Research Questions
... 1. How does a gene become a protein ? DNA creates mRNA to send to ribosomes through transcription , then ribosomes read the mRNA and convert the three nitrogen bases into an amino acid. Which then are fixed together , more complex ...
... 1. How does a gene become a protein ? DNA creates mRNA to send to ribosomes through transcription , then ribosomes read the mRNA and convert the three nitrogen bases into an amino acid. Which then are fixed together , more complex ...
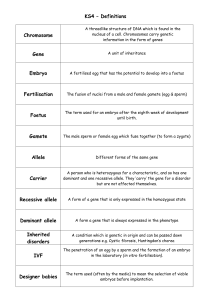
Heredity and Genetics Vocabulary
... The following document is a running list of vocabulary terms for the Carbohydrate, Lipid and Protein unit for Biology. The unit is one of the larger units and contains a lot of vocabulary to keep straight. In order the help the students I have created this study option for home. ...
... The following document is a running list of vocabulary terms for the Carbohydrate, Lipid and Protein unit for Biology. The unit is one of the larger units and contains a lot of vocabulary to keep straight. In order the help the students I have created this study option for home. ...
My CHXE Carrot BAC Research Poster
... At this time I would like to thank Dr. Simon for his mentorship throughout this project, the use of his laboratory, his suggestions and editorial input. I would like to thank Dr. Cavagnaro, Dr. Diaby, and Dr. Doug Senalik for their teachings in PCRs and the analysis of electrophoresis gels. I would ...
... At this time I would like to thank Dr. Simon for his mentorship throughout this project, the use of his laboratory, his suggestions and editorial input. I would like to thank Dr. Cavagnaro, Dr. Diaby, and Dr. Doug Senalik for their teachings in PCRs and the analysis of electrophoresis gels. I would ...
Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to
... regulatory genes, regulatory elements and transcription factors that act in concert. Explain the regulation of transcription inititiation. Be sure to mention control elements, enhancers, and cell type-specific transcription. ...
... regulatory genes, regulatory elements and transcription factors that act in concert. Explain the regulation of transcription inititiation. Be sure to mention control elements, enhancers, and cell type-specific transcription. ...
Whose DNA was sequenced for the Human Genome Project?
... very little idea about what each one does. One way of studying genes is to directly compare the entire genome with other organisms. This study is called comparative genomics. The human genome is extremely complicated and so, by comparing it with others, such as the mouse or fruit fly genome, we gain ...
... very little idea about what each one does. One way of studying genes is to directly compare the entire genome with other organisms. This study is called comparative genomics. The human genome is extremely complicated and so, by comparing it with others, such as the mouse or fruit fly genome, we gain ...
Microarray Data Analysis Normalization
... MarmiteScan: Use chemical and disease-related information to detect related 1255_g_at ...
... MarmiteScan: Use chemical and disease-related information to detect related 1255_g_at ...
Cloning - Cloudfront.net
... – clone – a group of cells, organisms, or genes that are exact copies of each other – donor gene inserted into a bacterium is copied every time the plasmid containing it replicates – genes can be cloned by growing genetically engineered bacteria ...
... – clone – a group of cells, organisms, or genes that are exact copies of each other – donor gene inserted into a bacterium is copied every time the plasmid containing it replicates – genes can be cloned by growing genetically engineered bacteria ...
Slide ()
... Effects of translocations. The first observed cancer-associated chromosomal abnormality was a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, resulting in the so-called Philadelphia chromosome, identified in CML patients. The functional result of this genetic event is the creation of the BCR- ...
... Effects of translocations. The first observed cancer-associated chromosomal abnormality was a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, resulting in the so-called Philadelphia chromosome, identified in CML patients. The functional result of this genetic event is the creation of the BCR- ...
Cloning - cloudfront.net
... – clone – a group of cells, organisms, or genes that are exact copies of each other – donor gene inserted into a bacterium is copied every time the plasmid containing it replicates – genes can be cloned by growing genetically engineered bacteria ...
... – clone – a group of cells, organisms, or genes that are exact copies of each other – donor gene inserted into a bacterium is copied every time the plasmid containing it replicates – genes can be cloned by growing genetically engineered bacteria ...
Genetics 1
... reducing the chromosome number from the diploid # to the haploid #. – Occurs only in the sex cells, sperm and ovum. ...
... reducing the chromosome number from the diploid # to the haploid #. – Occurs only in the sex cells, sperm and ovum. ...
Cell Theory Quiz Study Guide Name
... 15. __________________________ bases form the rungs of the ladder (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine). 16. ____________ matches with Thymine while Cytosine matches with _____________ These are the nitrogen base pairs. 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic ...
... 15. __________________________ bases form the rungs of the ladder (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine). 16. ____________ matches with Thymine while Cytosine matches with _____________ These are the nitrogen base pairs. 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic ...
what is happening to this weeks trendy gene/protein/cytokine?
... STILL has the same problems! • Separating cause from effect • Separating relevant from irrelevant. • Dominance of the ‘what is happening to this weeks trendy gene/protein/cytokine?’ approach. ...
... STILL has the same problems! • Separating cause from effect • Separating relevant from irrelevant. • Dominance of the ‘what is happening to this weeks trendy gene/protein/cytokine?’ approach. ...
BI_1_Yang
... events, SNPs located in gene structure, mitochondrial proteins, micro-RNA elements, biological pathways, and PPI networks ...
... events, SNPs located in gene structure, mitochondrial proteins, micro-RNA elements, biological pathways, and PPI networks ...
DNA and Heredity - Dr. Diamond`s Website
... Changes in Genes • Each ‘word’ in the recipe has three letters (nucleotides) • A change in a word is called a mutation • It may cause a change in the recipe for a protein • A mutation may be helpful, harmful or neither • Sickle cell anemia is an example of the result of a harmful mutation ...
... Changes in Genes • Each ‘word’ in the recipe has three letters (nucleotides) • A change in a word is called a mutation • It may cause a change in the recipe for a protein • A mutation may be helpful, harmful or neither • Sickle cell anemia is an example of the result of a harmful mutation ...
Case report
... interested in sensopathic toys than age-appropriate games. Socializing with peers has always been a problem. He has always been oversensitive for loud noises. He had problems to adjust to changes. Pediatric assessment of the encopresis did not show any somatic reasons for the problem. He had marked ...
... interested in sensopathic toys than age-appropriate games. Socializing with peers has always been a problem. He has always been oversensitive for loud noises. He had problems to adjust to changes. Pediatric assessment of the encopresis did not show any somatic reasons for the problem. He had marked ...
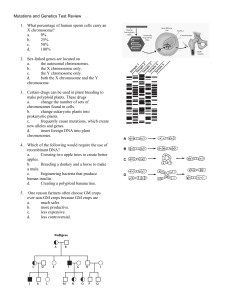
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... change the number of sets of chromosomes found in cells. b. change eukaryotic plants into prokaryotic plants. c. frequently cause mutations, which create new alleles and genes. d. insert foreign DNA into plant chromosomes. 4. Which of the following would require the use of recombinant DNA? a. Crossi ...
... change the number of sets of chromosomes found in cells. b. change eukaryotic plants into prokaryotic plants. c. frequently cause mutations, which create new alleles and genes. d. insert foreign DNA into plant chromosomes. 4. Which of the following would require the use of recombinant DNA? a. Crossi ...
Trnascription in eucaryotes
... the original form and that introns arose later by some unknown mechanism. Organisms which gained introns so that domain shuffling could occur would be advantaged in the long term. ...
... the original form and that introns arose later by some unknown mechanism. Organisms which gained introns so that domain shuffling could occur would be advantaged in the long term. ...
Mutations Justified True or False
... Yes, because we learned in the 4 PowerPoint’s that chemicals and smoke from buildings can cause, just like the birch trees, changes in the organisms. And the chemicals can also change genes inside the organism. I know this because Mr. Bormann told us to put it in our notes. The environment can alter ...
... Yes, because we learned in the 4 PowerPoint’s that chemicals and smoke from buildings can cause, just like the birch trees, changes in the organisms. And the chemicals can also change genes inside the organism. I know this because Mr. Bormann told us to put it in our notes. The environment can alter ...
Genetics and Heredity
... or physical traits are controlled by factors or genes that occur in pairs Genes (segments of DNA) are found in cells and responsible for inherited features Genes are located on chromosomes Most organisms have homologous pairs of chromosomes or one set from each parent ...
... or physical traits are controlled by factors or genes that occur in pairs Genes (segments of DNA) are found in cells and responsible for inherited features Genes are located on chromosomes Most organisms have homologous pairs of chromosomes or one set from each parent ...
Section 16-1 Genes and Variation (pages 393-396)
... c. They always affect an organism’s phenotype. d. They always affect an organism’s fitness. 11. Is the following sentence true or false? Most heritable differences are due to gene shuffling that occurs during the production of gametes. 12. Circle the letter of each choice that is true about sexual r ...
... c. They always affect an organism’s phenotype. d. They always affect an organism’s fitness. 11. Is the following sentence true or false? Most heritable differences are due to gene shuffling that occurs during the production of gametes. 12. Circle the letter of each choice that is true about sexual r ...
Transcription Control in Eukaryotes
... Eukaryotes Transcription control in eukaryotes is more complex than in prokaryotes, with more gene-gene interactions, presumably required to produce more different cell types in more complex organisms. We will consider some examples and models to illustrate some general principles. ...
... Eukaryotes Transcription control in eukaryotes is more complex than in prokaryotes, with more gene-gene interactions, presumably required to produce more different cell types in more complex organisms. We will consider some examples and models to illustrate some general principles. ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.