Ch 23 Evolution of Populations
... • Mutations may be random or induced by the environment. The ONLY source of new genes and NEW alleles. • Deletions, duplications or rearrangements of many loci are usually harmful. • Point mutations may or may not change an amino acid/protein. • Duplications within ONE gene provide a large variation ...
... • Mutations may be random or induced by the environment. The ONLY source of new genes and NEW alleles. • Deletions, duplications or rearrangements of many loci are usually harmful. • Point mutations may or may not change an amino acid/protein. • Duplications within ONE gene provide a large variation ...
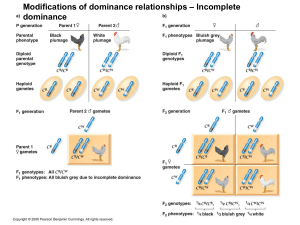
Modifications of dominance relationships – Incomplete dominance
... At the molecular level, the mutation that causes TSD is in a gene that encodes for the enzyme hexaminidase A (hex A). Enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of gangliosides. ...
... At the molecular level, the mutation that causes TSD is in a gene that encodes for the enzyme hexaminidase A (hex A). Enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of gangliosides. ...
Mutations I
... Compare these two windflowers (genus Anemone) and their karyotypes—the one on the right is double the one on the left ...
... Compare these two windflowers (genus Anemone) and their karyotypes—the one on the right is double the one on the left ...
Genetics Guided Notes Use Chapter 12
... Define Polyploidy and provide two examples of these types of organisms from the text: ...
... Define Polyploidy and provide two examples of these types of organisms from the text: ...
Genetic Principles
... • Pleiotropy – a single gene may contribute to multiple phenotypes • Epistasis – a gene may interact with or modify the phenotype of another gene ...
... • Pleiotropy – a single gene may contribute to multiple phenotypes • Epistasis – a gene may interact with or modify the phenotype of another gene ...
Mutations - Lakeland Regional High School / Overview
... A change in the DNA sequence that affects genetic information ...
... A change in the DNA sequence that affects genetic information ...
4-14
... Subject: Gene mutation. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 15: Gene mutation ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts: How DNA changes affect phenotype (15-1, 15-2) ...
... Subject: Gene mutation. Reading in ‘An introduction to genetic analysis’ (Griffiths et al., 7th edition) Chapter 15: Gene mutation ________________________________________________________________________ Key concepts: How DNA changes affect phenotype (15-1, 15-2) ...
BSCS
... 24. Suppose you have a regulatory pathway (See Figure 3): A turns off B , B turns off C and C turns on or Activates X. “X" is an arbitrary developmental process. When A is on this leaves B off, which in turn lets C come on therefore X is ON. Therefore the net effect of A is to turn on X. If there wa ...
... 24. Suppose you have a regulatory pathway (See Figure 3): A turns off B , B turns off C and C turns on or Activates X. “X" is an arbitrary developmental process. When A is on this leaves B off, which in turn lets C come on therefore X is ON. Therefore the net effect of A is to turn on X. If there wa ...
Lecture 11 Beyond Mendel
... molecules under genetic control. Using genetic analysis one can often detect the patterns of these interactions. For example: • a. In the dihybrid cross AaBb´ x AaBb, nine genotypes will result. If each allelic pair controls a distinct trait and exhibits complete dominance, a 9;3;3;1 phenotypic rati ...
... molecules under genetic control. Using genetic analysis one can often detect the patterns of these interactions. For example: • a. In the dihybrid cross AaBb´ x AaBb, nine genotypes will result. If each allelic pair controls a distinct trait and exhibits complete dominance, a 9;3;3;1 phenotypic rati ...
Chapter 14 Outline
... Determine this by complementation test. Cross mutants together so resulting organism has one copy of each mutant allele. If the phenotype is wild type, the mutations are in different genes (they complement each other). If the phenotype is mutant, the mutations are in the same gene and form part of t ...
... Determine this by complementation test. Cross mutants together so resulting organism has one copy of each mutant allele. If the phenotype is wild type, the mutations are in different genes (they complement each other). If the phenotype is mutant, the mutations are in the same gene and form part of t ...
Genetic Mutation - Raymond Williams Foundation
... Genetic Mutation – and family history continued… Dc Tue 22 May at The Blue Mugge pub Based on the BBC IoT broadcast with title Genetic Mutation, in 2007. ...
... Genetic Mutation – and family history continued… Dc Tue 22 May at The Blue Mugge pub Based on the BBC IoT broadcast with title Genetic Mutation, in 2007. ...
APOC1 gene rs4420638 SNP
... and as a result the effect of the gene depends on the presence of one or more modifier genes. There is that one gene or allele masking the phenotypic expression of the other genes or alleles in the interaction. That gene or allele masking the effect is referred to as epistatic. In contrast, the othe ...
... and as a result the effect of the gene depends on the presence of one or more modifier genes. There is that one gene or allele masking the phenotypic expression of the other genes or alleles in the interaction. That gene or allele masking the effect is referred to as epistatic. In contrast, the othe ...
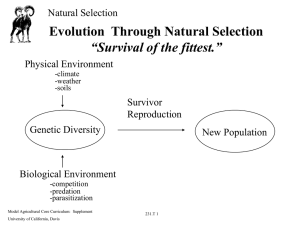
Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.”
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
... Evolution Through Natural Selection “Survival of the fittest.” Physical Environment -climate -weather -soils ...
1. Assuming simple dominance, out of a total of 160 offspring, how
... 6. What is the expected number of offspring phenotypes produced by a cross between heterozygotes for a gene that shows codominance? a) 2 b) 3 c) 1 d) 9 7. The allelic composition of an organism is called the _____. a) sequence b) phenotype c) genotype d) karyotype 8. What is the name of mode of inhe ...
... 6. What is the expected number of offspring phenotypes produced by a cross between heterozygotes for a gene that shows codominance? a) 2 b) 3 c) 1 d) 9 7. The allelic composition of an organism is called the _____. a) sequence b) phenotype c) genotype d) karyotype 8. What is the name of mode of inhe ...
The origin of genetic variation
... The origin of genetic variation I Motivation Evolution is a change in the genotype of the population over time. Phenotypic differences between species reflects genetic differences between species = genetic variation across species What is the origin of genetic variation?? Ultimate:MUTATION!!!!!!!!!! ...
... The origin of genetic variation I Motivation Evolution is a change in the genotype of the population over time. Phenotypic differences between species reflects genetic differences between species = genetic variation across species What is the origin of genetic variation?? Ultimate:MUTATION!!!!!!!!!! ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... • A change in the population because of a random event, such as a catastrophe • The smaller the population, the less genetic variety it has. • 2 Types: ...
... • A change in the population because of a random event, such as a catastrophe • The smaller the population, the less genetic variety it has. • 2 Types: ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.