past many years. Thirty ...
... At the outset, the senior author of the book welcomes his two sons, Dr. Sunjay Jain and Er. Nitin Jain who have joined me as coauthors of this text, a credit which would have been given earlier to them as they were helping in a latent way in the evolution of the book for the past many years. Thirty ...
Cell Respiration - Hollidaysburg Area School District
... Kilocalorie on food labels (1 Calorie = 1000 calories) When ...
... Kilocalorie on food labels (1 Calorie = 1000 calories) When ...
Ecology
... a process that uses energy from inorganic compounds to produce carbohydrates. Chemosynthesis is important in bacteria involved in nutrient cycling, and in some ecosystems such as ocean vent communities. ...
... a process that uses energy from inorganic compounds to produce carbohydrates. Chemosynthesis is important in bacteria involved in nutrient cycling, and in some ecosystems such as ocean vent communities. ...
Cell Respiration Notes Kelly
... Each NADH makes 3 ATP (drops its electrons at top of ETC; hits all 3 proton pumps) Each FADH2 makes 2 ATP (drops its electrons at Q; skips 1st proton pump; so makes less ATP) Electrons passing down ETC provide energy for pumping H + ions into INTERMEMBRANE SPACE Final electron acceptor at end of ETC ...
... Each NADH makes 3 ATP (drops its electrons at top of ETC; hits all 3 proton pumps) Each FADH2 makes 2 ATP (drops its electrons at Q; skips 1st proton pump; so makes less ATP) Electrons passing down ETC provide energy for pumping H + ions into INTERMEMBRANE SPACE Final electron acceptor at end of ETC ...
EXAM2
... the big four in a major pathway and I have 4 carbons. I play a prominent role in C4 plants. You may say that I catch CO2, but that is wrong. Some consider me the great communicator. I even have two enzymes named for me. When you think of fatty acid synthesis, I should come strongly in mind. Who am I ...
... the big four in a major pathway and I have 4 carbons. I play a prominent role in C4 plants. You may say that I catch CO2, but that is wrong. Some consider me the great communicator. I even have two enzymes named for me. When you think of fatty acid synthesis, I should come strongly in mind. Who am I ...
Exam 2
... used to pump protons into the lumen of the thylakoid, creating a gradient of protons across the thylakoid membrane. The electrons finally join NADP+ and, along with protons, form NADPH. The chloroplast ATP synthase uses the potential energy in the proton gradient to make ATP. Both NADPH and ATP are ...
... used to pump protons into the lumen of the thylakoid, creating a gradient of protons across the thylakoid membrane. The electrons finally join NADP+ and, along with protons, form NADPH. The chloroplast ATP synthase uses the potential energy in the proton gradient to make ATP. Both NADPH and ATP are ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.