An investigation of protective formulations containing
... inhibitors, as for example ibuprofen (COX-‐inhibitor). shown as a function of reaction coordinate The activity can also be affected by temperature, chemical environment as for example pH and the co ...
... inhibitors, as for example ibuprofen (COX-‐inhibitor). shown as a function of reaction coordinate The activity can also be affected by temperature, chemical environment as for example pH and the co ...
CO2 Capture from Flue gas using Amino acid salt
... based on chemical absorption, where CO2 in the flue gas is chemically bond by a solvent, usually an aqueous solution of amines, resulting in a cleaned gas being released to the atmosphere. Heating of the solution, desorbs the CO2 and regenerates the solvent, which is then ready for a new round of ab ...
... based on chemical absorption, where CO2 in the flue gas is chemically bond by a solvent, usually an aqueous solution of amines, resulting in a cleaned gas being released to the atmosphere. Heating of the solution, desorbs the CO2 and regenerates the solvent, which is then ready for a new round of ab ...
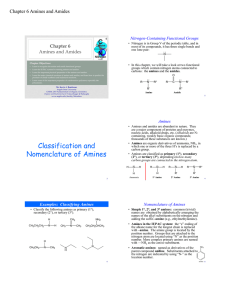
Classification and Nomenclature of Amines
... 1939), who observed the antibacterial action of the red dye Protonsil; further researched showed that it was the metabolic byproduct, sulfanilamide, which was the active form. It prevents bacteria from synthesizing folic acid, which they need in order to grow. Bacterial enzymes synthesize folic acid ...
... 1939), who observed the antibacterial action of the red dye Protonsil; further researched showed that it was the metabolic byproduct, sulfanilamide, which was the active form. It prevents bacteria from synthesizing folic acid, which they need in order to grow. Bacterial enzymes synthesize folic acid ...
Methods and strategies of peptide ligation
... occupying NT positions can be considered as NTamine-nucleophiles. Since not all amino acids contain a side-chain nucleophile and since NT-amine-nucleophiles have different reactivity toward the complementary CT-acyl-electrophiles, they provide a mechanism to distinguish one NT-amine from another. Th ...
... occupying NT positions can be considered as NTamine-nucleophiles. Since not all amino acids contain a side-chain nucleophile and since NT-amine-nucleophiles have different reactivity toward the complementary CT-acyl-electrophiles, they provide a mechanism to distinguish one NT-amine from another. Th ...
Biosynthesis of geranial, a potent aroma compound in ginger
... Abstract Fresh ginger (Zingiber officinale) rhizome is characterized by a pleasant citrus aroma and pungent flavor. The majority of the aroma-contributing volatiles are monoterpenoids, especially geraniol derivatives such as geranial, geranyl acetate, geraniol and citronellol. In this study, we inv ...
... Abstract Fresh ginger (Zingiber officinale) rhizome is characterized by a pleasant citrus aroma and pungent flavor. The majority of the aroma-contributing volatiles are monoterpenoids, especially geraniol derivatives such as geranial, geranyl acetate, geraniol and citronellol. In this study, we inv ...
Microbiology
... is a quaternary amine compound that can be produced by all domains of life, and was discovered in muscle extract in 1905 by Gulewitsch & Krimberg (1905) and Kutscher (1905). It was shown to be essential for larval development of the mealworm Tenebrio molitor and was originally designated vitamin BT ...
... is a quaternary amine compound that can be produced by all domains of life, and was discovered in muscle extract in 1905 by Gulewitsch & Krimberg (1905) and Kutscher (1905). It was shown to be essential for larval development of the mealworm Tenebrio molitor and was originally designated vitamin BT ...
ASD v2.0: updated content and novel features
... which not only provides insight into the allosteric mechanism in various biological processes but also contributes to the explanation of some disease-associated mutations away from the orthosteric site (27). Since the release of ASD v1.0, feedback from users has led to many excellent suggestions on ...
... which not only provides insight into the allosteric mechanism in various biological processes but also contributes to the explanation of some disease-associated mutations away from the orthosteric site (27). Since the release of ASD v1.0, feedback from users has led to many excellent suggestions on ...
EFFECTS OF BIOREACTOR OPERATION PARAMETERS ON
... 2.2 Summary of batch cell growth............................................................. 17 2.3 Definition of yield coefficients.............................................................. 19 2.4 The major macronutrient elements, their physiological functions, growth requirements and common s ...
... 2.2 Summary of batch cell growth............................................................. 17 2.3 Definition of yield coefficients.............................................................. 19 2.4 The major macronutrient elements, their physiological functions, growth requirements and common s ...
SUPPORTING FILE S1 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND
... Actinorhodin concentrations were calculated according to the molar extinction coefficient (640 = 25,320 L mol-1 cm-1) of the pure compound in KOH (1 mol L-1). To analyze the extracellular blue pigment (-actinorhodin), the supernatant was ...
... Actinorhodin concentrations were calculated according to the molar extinction coefficient (640 = 25,320 L mol-1 cm-1) of the pure compound in KOH (1 mol L-1). To analyze the extracellular blue pigment (-actinorhodin), the supernatant was ...
Mechanistic Studies of Two Selected Flavin
... graduate experience has been one that I will cherish forever. I would like to take this opportunity to express my gratitude to them for completing the dissertation successfully. My deepest gratitude is to my advisor, Dr. Giovanni Gadda, for his excellent guidance, encouragement, caring, supervising ...
... graduate experience has been one that I will cherish forever. I would like to take this opportunity to express my gratitude to them for completing the dissertation successfully. My deepest gratitude is to my advisor, Dr. Giovanni Gadda, for his excellent guidance, encouragement, caring, supervising ...
the role of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase in glucose and ketone
... 2. PDC activity in tissues of WT, PDK2 KO, PDK4 KO, and DKO mice in the fed state ..............................................................................................................................37 3. PDC activity in tissues of WT, PDK2 KO, PDK4 KO, and DKO mice in the fasted state .... ...
... 2. PDC activity in tissues of WT, PDK2 KO, PDK4 KO, and DKO mice in the fed state ..............................................................................................................................37 3. PDC activity in tissues of WT, PDK2 KO, PDK4 KO, and DKO mice in the fasted state .... ...
Physiology of Exercise
... exercise, is removed from the cell by muscle blood flow and eliminated from the body by ventilating the pulmonary blood flow. Acetate is produced from the catabolism of carbohydrates, fatty acids, and, in nutritionally deficient states, amino acids. It reacts with oxaloacetate in the mitochondrion, ...
... exercise, is removed from the cell by muscle blood flow and eliminated from the body by ventilating the pulmonary blood flow. Acetate is produced from the catabolism of carbohydrates, fatty acids, and, in nutritionally deficient states, amino acids. It reacts with oxaloacetate in the mitochondrion, ...
A plant vacuolar system : the lutoïds from Hevea brasiliensis latex
... result from pH measurements made directly on the medium of burst lutoids. Estimates were also made from the transmembrane distribution of lipophilic probes (such as 14C-methylamine) accross the intact organelle tonoplast (CRETIN,1982 a ; CRÉTINet al., 1982). Estimates of the transmembrane potential ...
... result from pH measurements made directly on the medium of burst lutoids. Estimates were also made from the transmembrane distribution of lipophilic probes (such as 14C-methylamine) accross the intact organelle tonoplast (CRETIN,1982 a ; CRÉTINet al., 1982). Estimates of the transmembrane potential ...
ESTUDIO DE LOS MECANISMOS DE INHIBICIÓN DE LA ACTIVIDAD CARNITINA PALMITOILTRANSFERASA 1
... The enzyme carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT)1 I catalyzes the conversion of long chain fatty acyl-CoAs to acylcarnitines, which is the first step in the transport of fatty acyl-CoA groups from the cytosol to mitochondria where they undergo -oxidation. This reaction is inhibited by malonyl-CoA, a ...
... The enzyme carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT)1 I catalyzes the conversion of long chain fatty acyl-CoAs to acylcarnitines, which is the first step in the transport of fatty acyl-CoA groups from the cytosol to mitochondria where they undergo -oxidation. This reaction is inhibited by malonyl-CoA, a ...
Riboflavin (Vitamin B )
... OneOne-electron transfers (e.g. NADH, succinate) (glycation and TCA cycle) TwoTwo-electron transfers (e.g. Fe-S proteins, heme proteins) (respiratory chain) ...
... OneOne-electron transfers (e.g. NADH, succinate) (glycation and TCA cycle) TwoTwo-electron transfers (e.g. Fe-S proteins, heme proteins) (respiratory chain) ...
Vanillin formation from ferulic acid in Vanilla planifolia is catalysed
... represents the first committed step in vanillin synthesis and demonstrates that vanillin formation in V. planifolia is catalysed by a single enzyme using a general substrate from phenylpropanoid metabolism. We designated the enzyme vanillin synthase and the gene VpVAN (gene sequence is given in Suppl ...
... represents the first committed step in vanillin synthesis and demonstrates that vanillin formation in V. planifolia is catalysed by a single enzyme using a general substrate from phenylpropanoid metabolism. We designated the enzyme vanillin synthase and the gene VpVAN (gene sequence is given in Suppl ...
Amines and Amides
... 1939), who observed the antibacterial action of the red dye Protonsil; further researched showed that it was the metabolic byproduct, sulfanilamide, which was the active form. It prevents bacteria from synthesizing folic acid, which they need in order to grow. Bacterial enzymes synthesize folic acid ...
... 1939), who observed the antibacterial action of the red dye Protonsil; further researched showed that it was the metabolic byproduct, sulfanilamide, which was the active form. It prevents bacteria from synthesizing folic acid, which they need in order to grow. Bacterial enzymes synthesize folic acid ...
Solid Phase Synthesis on SASRIN
... from triphenylphosphine and tetrachloromethane [26b] (SASRIN bromide could be obtained as well, by treating the resin with the dimethyl sulfide/N-bromosuccinimide complex [27]. Our own attempts to convert SASRIN into its bromide had failed). The resulting polymer is treated with the dry cesium salt ...
... from triphenylphosphine and tetrachloromethane [26b] (SASRIN bromide could be obtained as well, by treating the resin with the dimethyl sulfide/N-bromosuccinimide complex [27]. Our own attempts to convert SASRIN into its bromide had failed). The resulting polymer is treated with the dry cesium salt ...
Clinical Study The Relationship between
... A higher oxidative stress may contribute to the pathogenesis of coronary artery disease (CAD). The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between coenzyme Q10 concentration and lipid peroxidation, antioxidant enzymes activities and the risk of CAD. Patients who were identified by ...
... A higher oxidative stress may contribute to the pathogenesis of coronary artery disease (CAD). The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between coenzyme Q10 concentration and lipid peroxidation, antioxidant enzymes activities and the risk of CAD. Patients who were identified by ...
Food Biochemistry and Food Processing (2
... For details of our global editorial offices, for customer services and for information about how to apply for permission to reuse the copyright material in this book please see our website at www.wiley.com/wiley-blackwell. Authorization to photocopy items for internal or personal use, or the internal ...
... For details of our global editorial offices, for customer services and for information about how to apply for permission to reuse the copyright material in this book please see our website at www.wiley.com/wiley-blackwell. Authorization to photocopy items for internal or personal use, or the internal ...
Metabolism of heme
... Heme is the prosthetic group of hemoglobin, myoglobin, & cytochromes and so on. - most common porphyrin in humans is heme - one ferrous goup in tetrapyrole ring - heme proteins (hemoproteins) are rapidly synthsized and degraded - 6 to 7 g per day hemoglobin turned over ...
... Heme is the prosthetic group of hemoglobin, myoglobin, & cytochromes and so on. - most common porphyrin in humans is heme - one ferrous goup in tetrapyrole ring - heme proteins (hemoproteins) are rapidly synthsized and degraded - 6 to 7 g per day hemoglobin turned over ...
Characterization of the Two-Component, FAD-Dependent Monooxygenase SgcC That Requires Carrier Protein-Tethered
... different classes of enzymes that have no structural or sequence similarities.17–19 The first class, or one-component monooxygenases, are single polypeptides that utilize FAD or FMN as a cofactor and require NADH or NADPH to initiate oxidation of substrates; thus, these monooxygenases have both flav ...
... different classes of enzymes that have no structural or sequence similarities.17–19 The first class, or one-component monooxygenases, are single polypeptides that utilize FAD or FMN as a cofactor and require NADH or NADPH to initiate oxidation of substrates; thus, these monooxygenases have both flav ...
Structure of a Pheromone Receptor-Associated MHC Molecule with
... not bind small molecule ligands, have collapsed grooves with a smaller separation between the a1–a2 domain helices [32–34]. A superposition of the a1–a2 platforms of M10.5, H-2Dd, FcRn, and HFE illustrates the variation in groove size (Figure 1C) and demonstrates that M10.5 has an open groove more s ...
... not bind small molecule ligands, have collapsed grooves with a smaller separation between the a1–a2 domain helices [32–34]. A superposition of the a1–a2 platforms of M10.5, H-2Dd, FcRn, and HFE illustrates the variation in groove size (Figure 1C) and demonstrates that M10.5 has an open groove more s ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.