A thermodynamic model for the prediction of phase equilibria and
... solutions and their phase transitions under different temperatures and pressures (Hulett and Allen, 1902; Partridge and White, 1929; Hill, 1937; Booth and Bidwell, 1950; Madgin and Swales, 1956; Dickson et al., 1963; Power and Fabuss, 1964; Blount and Dickson, 1969; Blount and Dickson, 1973), but the ...
... solutions and their phase transitions under different temperatures and pressures (Hulett and Allen, 1902; Partridge and White, 1929; Hill, 1937; Booth and Bidwell, 1950; Madgin and Swales, 1956; Dickson et al., 1963; Power and Fabuss, 1964; Blount and Dickson, 1969; Blount and Dickson, 1973), but the ...
File
... But when you consider a solid, the number of moles per litre or molecules in a certain volume is constant. The molecules everywhere in the solid are about the same distance apart and are the same size: Since CaO and CaCO3 are __________, we can assume that their concentrations are _________. We can ...
... But when you consider a solid, the number of moles per litre or molecules in a certain volume is constant. The molecules everywhere in the solid are about the same distance apart and are the same size: Since CaO and CaCO3 are __________, we can assume that their concentrations are _________. We can ...
Lecture 14 Notes
... if graphite is added? (d) will reaction go left or right if container is crushed to one-eighths of original volume? (e) Does “Q” get larger or smaller if vessel is ...
... if graphite is added? (d) will reaction go left or right if container is crushed to one-eighths of original volume? (e) Does “Q” get larger or smaller if vessel is ...
10. Solution Guide to Supplementary Exercises
... The direction in which a net reaction will proceed to achieve equilibrium can be predicted by constant (Kc). ...
... The direction in which a net reaction will proceed to achieve equilibrium can be predicted by constant (Kc). ...
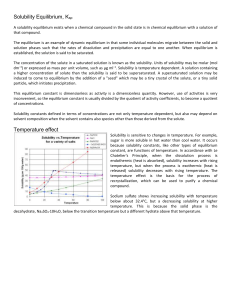
Solubility
... • We can also determine the concentration of an ion necessary for precipitation to begin. • Assume that precipitation begins when Qsp = Ksp • Example: If a solution contains 0.0020 mol CrO42per liter, what concentration of Ag+ ion must be added as AgNO3 before Ag2CrO4 begins to precipitate. (Neglect ...
... • We can also determine the concentration of an ion necessary for precipitation to begin. • Assume that precipitation begins when Qsp = Ksp • Example: If a solution contains 0.0020 mol CrO42per liter, what concentration of Ag+ ion must be added as AgNO3 before Ag2CrO4 begins to precipitate. (Neglect ...
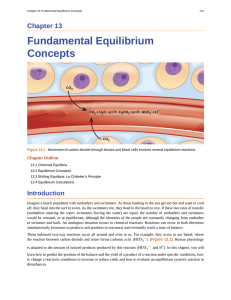
Fundamental Equilibrium Concepts
... Imagine a beach populated with sunbathers and swimmers. As those basking in the sun get too hot and want to cool off, they head into the surf to swim. As the swimmers tire, they head to the beach to rest. If these two rates of transfer (sunbathers entering the water, swimmers leaving the water) are ...
... Imagine a beach populated with sunbathers and swimmers. As those basking in the sun get too hot and want to cool off, they head into the surf to swim. As the swimmers tire, they head to the beach to rest. If these two rates of transfer (sunbathers entering the water, swimmers leaving the water) are ...
equilibrium - eVirtualGuru
... remains the same even though some of the reactants are still present. This constancy in composition indicates that the reaction has reached equilibrium. In order to understand the dynamic nature of the reaction, synthesis of ammonia is carried out with exactly the same starting conditions (of partia ...
... remains the same even though some of the reactants are still present. This constancy in composition indicates that the reaction has reached equilibrium. In order to understand the dynamic nature of the reaction, synthesis of ammonia is carried out with exactly the same starting conditions (of partia ...
Thermodynamics of Crystal-Melt Phase Change
... liquid and solid occupy distinct, non-overlapping regions within the H -T plane, with P fixed. Specifically, either solid or liquid exists as the preferred phase anywhere along their individual existence lines, each located, respectively, below and above the thermodynamic transition point, Teq . A d ...
... liquid and solid occupy distinct, non-overlapping regions within the H -T plane, with P fixed. Specifically, either solid or liquid exists as the preferred phase anywhere along their individual existence lines, each located, respectively, below and above the thermodynamic transition point, Teq . A d ...
Chapter 18: Chemical Equilibrium
... Waage proposed the law of chemical equilibrium, which states that at a given temperature, a chemical system may reach a state in which a particular ratio of reactant and product concentrations has a constant value. For example, the general equation for a reaction at equilibrium can be written as fol ...
... Waage proposed the law of chemical equilibrium, which states that at a given temperature, a chemical system may reach a state in which a particular ratio of reactant and product concentrations has a constant value. For example, the general equation for a reaction at equilibrium can be written as fol ...
Chapter 18 pdf
... Waage proposed the law of chemical equilibrium, which states that at a given temperature, a chemical system may reach a state in which a particular ratio of reactant and product concentrations has a constant value. For example, the general equation for a reaction at equilibrium can be written as fol ...
... Waage proposed the law of chemical equilibrium, which states that at a given temperature, a chemical system may reach a state in which a particular ratio of reactant and product concentrations has a constant value. For example, the general equation for a reaction at equilibrium can be written as fol ...
CHAPTER 18
... Some reactions favor products, and others reactants. In equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products ...
... Some reactions favor products, and others reactants. In equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products ...
chemical equilibrium type 1
... Before we consider the applications of equilibrium constants, let us consider its important features: the expression for equilibrium constant, K is applicable only when concentrations of the reactants and products have attained their equilibrium values and do not change with time. The value of equil ...
... Before we consider the applications of equilibrium constants, let us consider its important features: the expression for equilibrium constant, K is applicable only when concentrations of the reactants and products have attained their equilibrium values and do not change with time. The value of equil ...
Document
... The value of Kc for the reaction is 1.2 . The reaction is started with [H2 ]0 = 0.76 M, [N2]0 = 0.60 M and [NH3]0= 0.48 M. Which of the following is correct as the reaction comes to equilibrium? A) The concentration of N2will increase B) The concentration of H2will decrease C) The concentration of N ...
... The value of Kc for the reaction is 1.2 . The reaction is started with [H2 ]0 = 0.76 M, [N2]0 = 0.60 M and [NH3]0= 0.48 M. Which of the following is correct as the reaction comes to equilibrium? A) The concentration of N2will increase B) The concentration of H2will decrease C) The concentration of N ...
Chapter 16
... An isolated system is in mechanical equilibrium if no changes occur in pressure, in thermal equilibrium if no changes occur in temperature, in phase equilibrium if no transformations occur from one phase to another, and in chemical equilibrium if no changes occur in the chemical composition of the s ...
... An isolated system is in mechanical equilibrium if no changes occur in pressure, in thermal equilibrium if no changes occur in temperature, in phase equilibrium if no transformations occur from one phase to another, and in chemical equilibrium if no changes occur in the chemical composition of the s ...
14.1 Dynamic Equilibrium, Keq , and the Mass Action Expression
... i) At equilibrium pSO3 = 300. atm and pO2 = 100. atm. Calculate pSO2 ii) The engineer places a mixture of 0.0040 mol of SO2(g) and 0.0028 mol of O2(g) in a 1.0-L container and raises the temperature to 1000K. The reaction reaches equilibrium and 0.0020 mol of SO3 (g) is present. What would the engin ...
... i) At equilibrium pSO3 = 300. atm and pO2 = 100. atm. Calculate pSO2 ii) The engineer places a mixture of 0.0040 mol of SO2(g) and 0.0028 mol of O2(g) in a 1.0-L container and raises the temperature to 1000K. The reaction reaches equilibrium and 0.0020 mol of SO3 (g) is present. What would the engin ...
wiley_ch6_Chemical_Equilibrium
... disturbance (Q ≠ K) will shift to offset stress System said to “shift to right” when forward reaction is dominant (Q < K) System said to “shift to left” when reverse direction is dominant (Q > K) Jespersen/Brady/Hyslop ...
... disturbance (Q ≠ K) will shift to offset stress System said to “shift to right” when forward reaction is dominant (Q < K) System said to “shift to left” when reverse direction is dominant (Q > K) Jespersen/Brady/Hyslop ...
Chapter 15: Chemical Equilibrium
... is not appropriate. For example, when hydrogen and oxygen react to form water vapor, essentially all reactants are converted to product and no noticeable amounts of reactants are formed by the reverse reaction. The chemical equation representing this reaction therefore uses a single reaction arrow ( ...
... is not appropriate. For example, when hydrogen and oxygen react to form water vapor, essentially all reactants are converted to product and no noticeable amounts of reactants are formed by the reverse reaction. The chemical equation representing this reaction therefore uses a single reaction arrow ( ...
Chemical Equilibria - Beck-Shop
... as [A] and [B] decrease, since these are used to form the products C and D. At the same time, as soon as C and D are formed, the backward reaction proceeds, albeit at a slow rate initially since [products] is low. This helps to regenerate A and B. As [C] and [D] increase over time, the rate of the b ...
... as [A] and [B] decrease, since these are used to form the products C and D. At the same time, as soon as C and D are formed, the backward reaction proceeds, albeit at a slow rate initially since [products] is low. This helps to regenerate A and B. As [C] and [D] increase over time, the rate of the b ...
102MSJc14 - Louisiana Tech University
... long period of time, the contents of the reaction vessel do not become colorless. Instead, the intensity of the brown color eventually becomes constant, which means that the concentration of NO2 is no longer changing. Making the container colder makes equilibrium to shift to left and warming shift ...
... long period of time, the contents of the reaction vessel do not become colorless. Instead, the intensity of the brown color eventually becomes constant, which means that the concentration of NO2 is no longer changing. Making the container colder makes equilibrium to shift to left and warming shift ...