CK12 Homework Sections 1.27 to 1.30 Section 1.27 Glycolysis 1
... Most living things use oxygen to make ATP from glucose. However, many living things can also make ATP without oxygen. This is true of some plants and fungi and also of many bacteria. These organisms use aerobic respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobi ...
... Most living things use oxygen to make ATP from glucose. However, many living things can also make ATP without oxygen. This is true of some plants and fungi and also of many bacteria. These organisms use aerobic respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobi ...
DNA Synthesis (Replication)
... to ribosomal precursors; makes Ribosome, and is the central component of the Ribosome’s protein-manufacturing machinery. ...
... to ribosomal precursors; makes Ribosome, and is the central component of the Ribosome’s protein-manufacturing machinery. ...
BiochemReview
... • The misfolded molecule is dubbed “PrPSc”. • The misfolding of a “PrPc” molecule initiates a cascade of further misfolding… • PrPSc induces other properly folded to misfold. ...
... • The misfolded molecule is dubbed “PrPSc”. • The misfolding of a “PrPc” molecule initiates a cascade of further misfolding… • PrPSc induces other properly folded to misfold. ...
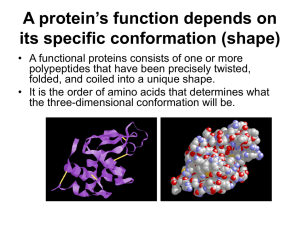
A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation
... • A functional proteins consists of one or more polypeptides that have been precisely twisted, folded, and coiled into a unique shape. • It is the order of amino acids that determines what the three-dimensional conformation will be. ...
... • A functional proteins consists of one or more polypeptides that have been precisely twisted, folded, and coiled into a unique shape. • It is the order of amino acids that determines what the three-dimensional conformation will be. ...
Cellular respiration
... What 2 molecules transform pyrvate?___ What molecule is made and released through the cell membrane?___ What molecule is made and will go to the ETC?___ What does acetyl-Co A join with?_____ How many carbon atoms is citrate?_____ What gets recycled when citrate is made?___ After 1 cycle of Krebs cyc ...
... What 2 molecules transform pyrvate?___ What molecule is made and released through the cell membrane?___ What molecule is made and will go to the ETC?___ What does acetyl-Co A join with?_____ How many carbon atoms is citrate?_____ What gets recycled when citrate is made?___ After 1 cycle of Krebs cyc ...
Control of microbial growth: Sterilization and disinfectants
... • Numerous terms are defined in the text: be familiar with them. Sterile, disinfection, antiseptic, bacteriostatic, and bactericidal, plus others. • Sterile: devoid of life. Something is either sterile or not. • Disinfect: kill most microbes, especially harmful ones, but probably not spores which ar ...
... • Numerous terms are defined in the text: be familiar with them. Sterile, disinfection, antiseptic, bacteriostatic, and bactericidal, plus others. • Sterile: devoid of life. Something is either sterile or not. • Disinfect: kill most microbes, especially harmful ones, but probably not spores which ar ...
Amino Acid Answers: 1. Determine if the amino acids shown are of
... neutral neutral basic Compounds containing the carboxylic acid functional group in their side chain are acidic amino acids. Compounds containing amines in their side chair are basic amino acids. Those side chains containing alkyl groups, alcohols, or even sulfur-containing groups are neutral. ...
... neutral neutral basic Compounds containing the carboxylic acid functional group in their side chain are acidic amino acids. Compounds containing amines in their side chair are basic amino acids. Those side chains containing alkyl groups, alcohols, or even sulfur-containing groups are neutral. ...
103 Rev Ex2 key Win06
... 29. Which vitamin is involved in cholesterol synthesis? Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) is involved in cholesterol synthesis. 30. Why does a deficiency of vitamin C lead to weakened connective tissue? Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is essential for the synthesis of hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine, which a ...
... 29. Which vitamin is involved in cholesterol synthesis? Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) is involved in cholesterol synthesis. 30. Why does a deficiency of vitamin C lead to weakened connective tissue? Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is essential for the synthesis of hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine, which a ...
Biology Chapter 4
... Two ATP are used to energize a glucose molecule. The glucose is split into 2 three carbon molecules, and then through enzymes and chemical reactions is rearranged. Energized electrons from the three carbon molecules are transferred to molecules of NAD+. Molecules of NADH are formed. A series of reac ...
... Two ATP are used to energize a glucose molecule. The glucose is split into 2 three carbon molecules, and then through enzymes and chemical reactions is rearranged. Energized electrons from the three carbon molecules are transferred to molecules of NAD+. Molecules of NADH are formed. A series of reac ...
Cells
... Homeostasis-> Cell membrane is a huge part of this because it regulates what enters and leaves your cells. * Maintains internal conditions such as body temperature, respiration, nutritional balance * Cells communicate needs to each other by sending chemical messages that tell the hypothalamus gland ...
... Homeostasis-> Cell membrane is a huge part of this because it regulates what enters and leaves your cells. * Maintains internal conditions such as body temperature, respiration, nutritional balance * Cells communicate needs to each other by sending chemical messages that tell the hypothalamus gland ...
Hypoxia Oxidative phosphorylation contribution to ATP production
... Extracellular pH decreases reduce the cost of membrane transport processes associated with pH regulation. Inhibitors: Ouabain (Na/K ATPase), DMA (amiloride, Na/H antiport), DIDS (anion exchange, such as Na+ dependent Cl/HCO3- exchange), Bafilomycin (V-ATPase H+ pump inhibitor). ...
... Extracellular pH decreases reduce the cost of membrane transport processes associated with pH regulation. Inhibitors: Ouabain (Na/K ATPase), DMA (amiloride, Na/H antiport), DIDS (anion exchange, such as Na+ dependent Cl/HCO3- exchange), Bafilomycin (V-ATPase H+ pump inhibitor). ...
Chapter 2. Fuel for Exercising Muscle
... before entering Krebs cycle • Requires up-front expenditure of 2 ATP • Number of steps depends on number of carbons on FFA – 16-carbon FFA yields 8 acetyl-CoA – Compare: 1 glucose yields 2 acetyl-CoA – Fat oxidation requires more O2 now, yields far more ATP later ...
... before entering Krebs cycle • Requires up-front expenditure of 2 ATP • Number of steps depends on number of carbons on FFA – 16-carbon FFA yields 8 acetyl-CoA – Compare: 1 glucose yields 2 acetyl-CoA – Fat oxidation requires more O2 now, yields far more ATP later ...
The Endoplasmic Reticulum Train
... The endoplasmic reticulum is like a train route because it transports the proteins and lipids manufactured in the different parts of the organelle to other parts in the cell. The ribosomes, rough ER, and smooth ER act as the train stops where the product (lipids and proteins) is manufactured. ...
... The endoplasmic reticulum is like a train route because it transports the proteins and lipids manufactured in the different parts of the organelle to other parts in the cell. The ribosomes, rough ER, and smooth ER act as the train stops where the product (lipids and proteins) is manufactured. ...
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... Glycolysis: oxidation and cleavage of glucose ATP generation (with and without oxygen) all cells in the cytosol (the reducing equivalents are transferred to the electron-transport chain by the shuttle) ...
... Glycolysis: oxidation and cleavage of glucose ATP generation (with and without oxygen) all cells in the cytosol (the reducing equivalents are transferred to the electron-transport chain by the shuttle) ...
- Circle of Docs
... 61. The positive functions of iodine A. to regulate the size and function of the thymus gland B. to regulate the size and function of the parathyroid glands C. maintain the normal structure of ...
... 61. The positive functions of iodine A. to regulate the size and function of the thymus gland B. to regulate the size and function of the parathyroid glands C. maintain the normal structure of ...
Chapter 11 Problem Set
... oxidative phosphorylation to make ATP. In this process, electrons removed in the oxidation of fuel substrates such as glucose or fatty acids are passed to O2 releasing energy that is used to make ATP by the F1Fo ATPase (ATP synthase). If ouabain reduces O2 consumption by 66%, then ATP hydrolyzed by ...
... oxidative phosphorylation to make ATP. In this process, electrons removed in the oxidation of fuel substrates such as glucose or fatty acids are passed to O2 releasing energy that is used to make ATP by the F1Fo ATPase (ATP synthase). If ouabain reduces O2 consumption by 66%, then ATP hydrolyzed by ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
... In your group: 5. See if you can write the chemical equation for respiration (inputs and outputs) 6. What is the organelle in cells that is “releasing” energy during respiration? 7. What primary molecule is energy being “released” from? 8. How is the sun indirectly involved in respiration? ...
... In your group: 5. See if you can write the chemical equation for respiration (inputs and outputs) 6. What is the organelle in cells that is “releasing” energy during respiration? 7. What primary molecule is energy being “released” from? 8. How is the sun indirectly involved in respiration? ...
PracticeFinalSP2003
... 14. Triglyceride fats can be made (and indeed, your body does this) by reacting fatty acids with glycerol in a ester hydrolysis reaction similar to the ones you studied in lab. Draw a mechaism for this type of reaction to form a triglyceride fat. 15. Soaps are made from triglyceride fats, how is thi ...
... 14. Triglyceride fats can be made (and indeed, your body does this) by reacting fatty acids with glycerol in a ester hydrolysis reaction similar to the ones you studied in lab. Draw a mechaism for this type of reaction to form a triglyceride fat. 15. Soaps are made from triglyceride fats, how is thi ...
GLUCOGENIC & KETOGENIC AMINO ACIDS
... All tissues have some capability for synthesis of: The non-essential amino acids, Amino acid remodeling, and Conversion of non-amino acid carbon skeletons into amino acids and other derivatives that contain nitrogen. Liver is the major site of nitrogen metabolism in the ...
... All tissues have some capability for synthesis of: The non-essential amino acids, Amino acid remodeling, and Conversion of non-amino acid carbon skeletons into amino acids and other derivatives that contain nitrogen. Liver is the major site of nitrogen metabolism in the ...
7-12 Enzyme Demonstration Instructions
... getting to fructose are stabilized and thus less energy is needed to get the chemical to transition through these states to fructose. Depending on the class size, you can have the students practice the transition with their own ball and stick model or with a single model that you pass around. 5 ...
... getting to fructose are stabilized and thus less energy is needed to get the chemical to transition through these states to fructose. Depending on the class size, you can have the students practice the transition with their own ball and stick model or with a single model that you pass around. 5 ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.