1From neuronal activity to scalp potential fields - Assets
... potentials15 . These reflect neural mass activity due to linear superposition of those fields which do not form closed field current loops. In brain regions such as the neocortex, this extracellular activity is synchronized well beyond the sub-millimeter scale and reflects summation of excitatory or ...
... potentials15 . These reflect neural mass activity due to linear superposition of those fields which do not form closed field current loops. In brain regions such as the neocortex, this extracellular activity is synchronized well beyond the sub-millimeter scale and reflects summation of excitatory or ...
Modeling and Detecting Deep Brain Activity with MEG
... Parkinson, Huntington and Alzheimer diseases, etc.). They form with the cortex a dense array of interconnected functional networks that are essential to be explored using functional brain imaging. The millisecond time resolution asset of MEG and EEG source imaging is unfortunately compensated by the ...
... Parkinson, Huntington and Alzheimer diseases, etc.). They form with the cortex a dense array of interconnected functional networks that are essential to be explored using functional brain imaging. The millisecond time resolution asset of MEG and EEG source imaging is unfortunately compensated by the ...
An alarm pheromone increases the responsivity of
... dorsal periaqueductal gray, superior colliculus, and medial thalamus, but it is reduced in medial raphe, locus coeruleus, accumbens nucleis, ventral tegmental area, ventral pallidum ...
... dorsal periaqueductal gray, superior colliculus, and medial thalamus, but it is reduced in medial raphe, locus coeruleus, accumbens nucleis, ventral tegmental area, ventral pallidum ...
English - SciELO México
... dorsal periaqueductal gray, superior colliculus, and medial thalamus, but it is reduced in medial raphe, locus coeruleus, accumbens nucleis, ventral tegmental area, ventral pallidum ...
... dorsal periaqueductal gray, superior colliculus, and medial thalamus, but it is reduced in medial raphe, locus coeruleus, accumbens nucleis, ventral tegmental area, ventral pallidum ...
The case for a relationship between human memory
... A light-microscope fitted with a grid (10 x 10) in the eyepiece was used to count nucleolated neurons in 27 cases (14 right, 13 left). The thickness of each slice was 20µm; it was taken from the body of the hippocampus. The clinical identity of the patients was not known at the time of the counts we ...
... A light-microscope fitted with a grid (10 x 10) in the eyepiece was used to count nucleolated neurons in 27 cases (14 right, 13 left). The thickness of each slice was 20µm; it was taken from the body of the hippocampus. The clinical identity of the patients was not known at the time of the counts we ...
5. Ruiz G., en Homeopathy Jorurnal, 91, 80-84 (2002)
... certain systems when perturbed by noise and a weak periodic signal, which increasingly enhanced at the output as the magnitude of the noise grows towards an optimal value for maximum signal amplification. The possible relevance of stochastic resonance in other physiological phenomena like the kindli ...
... certain systems when perturbed by noise and a weak periodic signal, which increasingly enhanced at the output as the magnitude of the noise grows towards an optimal value for maximum signal amplification. The possible relevance of stochastic resonance in other physiological phenomena like the kindli ...
The History of the EEG
... • Fast Fourier Transform seperates spontaneous EEG signal to component frequencies and amplitudes • Restriction: high frequency resolution demands long (in the range of seconds) analysis windows ...
... • Fast Fourier Transform seperates spontaneous EEG signal to component frequencies and amplitudes • Restriction: high frequency resolution demands long (in the range of seconds) analysis windows ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... 1.,2. Stages of sleep - for humans, sleep is s state of decreased but not abolished consciousness, from which we can be aroused - sleep is an actively induced state - sleep stages defined by EEG criteria (measures movement of ions across cell membranes in layers 4-5 of cortex), 2 types: 1. synchroni ...
... 1.,2. Stages of sleep - for humans, sleep is s state of decreased but not abolished consciousness, from which we can be aroused - sleep is an actively induced state - sleep stages defined by EEG criteria (measures movement of ions across cell membranes in layers 4-5 of cortex), 2 types: 1. synchroni ...
20-Limbic
... hypothalamus and the neighboring septal region. In the male, erection of the penis and ejaculation are organized in this area, which is adjacent to the area for urination. Under normal circumstances the neurons that organize mating behavior do so only when they receive relevant hormones in their blo ...
... hypothalamus and the neighboring septal region. In the male, erection of the penis and ejaculation are organized in this area, which is adjacent to the area for urination. Under normal circumstances the neurons that organize mating behavior do so only when they receive relevant hormones in their blo ...
Hippocampal Formation
... cell activity in awake, active, and sleeping animals, typically rats or mice. The LFP is generated by local voltage changes in the brain region due to the combined electrical effects of a synchronously active population of neurons. Two predominant LFP states have been observed during awake behavior: ...
... cell activity in awake, active, and sleeping animals, typically rats or mice. The LFP is generated by local voltage changes in the brain region due to the combined electrical effects of a synchronously active population of neurons. Two predominant LFP states have been observed during awake behavior: ...
Hippocampal mechanisms for the context-dependent retrieval of episodes 2005 Special issue
... As the virtual rat moves through the environment, sensory input to the model identifies its current location (behavioral state) and indicates food reward when it is received. At each location, the hippocampal model retrieves the prior episode experienced at that location, and provides this informati ...
... As the virtual rat moves through the environment, sensory input to the model identifies its current location (behavioral state) and indicates food reward when it is received. At each location, the hippocampal model retrieves the prior episode experienced at that location, and provides this informati ...
International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science
... motor neurons by electric signals. This communication can be seen as a logic circuit where some action is done if signals from a certain group of input sensory neurons are present. This kind of activity, known as bioelectromagnetism, already produces a measurable electromagnetic field. In the human ...
... motor neurons by electric signals. This communication can be seen as a logic circuit where some action is done if signals from a certain group of input sensory neurons are present. This kind of activity, known as bioelectromagnetism, already produces a measurable electromagnetic field. In the human ...
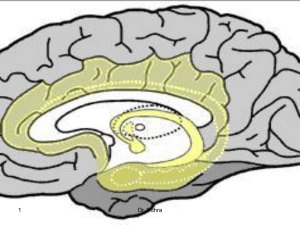
Gap Junctions in the Ventral Hippocampal-Medial
... Departments of 1Psychology and 2Molecular Biology and Princeton Neuroscience Institute, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey 08544 ...
... Departments of 1Psychology and 2Molecular Biology and Princeton Neuroscience Institute, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey 08544 ...
Fast Network Oscillations in the Hippocampal CA1
... The findings of the present experiments indicate that fast oscillatory waves (100 –200 Hz) in the hippocampal CA1 region can be induced by two different mechanisms. We suggest that fast ripples (180 Hz) emerge in the CA1 region, whereas the rhythm with a 110 Hz peak reflects a CA3 region-induced osc ...
... The findings of the present experiments indicate that fast oscillatory waves (100 –200 Hz) in the hippocampal CA1 region can be induced by two different mechanisms. We suggest that fast ripples (180 Hz) emerge in the CA1 region, whereas the rhythm with a 110 Hz peak reflects a CA3 region-induced osc ...
Hippocampus – Why is it studied so frequently?
... the name “polysynaptic pathway”, based on the findings that the subiculum also takes part in the intrinsic hippocampal circuitry. The polysynaptic pathway thus, is the chain of at least four synapses connecting the entorhinal area (presubiculum, parasubiculum and entorhinal cortex), the gyrus dentat ...
... the name “polysynaptic pathway”, based on the findings that the subiculum also takes part in the intrinsic hippocampal circuitry. The polysynaptic pathway thus, is the chain of at least four synapses connecting the entorhinal area (presubiculum, parasubiculum and entorhinal cortex), the gyrus dentat ...
Prefrontal Phase Locking to Hippocampal Theta Oscillations
... these interactions, we monitored the simultaneous activity of multiple single neurons in the hippocampus and mPFC of freely behaving rats using chronic multitetrode recordings. Here, we focus on characterizing the timing relationships between neuronal activity in the medial prefrontal cortex and the ...
... these interactions, we monitored the simultaneous activity of multiple single neurons in the hippocampus and mPFC of freely behaving rats using chronic multitetrode recordings. Here, we focus on characterizing the timing relationships between neuronal activity in the medial prefrontal cortex and the ...
ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAM_(EEG).
... • Gamma is measured between 36 – 44 (Hz) and is the only frequency group found in every part of the brain. • When the brain needs to simultaneously process information from different areas, its hypothesized that the 40Hz activity consolidates the required areas for simultaneous processing. • A good ...
... • Gamma is measured between 36 – 44 (Hz) and is the only frequency group found in every part of the brain. • When the brain needs to simultaneously process information from different areas, its hypothesized that the 40Hz activity consolidates the required areas for simultaneous processing. • A good ...
Functional differences between dorsal and ventral hippocampus
... in the dorsal region in basal condition. The parcellation of hippocampus into dorsal and ventral zones has been considered by other authors, which found morphological and functional differences that could explain the reported results (Moser et al., 1993; Jung et al., 1994). Thus, from a behavioral p ...
... in the dorsal region in basal condition. The parcellation of hippocampus into dorsal and ventral zones has been considered by other authors, which found morphological and functional differences that could explain the reported results (Moser et al., 1993; Jung et al., 1994). Thus, from a behavioral p ...
Diverse Origins of Network Rhythms in Local Cortical Circuits
... magnitude larger than local circuit connections using gap junctions (above). It should be noted that some synaptic inhibition can originate from principal, projection neurons over much greater spatial scales (e.g., cerebellar Purkinje cells), but they will not be dealt with here. Synaptic inhibition ...
... magnitude larger than local circuit connections using gap junctions (above). It should be noted that some synaptic inhibition can originate from principal, projection neurons over much greater spatial scales (e.g., cerebellar Purkinje cells), but they will not be dealt with here. Synaptic inhibition ...
Age-related changes in the hippocampal subdivisions of the rat
... Reports on age-related alterations in morphology of the rodent CA fields have been inconsistent, however. Some indicate a reduction in synaptic contacts and dendrites while others suggest preservation of connectivity. It is likely that methodological differences, such as rodent strain, age of subjec ...
... Reports on age-related alterations in morphology of the rodent CA fields have been inconsistent, however. Some indicate a reduction in synaptic contacts and dendrites while others suggest preservation of connectivity. It is likely that methodological differences, such as rodent strain, age of subjec ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... So, in this case when we are considering the spring mass system we are always taking this small spring mass system as very representative problem; it is very easy to understand the concept of this. So, all the basic concepts we are trying to understand using this simple problem. So, in this particul ...
... So, in this case when we are considering the spring mass system we are always taking this small spring mass system as very representative problem; it is very easy to understand the concept of this. So, all the basic concepts we are trying to understand using this simple problem. So, in this particul ...
Amygdala oscillations and the consolidation of
... low-amplitude, high-frequency activity (so-called ‘activated EEG’). By contrast, slow waves of high amplitude dominate the neocortical EEG during slow-wave sleep (SWS) (called ‘synchronized EEG’). Although spectral analyses of the neocortical EEG reveal a continuum of frequencies during SWS, it incl ...
... low-amplitude, high-frequency activity (so-called ‘activated EEG’). By contrast, slow waves of high amplitude dominate the neocortical EEG during slow-wave sleep (SWS) (called ‘synchronized EEG’). Although spectral analyses of the neocortical EEG reveal a continuum of frequencies during SWS, it incl ...
Examination of Rhythmicity of Extracellularly Recorded Neurons in the Entorhinal Cortex
... ABSTRACT: A number of studies have examined the theta-rhythmic modulation of neuronal firing in the hippocampal circuit. For extracellular recordings, this is often done by examining spectral properties of the spike-time autocorrelogram, most significantly, for validating the presence or absence of ...
... ABSTRACT: A number of studies have examined the theta-rhythmic modulation of neuronal firing in the hippocampal circuit. For extracellular recordings, this is often done by examining spectral properties of the spike-time autocorrelogram, most significantly, for validating the presence or absence of ...
1 OSCILLATORY ENTRAINMENT OF THALAMIC NEURONS BY
... spindle periods. We found that theta and spindle oscillations differ in their spatial distribution ...
... spindle periods. We found that theta and spindle oscillations differ in their spatial distribution ...
Pathophysiology of Epilepsy
... The major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS – GABA A: presynaptic, mediated by Cl channels – GABA B: postsynaptic, mediated by K currents ...
... The major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS – GABA A: presynaptic, mediated by Cl channels – GABA B: postsynaptic, mediated by K currents ...