Topics Tested: Physics – Nine questions each on the topics below:
... allows an endergonic reaction to proceed more quickly. increases the activation energy so a reaction can proceed more quickly. lowers the amount of energy needed for a reaction to proceed. is required for an exergonic reaction to occur. ...
... allows an endergonic reaction to proceed more quickly. increases the activation energy so a reaction can proceed more quickly. lowers the amount of energy needed for a reaction to proceed. is required for an exergonic reaction to occur. ...
Solutions
... (2) State whether the following characteristics are for a plant that is CAM or C4 or both (C4 and CAM), C3 or ALL (C3, C4 and CAM (1 point each). Fix CO2 using PEP carboxylase to create a 4 carbon molecule ____BOTH______ Accumulate malic acid in vacuoles ____CAM_______ Have increased CO2 in mesophy ...
... (2) State whether the following characteristics are for a plant that is CAM or C4 or both (C4 and CAM), C3 or ALL (C3, C4 and CAM (1 point each). Fix CO2 using PEP carboxylase to create a 4 carbon molecule ____BOTH______ Accumulate malic acid in vacuoles ____CAM_______ Have increased CO2 in mesophy ...
Metabolism and Energy
... ferredoxin and to NADP+ reductase, where they are accepted by NADPH. This stores the energy of the electrons into a form that can be transferred to the Calvin Cycle. (No chemiosmosis, thus no ATP in this ETC) ...
... ferredoxin and to NADP+ reductase, where they are accepted by NADPH. This stores the energy of the electrons into a form that can be transferred to the Calvin Cycle. (No chemiosmosis, thus no ATP in this ETC) ...
Chemistry, Biomolecules, and Enzymes
... – Primary (1ー) - sequence and types of amino acids used in a protein – Secondary (2ー)- shape (α –helix, β- pleated sheet) that different sections of the protein strand will take based on hydrogen bonds (between R- groups) – Tertiary (3ー)- 3D shape of protein caused by hydrogen bonds and other bonds ...
... – Primary (1ー) - sequence and types of amino acids used in a protein – Secondary (2ー)- shape (α –helix, β- pleated sheet) that different sections of the protein strand will take based on hydrogen bonds (between R- groups) – Tertiary (3ー)- 3D shape of protein caused by hydrogen bonds and other bonds ...
Cell Respiration notes
... Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that generates ATP during fermentation. No O2 is required; it generates a net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH Significantly less ATP is generated, but it is enough to keep your muscles contracting for a short while when the need for ATP outpaces the delivery of O2 via th ...
... Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that generates ATP during fermentation. No O2 is required; it generates a net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH Significantly less ATP is generated, but it is enough to keep your muscles contracting for a short while when the need for ATP outpaces the delivery of O2 via th ...
...the story of making proteins continued… After transcription occurs
... read the mRNA in 3’s. These 3letter chunks are called ___________________________. Each codon represents a specific _________________________________. Remember, amino acids make up ________________________! We are going to take this nucleotide message (mRNA) and use the coded dictionary to translat ...
... read the mRNA in 3’s. These 3letter chunks are called ___________________________. Each codon represents a specific _________________________________. Remember, amino acids make up ________________________! We are going to take this nucleotide message (mRNA) and use the coded dictionary to translat ...
3.7 Polysaccharides are long chains of sugar units
... Carbohydrates range from small sugar molecules (monomers) to large polysaccharides – Sugar monomers are monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose – These can be hooked together to form the polysaccharides ...
... Carbohydrates range from small sugar molecules (monomers) to large polysaccharides – Sugar monomers are monosaccharides, such as glucose and fructose – These can be hooked together to form the polysaccharides ...
Chapter 15 Lecture Notes: Metabolism
... It is critical that oligosaccharides and polysaccharides be converted to monosaccharides in order for the sugars to pass through the intestine wall and into the bloodstream so that they are available to cells throughout the body. Monosaccharides are transported into the cells by passive diffusion th ...
... It is critical that oligosaccharides and polysaccharides be converted to monosaccharides in order for the sugars to pass through the intestine wall and into the bloodstream so that they are available to cells throughout the body. Monosaccharides are transported into the cells by passive diffusion th ...
Key Terms
... ATP production by ATP synthase. First, the carrier molecule NADH transfers electrons from the original glucose molecule to an electron transport chain (Figure 7-19). As you read in Concept 7.4, electrons move to carriers that attract them more strongly. In this way the electrons move from carrier to ...
... ATP production by ATP synthase. First, the carrier molecule NADH transfers electrons from the original glucose molecule to an electron transport chain (Figure 7-19). As you read in Concept 7.4, electrons move to carriers that attract them more strongly. In this way the electrons move from carrier to ...
Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) regulate receptor function
... Exercise is known to help prevent or treat a host of pathological conditions, including metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. ...
... Exercise is known to help prevent or treat a host of pathological conditions, including metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. ...
Amyloid precursor
... Following the -secretase pathway, APP is clipped between amino acids 612 and 613, or between the 16th and 17th amino acids with regards to the A protein. A full-length version of A is not formed. The -secretase pathway clips APP between amino acids 596 and 597 and is followed by a presenilin-1 r ...
... Following the -secretase pathway, APP is clipped between amino acids 612 and 613, or between the 16th and 17th amino acids with regards to the A protein. A full-length version of A is not formed. The -secretase pathway clips APP between amino acids 596 and 597 and is followed by a presenilin-1 r ...
Biology
... carbon atoms. This allows it to form chains, rings, chains of rings, or a combination of all. ...
... carbon atoms. This allows it to form chains, rings, chains of rings, or a combination of all. ...
Middle-Term Test Paper on Biochemistry
... D. The combination of some of cofactors with apoenzymes are loose E. There are some groups among diverse coenzymes that can proceed with the reversible change 10) Which is error about the narration on glycolysis A. Glycolysis in diverse tissues only proceed under the anaerobic condition or oxygen un ...
... D. The combination of some of cofactors with apoenzymes are loose E. There are some groups among diverse coenzymes that can proceed with the reversible change 10) Which is error about the narration on glycolysis A. Glycolysis in diverse tissues only proceed under the anaerobic condition or oxygen un ...
ATP
... •Food molecules are the $1000 dollar bills of energy storage •Food molecules function as fuel molecules, storing large quantities of energy in a stable form over long periods of time! They are the long-term energy currency of the cell. •For “pocket change”, cells require a molecule that stores much ...
... •Food molecules are the $1000 dollar bills of energy storage •Food molecules function as fuel molecules, storing large quantities of energy in a stable form over long periods of time! They are the long-term energy currency of the cell. •For “pocket change”, cells require a molecule that stores much ...
Document
... undergoes a pyrophosphate cleavage to AMP and pyrophosphate, which may be hydrolyzed to yield two Pi. ...
... undergoes a pyrophosphate cleavage to AMP and pyrophosphate, which may be hydrolyzed to yield two Pi. ...
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ
... Control tasks are required to perform and should be given on time. The work carried out with a delay, will automatically be assessed below. The results of the Midterm Examination are marked based on attendance, performance of students independent work in a timely manner, activity at lessons in oral ...
... Control tasks are required to perform and should be given on time. The work carried out with a delay, will automatically be assessed below. The results of the Midterm Examination are marked based on attendance, performance of students independent work in a timely manner, activity at lessons in oral ...
Lect 1 (Metabolic Pathways) Lect 2 (Enzymes) Lect 3 (Glucose
... and have high enzyme turn-over. Enzyme levels vary depending on feeding or fasting, as well as needs of other tissues. Glucokinase: hexokinase converts glucose > G6P. Has a low affinity for glucose & a maximal Km at 10Km. only found in liver cells. G6P is used to keep [blood glucose] low. Converted ...
... and have high enzyme turn-over. Enzyme levels vary depending on feeding or fasting, as well as needs of other tissues. Glucokinase: hexokinase converts glucose > G6P. Has a low affinity for glucose & a maximal Km at 10Km. only found in liver cells. G6P is used to keep [blood glucose] low. Converted ...
Code Questions Answers 1. Write the reactions of glycolysis
... Action of Vitamin D Increases the absorption of Ca (and phosphate) from the small intestine and causes removal of Ca from bone (bone resorption). Mechanism of calcium absorption from intestine through 1-25-dihydroxy Vitamin. D3: The mechanism of action of 1-25-dihydroxy Vit. D3 is typical of steroid ...
... Action of Vitamin D Increases the absorption of Ca (and phosphate) from the small intestine and causes removal of Ca from bone (bone resorption). Mechanism of calcium absorption from intestine through 1-25-dihydroxy Vitamin. D3: The mechanism of action of 1-25-dihydroxy Vit. D3 is typical of steroid ...
Cellular Respiration 2010
... a. All of the NADH and FADH2 give their electrons to the ETC to be turned into ATP b. Occurs Across mitochondria ...
... a. All of the NADH and FADH2 give their electrons to the ETC to be turned into ATP b. Occurs Across mitochondria ...
Lecture 23 – SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION: G
... Identify features of the H4 isozyme of lactate dehydrogenase that makes it different from the M4 isozyme. H4 has a high affinity (or low Km) for lactate H4 is inhibited by pyruvate H4 found in heart not anaerobic skeletal muscle Intravenous infusion of fructose into healthy volunteers increases lact ...
... Identify features of the H4 isozyme of lactate dehydrogenase that makes it different from the M4 isozyme. H4 has a high affinity (or low Km) for lactate H4 is inhibited by pyruvate H4 found in heart not anaerobic skeletal muscle Intravenous infusion of fructose into healthy volunteers increases lact ...
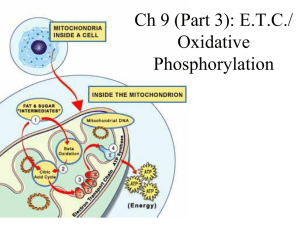
Ch 9: E.T.C./ Oxidative Phosphorylation
... electronegative than the group before it, so the electrons are “pulled downhill” towards OXYGEN (the final electron carrier!) ...
... electronegative than the group before it, so the electrons are “pulled downhill” towards OXYGEN (the final electron carrier!) ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.