Anemia
... i.e. mucocutaneous bleeding. “Oozing and bruising” NOT hematomas or bleeding into joints. Three causes: 1. underproduction – inadequate megakaryocytes in the marrow due to failure, invasion, injury (especially EtOH), congenital 2. peripheral destruction – DIC, TTP, ITP - non-immune mechanisms, immun ...
... i.e. mucocutaneous bleeding. “Oozing and bruising” NOT hematomas or bleeding into joints. Three causes: 1. underproduction – inadequate megakaryocytes in the marrow due to failure, invasion, injury (especially EtOH), congenital 2. peripheral destruction – DIC, TTP, ITP - non-immune mechanisms, immun ...
NURSING CARE OF THE CHILD WITH A HEMATOLOGIC …
... – RBCs are pale and smaller • Iron Deficiency Anemia – Most common anemia caused by improper iron intake » Giving cow’s milk instead of baby formula is main culprit during the first year » Adolescent girls are at risk because of menstruation » Causes poor growth, poor test scores later – Treatment » ...
... – RBCs are pale and smaller • Iron Deficiency Anemia – Most common anemia caused by improper iron intake » Giving cow’s milk instead of baby formula is main culprit during the first year » Adolescent girls are at risk because of menstruation » Causes poor growth, poor test scores later – Treatment » ...
Effects of membrane shape and lipid composition in extracellular
... In this work, we examine the importance of fundamental properties of lipid membranes, such as membrane curvature or lipid composition, in the context of extracellular vesicle and platelet biology. Although differing in biologic function, both extracellular vesicles and platelets are comparatively sm ...
... In this work, we examine the importance of fundamental properties of lipid membranes, such as membrane curvature or lipid composition, in the context of extracellular vesicle and platelet biology. Although differing in biologic function, both extracellular vesicles and platelets are comparatively sm ...
Human Physiology
... • The 3 components of hemostasis are: – The vessel wall – ________________________ – The coagulation cascade • The 3 major steps of hemostasis are: – Vascular Spasm (initial response, constricts) – Platelet plug formation – Blood coagulation (clotting) ...
... • The 3 components of hemostasis are: – The vessel wall – ________________________ – The coagulation cascade • The 3 major steps of hemostasis are: – Vascular Spasm (initial response, constricts) – Platelet plug formation – Blood coagulation (clotting) ...
INDICATIONS FOR EMERGENT TRANSFUSIONS
... • Bleeding/ massive transfusion (maintain the platelets > 100, 000 ) • Ie. DIC or CNS trauma ...
... • Bleeding/ massive transfusion (maintain the platelets > 100, 000 ) • Ie. DIC or CNS trauma ...
Bleeding tendency
... bleeding into joints and muscles, which can lead to crippling arthritis if not properly treated. Most children present towards the end of the first year of life, when they start to crawl then walk (and fall over). Almost 40% of cases with severe disease present in the neonatal period, particularly w ...
... bleeding into joints and muscles, which can lead to crippling arthritis if not properly treated. Most children present towards the end of the first year of life, when they start to crawl then walk (and fall over). Almost 40% of cases with severe disease present in the neonatal period, particularly w ...
Coagulation Made Simple
... • Hemostasis requires the interaction of platelets, coagulation and fibrinolytic factors, endothelium, proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators, and leukocytes • Clot formation is typically initiated by vascular injury, in which a platelet plug forms and is reinforced with fibrin produced via ...
... • Hemostasis requires the interaction of platelets, coagulation and fibrinolytic factors, endothelium, proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators, and leukocytes • Clot formation is typically initiated by vascular injury, in which a platelet plug forms and is reinforced with fibrin produced via ...
Blood type Antigen Antibody
... Named according to the abnormal WBC clone involved Mononucleosis highly contagious viral disease caused by Epstein-Barr virus; excessive # of agranulocytes; fatigue, sore throat, recover in a few weeks ...
... Named according to the abnormal WBC clone involved Mononucleosis highly contagious viral disease caused by Epstein-Barr virus; excessive # of agranulocytes; fatigue, sore throat, recover in a few weeks ...
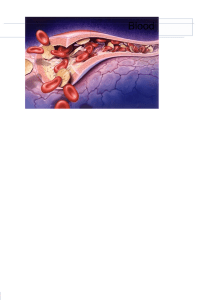
Haemostasis
... It is due to local spasm of the smooth muscle It can be maintained by platelet vasoconstrictors e.g. serotonin ...
... It is due to local spasm of the smooth muscle It can be maintained by platelet vasoconstrictors e.g. serotonin ...
management of hemorrhage in dental surgery
... Platelet adhere to the damaged surface and form a temporary plug. ...
... Platelet adhere to the damaged surface and form a temporary plug. ...
Worksheets.hip.cbc.knee
... b. Increased bleeding with the ability to form an adequate clot. c. Increased bleeding with the inability to form an adequate clot. d. Decreased bleeding 17. All of the following are possible causes of increased platelet counts except: a. Exercise b. Stress c. Hemorrhage d. Recent splenectomy e. Men ...
... b. Increased bleeding with the ability to form an adequate clot. c. Increased bleeding with the inability to form an adequate clot. d. Decreased bleeding 17. All of the following are possible causes of increased platelet counts except: a. Exercise b. Stress c. Hemorrhage d. Recent splenectomy e. Men ...
Chapter 3 Blood
... Functions of blood 1. Place of exchange of substances between interstitial fluid and external environment ...
... Functions of blood 1. Place of exchange of substances between interstitial fluid and external environment ...
I need to know about irradiation
... the transfused cells grow in the bone marrow and start to take over. The engrafted donor’s white cells then attack the recipient’s cells. Typically, TA-GVHD occurs within 10–14 days post-transfusion causing fever, skin rash, hepatitis, diarrhoea and pancytopenia (very low platelets and total white c ...
... the transfused cells grow in the bone marrow and start to take over. The engrafted donor’s white cells then attack the recipient’s cells. Typically, TA-GVHD occurs within 10–14 days post-transfusion causing fever, skin rash, hepatitis, diarrhoea and pancytopenia (very low platelets and total white c ...
Bleeding Diathesis – Dr Koplolovich
... ●Platelet functions as cellular based platform for hemostasis ...
... ●Platelet functions as cellular based platform for hemostasis ...
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
... This is because these drugs interfere with platelet function and may increase their risk of bleeding. Herbal medicines and Vitamins and Minerals, like cod liver oil and Vitamin E,,5 should also be avoided. If you are unsure ask your hematologist or a pharmacist. You should make sure that doctors and ...
... This is because these drugs interfere with platelet function and may increase their risk of bleeding. Herbal medicines and Vitamins and Minerals, like cod liver oil and Vitamin E,,5 should also be avoided. If you are unsure ask your hematologist or a pharmacist. You should make sure that doctors and ...
Leukemia - Liberty Hill High School
... • Either may block circulation to tissues beyond the occlusion and cause death to those tissues • Pulmonary embolism, stroke, heart attack ...
... • Either may block circulation to tissues beyond the occlusion and cause death to those tissues • Pulmonary embolism, stroke, heart attack ...
A Rapid Platelet Function Assay Used to Regulate
... Open-heart surgery activates platelets and elicits a decrease in platelet number and function with a potential increase in postoperative bleeding. The magnitude of thrombocytopenia and platelet dysfunction is variable both among perfusion systems and patients and is a major cause of hemorrhage (7). ...
... Open-heart surgery activates platelets and elicits a decrease in platelet number and function with a potential increase in postoperative bleeding. The magnitude of thrombocytopenia and platelet dysfunction is variable both among perfusion systems and patients and is a major cause of hemorrhage (7). ...
DISORDERS OF HEMOSTASIS
... 1.1. Blood vessels contribute to hemostasis via several processes: vasoconstriction: an immediate and transient response (less than 1 minute duration), which reduces the blood loss from the damaged zone through: Reflex (neurogenic) mechanisms Humoral mechanisms: endothelin released by endothelial ce ...
... 1.1. Blood vessels contribute to hemostasis via several processes: vasoconstriction: an immediate and transient response (less than 1 minute duration), which reduces the blood loss from the damaged zone through: Reflex (neurogenic) mechanisms Humoral mechanisms: endothelin released by endothelial ce ...
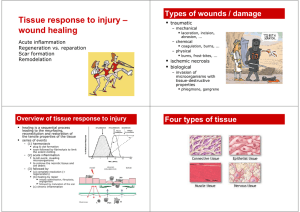
Tissue response to injury wound healing
... activated protein C is an enzyme that destroys certain clotting factors and inhibits coagulation ...
... activated protein C is an enzyme that destroys certain clotting factors and inhibits coagulation ...
Blood Banking Theory and Component Therapy
... risk of hemorrhage (e.g. <10,000/ml) • Thrombocytopenia (e.g. <50,000/ml) with bleeding or invasive procedure ...
... risk of hemorrhage (e.g. <10,000/ml) • Thrombocytopenia (e.g. <50,000/ml) with bleeding or invasive procedure ...
The Blood - West Virginia University
... – Entraps cellular elements of the blood forms CLOT – Contraction of platelets pulls the damaged vessel close together: • Fluid squeezes out as the clot contracts (Serum) ...
... – Entraps cellular elements of the blood forms CLOT – Contraction of platelets pulls the damaged vessel close together: • Fluid squeezes out as the clot contracts (Serum) ...
The Blood
... – Entraps cellular elements of the blood forms CLOT – Contraction of platelets pulls the damaged vessel close together: • Fluid squeezes out as the clot contracts (Serum) ...
... – Entraps cellular elements of the blood forms CLOT – Contraction of platelets pulls the damaged vessel close together: • Fluid squeezes out as the clot contracts (Serum) ...
Blood Component Preparation: From Benchtop to Bedside Brochure
... Blood Bag Systems and Automated Separators Production of BC-Derived Platelet Concentrates BC-Reduced Red Cell Concentrates and Plasma Overnight Hold of Whole Blood Further Automation of Centrifugation and Separation ...
... Blood Bag Systems and Automated Separators Production of BC-Derived Platelet Concentrates BC-Reduced Red Cell Concentrates and Plasma Overnight Hold of Whole Blood Further Automation of Centrifugation and Separation ...
Platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to stop bleeding by clumping and clogging blood vessel injuries. Platelets have no cell nucleus: they are fragments of cytoplasm which are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow, and then enter the circulation. These unactivated platelets are biconvex discoid (lens-shaped) structures, 2–3 µm in greatest diameter. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other animals (e.g. birds, amphibians) thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells.On a stained blood smear, platelets appear as dark purple spots, about 20% the diameter of red blood cells. The smear is used to examine platelets for size, shape, qualitative number, and clumping. The ratio of platelets to red blood cells in a healthy adult is 1:10 to 1:20. The main function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site of interrupted endothelium. They gather at the site and unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: adhesion. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: activation. Third, they connect to each other through receptor bridges: aggregation. Formation of this platelet plug (primary hemostasis) is associated with activation of the coagulation cascade with resultant fibrin deposition and linking (secondary hemostasis). These processes may overlap: the spectrum is from a predominantly platelet plug, or ""white clot"" to a predominantly fibrin clot, or ""red clot"" or the more typical mixture. The final result is the clot. Some would add the subsequent clot retraction and platelet inhibition as fourth and fifth steps to the completion of the process and still others a sixth step wound repair.Low platelet concentration is thrombocytopenia and is due to either decreased production or increased destruction. Elevated platelet concentration is thrombocytosis and is either congenital, reactive (to cytokines), or due to unregulated production: one of the myeloprolerative neoplasms or certain other myeloid neoplasms. A disorder of platelet function is a thrombocytopathy.Normal platelets can respond to an abnormality on the vessel wall rather than to hemorrhage, resulting in inappropriate platelet adhesion/activation and thrombosis: the formation of a clot within an intact vessel. These arise by different mechanisms than a normal clot. Examples are: extending the fibrin clot of venous thrombosis; extending an unstable or ruptured arterial plaque, causing arterial thrombosis; and microcirculatory thrombosis. An arterial thrombus may partially obstruct blood flow, causing downstream ischemia; or completely obstruct it, causing downstream tissue death.