Preparation for Exam 1
... glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. These are the premiere catabolic pathways in cells for providing energy. You also were shown anabolic pathways: gluconeogenesis, glycogen synthesis, pentose phosphate. Glycogenolysis (glycogen breakdown) fell in the cracks between glycolysis an ...
... glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. These are the premiere catabolic pathways in cells for providing energy. You also were shown anabolic pathways: gluconeogenesis, glycogen synthesis, pentose phosphate. Glycogenolysis (glycogen breakdown) fell in the cracks between glycolysis an ...
Alkaloid
... complex Electrons (& energy from reduction potential) are derived from 4 NADH At least 16 ATP must be hydrolyzed The ammonia (NH3) produced is either utilized by the nitrogen-fixing bacteria, or secreted into the environment In the case of symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria, the NH3 is transported i ...
... complex Electrons (& energy from reduction potential) are derived from 4 NADH At least 16 ATP must be hydrolyzed The ammonia (NH3) produced is either utilized by the nitrogen-fixing bacteria, or secreted into the environment In the case of symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria, the NH3 is transported i ...
Why Plants Need Phosphorus (Missouri)
... There are many important biochemicals in plants that contain P. enter the chloroplast in order for triose phosPhospholipids are the primary structural com- phates to get out of the chloropast for use in ponent of membranes that surround each other parts of the cell and in other plant parts. plant ce ...
... There are many important biochemicals in plants that contain P. enter the chloroplast in order for triose phosPhospholipids are the primary structural com- phates to get out of the chloropast for use in ponent of membranes that surround each other parts of the cell and in other plant parts. plant ce ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... 3. Which group of organic compounds includes the enzymes? a) nucleic acids b) lipids c) carbohydrates d) proteins e) amino acids 4. Of the following characteristics, which one is not true about enzymes? a) They are essential to the metabolism of cells for the conversion of energy. b) They function b ...
... 3. Which group of organic compounds includes the enzymes? a) nucleic acids b) lipids c) carbohydrates d) proteins e) amino acids 4. Of the following characteristics, which one is not true about enzymes? a) They are essential to the metabolism of cells for the conversion of energy. b) They function b ...
link-1 to past exam paper - Personal Webspace for QMUL
... A ____________________________ reaction has a G (the change in freeenergy) that is negative in sign. A reaction of this kind can be used to drive one that is ____________________________ that is coupled to it in a series of reactions. The key molecule most used as the energy currency of biological ...
... A ____________________________ reaction has a G (the change in freeenergy) that is negative in sign. A reaction of this kind can be used to drive one that is ____________________________ that is coupled to it in a series of reactions. The key molecule most used as the energy currency of biological ...
Ch. 2-4 Review
... c. Side chains (R-groups) of amino acids can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic. d. Proteins made of two or more polypeptide chains have quaternary structure. e. All statements are true. 2. Which statement regarding enzyme function is true? a. Higher temperatures allow greater contact between enzymes and ...
... c. Side chains (R-groups) of amino acids can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic. d. Proteins made of two or more polypeptide chains have quaternary structure. e. All statements are true. 2. Which statement regarding enzyme function is true? a. Higher temperatures allow greater contact between enzymes and ...
A. glycolysis
... delivered to the electron transport chain 2. the electron transport chain is responsible for the majority of ATPs made during cellular respiration 3. series of oxidation-reduction reactions ...
... delivered to the electron transport chain 2. the electron transport chain is responsible for the majority of ATPs made during cellular respiration 3. series of oxidation-reduction reactions ...
CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF LARGE
... 16. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 17. Name the two ends of a protein and explain the reason for their names. 18. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R ...
... 16. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 17. Name the two ends of a protein and explain the reason for their names. 18. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R ...
Enzymes and Metabolic Pathways
... glucose and break the bonds so that the energy trapped in those bonds is released, transferred to ATP, and can be used by the cell to make other things that it needs. 29. Glycolysis: The first sentence is self-explanatory. Note that oxygen is not required for this first step in cellular respiration. ...
... glucose and break the bonds so that the energy trapped in those bonds is released, transferred to ATP, and can be used by the cell to make other things that it needs. 29. Glycolysis: The first sentence is self-explanatory. Note that oxygen is not required for this first step in cellular respiration. ...
Midterm Exam Key
... 23) __I___ this enzyme phosphorylates glucose 24) __H__ membranes containing this molecule will be more fluid than membranes which do not contain this molecule 25) __C__ the only protein of the electron transport chain that is not a proton pump 26) __J___ the activity of this enzyme can be allosteri ...
... 23) __I___ this enzyme phosphorylates glucose 24) __H__ membranes containing this molecule will be more fluid than membranes which do not contain this molecule 25) __C__ the only protein of the electron transport chain that is not a proton pump 26) __J___ the activity of this enzyme can be allosteri ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration, Harvesting Chemical Energy
... The CAC functions as a metabolic furnace that oxidizes organic fuel derived from pyruvate (Acetyl CoA) o The Cycle generates 1 ATP per turn by substrate-level phosphorylation o Most of the chemical energy is transferred to NAD+ and the related coenzyme FAD (create NADH and FADH2) ...
... The CAC functions as a metabolic furnace that oxidizes organic fuel derived from pyruvate (Acetyl CoA) o The Cycle generates 1 ATP per turn by substrate-level phosphorylation o Most of the chemical energy is transferred to NAD+ and the related coenzyme FAD (create NADH and FADH2) ...
Cellular Respiration - Local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... organelles suggests it was found in early prokaryotic cells since eukaryotes appeared 1 billion years after prokaryotes ...
... organelles suggests it was found in early prokaryotic cells since eukaryotes appeared 1 billion years after prokaryotes ...
questions for lipids
... b. write the reaction for the rate-limiting step (no structures required) ...
... b. write the reaction for the rate-limiting step (no structures required) ...
Enzyme Notes
... metabolism is the process of breaking down and creating molecules necessary for life ◦ each step in this process is driven by an enzyme which directs the speed of the reaction (enzymes are proteins!) catabolic--breakdown molecules cellular respiration ...
... metabolism is the process of breaking down and creating molecules necessary for life ◦ each step in this process is driven by an enzyme which directs the speed of the reaction (enzymes are proteins!) catabolic--breakdown molecules cellular respiration ...
Cell Structures and Their Functions - GCG-42
... formed from the golgi apparatus . They contain a variety of enzymes that functions as intracellular digestive systems Peroxisomes small membrane bound vesicles containing enzymes that break down fatty acids , amino acids and hydrogen peroxide. ...
... formed from the golgi apparatus . They contain a variety of enzymes that functions as intracellular digestive systems Peroxisomes small membrane bound vesicles containing enzymes that break down fatty acids , amino acids and hydrogen peroxide. ...
ppt-file
... producing lysine [4]. 2 modes only use glucose as a substrate (yield: ¾), five modes only use acetate, and 29 use both. The optimal lysine over glucose yield of ¾ coincides with earlier results obtained by metabolite balancing in [3]. It is understandable that the yield is lower than when ATP and AD ...
... producing lysine [4]. 2 modes only use glucose as a substrate (yield: ¾), five modes only use acetate, and 29 use both. The optimal lysine over glucose yield of ¾ coincides with earlier results obtained by metabolite balancing in [3]. It is understandable that the yield is lower than when ATP and AD ...
Cellular Respiration
... Place in fermentation tube – invert to get rid of air Place all tubes in incubator ...
... Place in fermentation tube – invert to get rid of air Place all tubes in incubator ...
Biochemistry 2000 Sample Questions 5 Transport, Carbohydrates, Metabolism
... (20) When [GAP] = 10-4 M, [DHAP] = 5.5 x 10-4 M. ∆G°’ = -RT ln K, thus K = e (-∆G°’/RT) = [GAP] [DHAP] / [FBP] = e (– 22,800 J mol-1) / 8.3145 J K-1 mol-1) (310K) = 1.4 x 10-4 Thus: (10-4) (5.5 x 10-4) / [FBP] = 1.4 x 10-4 Thus: [FBP] = 3.8 x 10-4 M And [FBP]/[GAP] = (3.8 x 10-4 M) / (10-4 M) = 3.8 ...
... (20) When [GAP] = 10-4 M, [DHAP] = 5.5 x 10-4 M. ∆G°’ = -RT ln K, thus K = e (-∆G°’/RT) = [GAP] [DHAP] / [FBP] = e (– 22,800 J mol-1) / 8.3145 J K-1 mol-1) (310K) = 1.4 x 10-4 Thus: (10-4) (5.5 x 10-4) / [FBP] = 1.4 x 10-4 Thus: [FBP] = 3.8 x 10-4 M And [FBP]/[GAP] = (3.8 x 10-4 M) / (10-4 M) = 3.8 ...
file
... • Spontaneously form sheets (lipid bilayers, membranes) in which all the hydrophilic ends align on the outside, and hydrophobic ends align on the inside. • Creates a very stable separation, not easy to pass through except for water and a few other small atoms/molecules. ...
... • Spontaneously form sheets (lipid bilayers, membranes) in which all the hydrophilic ends align on the outside, and hydrophobic ends align on the inside. • Creates a very stable separation, not easy to pass through except for water and a few other small atoms/molecules. ...
L11_lipogenesis
... • Activates acetyl-CoA and ‘primes’ it for lipogenesis • Unusual in that it ‘fixes’ carbon dioxide – In the form of bicarbonate – A carboxylation reaction ...
... • Activates acetyl-CoA and ‘primes’ it for lipogenesis • Unusual in that it ‘fixes’ carbon dioxide – In the form of bicarbonate – A carboxylation reaction ...
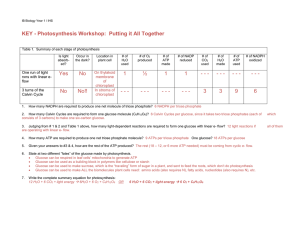
KEY - Photosynthesis Workshop: Putting it All Together
... 3. Judging from # 1 & 2 and Table 1 above, how many light-dependent reactions are required to form one glucose with linear e- flow? 12 light reactions if are operating with linear e- flow. ...
... 3. Judging from # 1 & 2 and Table 1 above, how many light-dependent reactions are required to form one glucose with linear e- flow? 12 light reactions if are operating with linear e- flow. ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.