What are we measuring in EEG and MEG?
... Measures secondary (volume) Measures fields generated by ...
... Measures secondary (volume) Measures fields generated by ...
Gamma band activity in the nuclei of the Reticular Activating System
... characterized by low amplitude, high frequency oscillatory activity in the gamma band range (~20-100 Hz). Gamma frequency oscillations have been proposed to participate in conscious perception, problem solving, memory, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. It has been suggested that such coherent acti ...
... characterized by low amplitude, high frequency oscillatory activity in the gamma band range (~20-100 Hz). Gamma frequency oscillations have been proposed to participate in conscious perception, problem solving, memory, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. It has been suggested that such coherent acti ...
Physiology 59 [5-12
... stress (disappointment and frustration) in adults; occur in degenerative brain states o Delta waves = all EEG waves less than 3.5 cycles/sec; high-voltage; in deep (slow-wave) sleep, infancy and organic brain disease; in cortex independent of lower brain activity Intensity of brain wave = neurons an ...
... stress (disappointment and frustration) in adults; occur in degenerative brain states o Delta waves = all EEG waves less than 3.5 cycles/sec; high-voltage; in deep (slow-wave) sleep, infancy and organic brain disease; in cortex independent of lower brain activity Intensity of brain wave = neurons an ...
Anterograde amnesia
... an animals moving around its env’t, some neurons fired at a high rate only when the rat was in a particular location – The suggests evidence that different neurons have different spatial receptive fields (i.e. they responded when the animals were in different locations) – these neurons were named pl ...
... an animals moving around its env’t, some neurons fired at a high rate only when the rat was in a particular location – The suggests evidence that different neurons have different spatial receptive fields (i.e. they responded when the animals were in different locations) – these neurons were named pl ...
Chapter 14
... an animals moving around its env’t, some neurons fired at a high rate only when the rat was in a particular location – The suggests evidence that different neurons have different spatial receptive fields (i.e. they responded when the animals were in different locations) – these neurons were named pl ...
... an animals moving around its env’t, some neurons fired at a high rate only when the rat was in a particular location – The suggests evidence that different neurons have different spatial receptive fields (i.e. they responded when the animals were in different locations) – these neurons were named pl ...
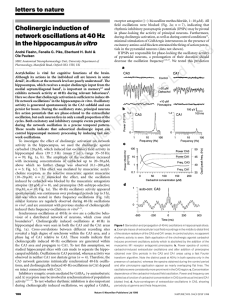
Cholinergic induction of network oscillations at 40 Hz in the
... Although its actions in the individual cell are known in some detail1, its effects at the network level are poorly understood2. The hippocampus, which receives a major cholinergic input from the medial septum/diagonal band3, is important in memory4,5 and exhibits network activity at 40 Hz during rel ...
... Although its actions in the individual cell are known in some detail1, its effects at the network level are poorly understood2. The hippocampus, which receives a major cholinergic input from the medial septum/diagonal band3, is important in memory4,5 and exhibits network activity at 40 Hz during rel ...
Theta rhythm and the encoding and retrieval of space and time ⁎ Michael E. Hasselmo , Chantal E. Stern
... pyramidal layer (s. pyr) at the same phase as a sink (“b” inward current) appears due to entorhinal input in stratum lacunosum moleculare (s. lac-mol). At the opposite phase of theta rhythm, a current sink (“c”) occurs due to CA3 input in stratum radiatum (s. rad) and a sink (“d”) appears due to spi ...
... pyramidal layer (s. pyr) at the same phase as a sink (“b” inward current) appears due to entorhinal input in stratum lacunosum moleculare (s. lac-mol). At the opposite phase of theta rhythm, a current sink (“c”) occurs due to CA3 input in stratum radiatum (s. rad) and a sink (“d”) appears due to spi ...
Functional roles of melanocortin-4 receptor in hippocampal synapse
... stimulating hormone (MSH), and adrenocorticotropin hormones. The central melanocortin signaling in the hypothalamus–pituitary-adrenal axis system is critical for regulating various aspects of energy homeostasis and feeding behavior. Although MC4R is highly expressed in other brain regions such as co ...
... stimulating hormone (MSH), and adrenocorticotropin hormones. The central melanocortin signaling in the hypothalamus–pituitary-adrenal axis system is critical for regulating various aspects of energy homeostasis and feeding behavior. Although MC4R is highly expressed in other brain regions such as co ...
LIMBIC SYSTEM
... anthropologist. He is best known for his research on Broca's area, a region of the frontal lobe that has been named after him. The term “le grand lobe limbique” (边缘叶)was first used by Broca in 1878. ...
... anthropologist. He is best known for his research on Broca's area, a region of the frontal lobe that has been named after him. The term “le grand lobe limbique” (边缘叶)was first used by Broca in 1878. ...
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA
... channels gives rise to low threshold Ca2+ potentials and associated high frequency bursts of action potentials that are present during sleep spindles and delta wave. In addition, the window component of the T-type current is essential for the generation of the slow (< 1Hz) oscillation (Hughes et al. ...
... channels gives rise to low threshold Ca2+ potentials and associated high frequency bursts of action potentials that are present during sleep spindles and delta wave. In addition, the window component of the T-type current is essential for the generation of the slow (< 1Hz) oscillation (Hughes et al. ...
Neural circuits underlying the generation of theta oscillations
... midline structure part of a vast region known as basal forebrain (Zaborszky et al., 2005). The MS projects to specific hippocampal subregions (Crutcher et al., 1981) such as: (i) dentate gyrus (the supragranular zone of the septal pole and the hilus), (ii) CA1 (stratum oriens and stratum lacunosum mo ...
... midline structure part of a vast region known as basal forebrain (Zaborszky et al., 2005). The MS projects to specific hippocampal subregions (Crutcher et al., 1981) such as: (i) dentate gyrus (the supragranular zone of the septal pole and the hilus), (ii) CA1 (stratum oriens and stratum lacunosum mo ...
Memory, navigation and theta rhythm in the
... data that support the hypothesis of phylogenetic continuity of navigation and memory. Most experiments that we discuss were carried out on rodents, but we believe that the conclusions and interpretations based on these ‘simpler’ animals bear validity for the mechanisms in the human brain as well. Al ...
... data that support the hypothesis of phylogenetic continuity of navigation and memory. Most experiments that we discuss were carried out on rodents, but we believe that the conclusions and interpretations based on these ‘simpler’ animals bear validity for the mechanisms in the human brain as well. Al ...
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
... voltages. EEG is a device that registers the brain’s cellular activity through a person’s several states, recording the activities from their being awake to being in a deep sleep [2]. The data is received via detectable electrodes attached to the scalp because measurements on the scalp can detect th ...
... voltages. EEG is a device that registers the brain’s cellular activity through a person’s several states, recording the activities from their being awake to being in a deep sleep [2]. The data is received via detectable electrodes attached to the scalp because measurements on the scalp can detect th ...
Declarative Memory
... (a). An ant leaves its nest (N) and forages with a very complicated path until it finds some food (F). It then carries the food back to the nest via a direct path. The ant must somehow take into account all the twists and turns it has made as well as the linear distance it has traveled in any direct ...
... (a). An ant leaves its nest (N) and forages with a very complicated path until it finds some food (F). It then carries the food back to the nest via a direct path. The ant must somehow take into account all the twists and turns it has made as well as the linear distance it has traveled in any direct ...
Anxiolytic action on the behavioural inhibition system implies
... The 1982 theory attempted to encompass all the information available at that time on the neural and behavioural actions of the anxiolytic drugs, the nature of theta activity and the neural and behavioural functions of the SHS. The explosion of data since its publication prompted us to produce a seco ...
... The 1982 theory attempted to encompass all the information available at that time on the neural and behavioural actions of the anxiolytic drugs, the nature of theta activity and the neural and behavioural functions of the SHS. The explosion of data since its publication prompted us to produce a seco ...
Buzsaki and Draguhn (2004), Neuronal Oscillations in Cortical
... network is independent of the temporal fluctuation of sensory signals. The oscillationrelated fluctuation of the membrane potentials in the participating neurons continuously and predictably biases the open-time probability of a multitude of voltage-gated channels (9). This design is an energy-effic ...
... network is independent of the temporal fluctuation of sensory signals. The oscillationrelated fluctuation of the membrane potentials in the participating neurons continuously and predictably biases the open-time probability of a multitude of voltage-gated channels (9). This design is an energy-effic ...
Cellular mechanisms underlying network synchrony in the medial
... Encoding interference problem Spike ...
... Encoding interference problem Spike ...
Cholinergic Basal Forebrain Neurons Burst with Theta during
... Single units were recorded using glass micropipettes (⬃1 m tip) that were filled with 0.5 M NaCl and ⬃5% Nb (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) and an intracellular amplifier (Neurodata IR-283A; Cygnus Technology, Delaware Water Gap, PA). The unit signal was amplified (2000⫻) and filtered (0.3–3 ...
... Single units were recorded using glass micropipettes (⬃1 m tip) that were filled with 0.5 M NaCl and ⬃5% Nb (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) and an intracellular amplifier (Neurodata IR-283A; Cygnus Technology, Delaware Water Gap, PA). The unit signal was amplified (2000⫻) and filtered (0.3–3 ...
凌树才_边缘系统
... anthropologist. He is best known for his research on Broca's area, a region of the frontal lobe that has been named after him. The term “le grand lobe limbique” (边缘叶)was first used by Broca in 1878. ...
... anthropologist. He is best known for his research on Broca's area, a region of the frontal lobe that has been named after him. The term “le grand lobe limbique” (边缘叶)was first used by Broca in 1878. ...
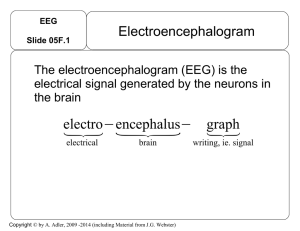
EEG - OCIBME
... Why are EEG signals on the surface of the scalp so small? Why are the brain neuronal signals obtained with needle electrodes so much larger? How accurately is it possible to know the thoughts in the brain from the EEG signals? The ECG is described as a vector field? Why not the EEG? What is the freq ...
... Why are EEG signals on the surface of the scalp so small? Why are the brain neuronal signals obtained with needle electrodes so much larger? How accurately is it possible to know the thoughts in the brain from the EEG signals? The ECG is described as a vector field? Why not the EEG? What is the freq ...
LIMBIC SYSTEM
... anthropologist. He is best known for his research on Broca's area, a region of the frontal lobe that has been named after him. The term “le grand lobe limbique” (边缘叶)was first used by Broca in 1878. ...
... anthropologist. He is best known for his research on Broca's area, a region of the frontal lobe that has been named after him. The term “le grand lobe limbique” (边缘叶)was first used by Broca in 1878. ...
The Generation of Brain Waves
... The second source of electrical activity in neurons occurs at the synapse. This is the junction of the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of the next neuron. As the impulse arrives at the end of the axon of one cell, transmitter substances (chemicals such as acetylcholine) are released into the syn ...
... The second source of electrical activity in neurons occurs at the synapse. This is the junction of the axon of one neuron and the dendrite of the next neuron. As the impulse arrives at the end of the axon of one cell, transmitter substances (chemicals such as acetylcholine) are released into the syn ...
Neuroanatomy 18 [4-20
... => postcommisural fornix => medial and lateral mamillary nuclei, => precommisural fornix => lateral septal nuclues, => or anterior thalamic nucleus ...
... => postcommisural fornix => medial and lateral mamillary nuclei, => precommisural fornix => lateral septal nuclues, => or anterior thalamic nucleus ...
Lecture 38 (Rhythms)
... One hypothesis is that perhaps the rhythmic waves are used to code information across different brain areas. However, as yet, there is no evidence for this. ...
... One hypothesis is that perhaps the rhythmic waves are used to code information across different brain areas. However, as yet, there is no evidence for this. ...