Chapter 16 powerpoint file
... Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. Originate in bone marrow and as they mature they expel their organelles before entering the blood stream. Most numerous component of formed elements. Contain no nucleus or organelles, instead they are packed with hemoglobin. There are three important characterist ...
... Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. Originate in bone marrow and as they mature they expel their organelles before entering the blood stream. Most numerous component of formed elements. Contain no nucleus or organelles, instead they are packed with hemoglobin. There are three important characterist ...
Concentration in pH 6.5 Citrate-Plasma
... Articles on similar topics can be found in the following Blood collections Information about reproducing this article in parts or in its entirety may be found online at: ...
... Articles on similar topics can be found in the following Blood collections Information about reproducing this article in parts or in its entirety may be found online at: ...
CBC Basic Interpretation - Thalassemia Center
... Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS) Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) Antiphospholipid syndrome Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) Post-transfusion purpura Neonatal al ...
... Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) Hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS) Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) Antiphospholipid syndrome Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) Post-transfusion purpura Neonatal al ...
Erythrocytes [Red Blood Cells]
... – Contain lysosomes, mitochondria, granules with secretions & open cnalicular system opening to the surface. – Secrete vasoconstrictors, procoagulants, chemical that attract neutrophils & monocytes, growth factors and more. ...
... – Contain lysosomes, mitochondria, granules with secretions & open cnalicular system opening to the surface. – Secrete vasoconstrictors, procoagulants, chemical that attract neutrophils & monocytes, growth factors and more. ...
Chapt06 Lecture 13ed Pt 2
... cells release prothrombin activator, which initiates a cascade of enzymatic reactions. ...
... cells release prothrombin activator, which initiates a cascade of enzymatic reactions. ...
Circulatory System and Blood
... D. Exocytosis of the debris , formation of phagosome, phagosome-lysosome merger phagolysosome, killing and digestion of the invading organism, engulfment by ...
... D. Exocytosis of the debris , formation of phagosome, phagosome-lysosome merger phagolysosome, killing and digestion of the invading organism, engulfment by ...
Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia - NAIT-FAIT
... unfortunately often overlooked and therefore incorrectly treated. The consequences of this can be grave. Similar observations have been made in other countries such as Great Britain (Murphy et al. 1999, Turner et al. 2005). About one third of all neonatal thrombocytopenias <150,000/µl and the majori ...
... unfortunately often overlooked and therefore incorrectly treated. The consequences of this can be grave. Similar observations have been made in other countries such as Great Britain (Murphy et al. 1999, Turner et al. 2005). About one third of all neonatal thrombocytopenias <150,000/µl and the majori ...
Essentials of Hematology
... fat soluble vitamins like vitamin K (A,E,D). Vitamin K in turn…. produces blood clotting factors Vll, lX, X) The liver converts bilirubin to bile and stores large quantities of blood and extra iron. ...
... fat soluble vitamins like vitamin K (A,E,D). Vitamin K in turn…. produces blood clotting factors Vll, lX, X) The liver converts bilirubin to bile and stores large quantities of blood and extra iron. ...
Case Presentation - Dr Modupe Elebute
... checking the unit the product appeared to be “greenish” in colour The unit was checked and was correct for this particular patient 15 minutes into the transfusion she collapsed and the transfusion was stopped What is the diagnosis? ...
... checking the unit the product appeared to be “greenish” in colour The unit was checked and was correct for this particular patient 15 minutes into the transfusion she collapsed and the transfusion was stopped What is the diagnosis? ...
Principles of Transfusion Medicine
... (Controversial) Chronic aplastic anemia or MDS (unless bleeding)* ...
... (Controversial) Chronic aplastic anemia or MDS (unless bleeding)* ...
Hereditary Hematological Disorders Red cell Enzyme
... Quantitative and Qualitative defects described Normal platelet number 150400,000 Platelet count is normal from birth,, can detect from birth Testing- CBC and film (characteristic blood film changessize of platelets, colour granules, inclusions ect), platelet function studies, flow cytometry for GP o ...
... Quantitative and Qualitative defects described Normal platelet number 150400,000 Platelet count is normal from birth,, can detect from birth Testing- CBC and film (characteristic blood film changessize of platelets, colour granules, inclusions ect), platelet function studies, flow cytometry for GP o ...
18. Cardiovascular System: Blood
... Coagulation, which is the true blood-clotting phase, begins 30 seconds or more after the injury. This is a complex process (Fig. 18.13), which may follow two pathways: the intrinsic pathway results from damage to the inside of the vessel, and the extrinsic pathway is initiated by damage to tissue ou ...
... Coagulation, which is the true blood-clotting phase, begins 30 seconds or more after the injury. This is a complex process (Fig. 18.13), which may follow two pathways: the intrinsic pathway results from damage to the inside of the vessel, and the extrinsic pathway is initiated by damage to tissue ou ...
The Blood
... vessels and arterioles, can reduce blood loss for several hours until other mechanisms can take over B. Platelet plug formation, 3 steps – 1. Platelet adhesion - platelets stick to exposed collagen underlying damaged endothelial cells in vessel wall 2. Platelet Release Reaction - platelets activated ...
... vessels and arterioles, can reduce blood loss for several hours until other mechanisms can take over B. Platelet plug formation, 3 steps – 1. Platelet adhesion - platelets stick to exposed collagen underlying damaged endothelial cells in vessel wall 2. Platelet Release Reaction - platelets activated ...
Pathogen Inactivation Making Decisions About New
... c) Should different criteria be used for certain patient populations? 2. Licensing requirements: What minimum acceptable safety and efficacy criteria should be put into place for the pre-approval assessment of pathogen inactivated products? Specifically: a) What criteria should govern acceptable tox ...
... c) Should different criteria be used for certain patient populations? 2. Licensing requirements: What minimum acceptable safety and efficacy criteria should be put into place for the pre-approval assessment of pathogen inactivated products? Specifically: a) What criteria should govern acceptable tox ...
lecture notes
... An embolus may become lodged in smaller blood vessels, blocking blood flow into the local tissue or organ and leading to ischemia. ...
... An embolus may become lodged in smaller blood vessels, blocking blood flow into the local tissue or organ and leading to ischemia. ...
The Circulatory System: Blood
... – Pseudopods contract - draw together a platelet plug – Platelets degranulate releasing a variety of substances • Serotonin is a vasoconstrictor • ADP attracts and degranulates more platelets • Thromboxane A2, an eicosanoid, promotes platelet aggregation, degranulation, and vasoconstriction – Positi ...
... – Pseudopods contract - draw together a platelet plug – Platelets degranulate releasing a variety of substances • Serotonin is a vasoconstrictor • ADP attracts and degranulates more platelets • Thromboxane A2, an eicosanoid, promotes platelet aggregation, degranulation, and vasoconstriction – Positi ...
Chapter 26 Clients with Hematopoietic and Lymphatic System
... ° Hemostasis – blood clotting o Platelets attracted to damage in vessel ° Thrombocytopenia: = decrease in platelet count lower than 100,000/ml of blood. o Caused by decreased production or increased destruction of platelets, or from storage of platelets in the spleen. o Primary thrombocytopenia most ...
... ° Hemostasis – blood clotting o Platelets attracted to damage in vessel ° Thrombocytopenia: = decrease in platelet count lower than 100,000/ml of blood. o Caused by decreased production or increased destruction of platelets, or from storage of platelets in the spleen. o Primary thrombocytopenia most ...
Pocket card - Roche Diagnostics (Schweiz)
... • Generally reported as international normalised ratio (INR) • INR relates the results obtained with a test and normal sample under particular analytical conditions to ...
... • Generally reported as international normalised ratio (INR) • INR relates the results obtained with a test and normal sample under particular analytical conditions to ...
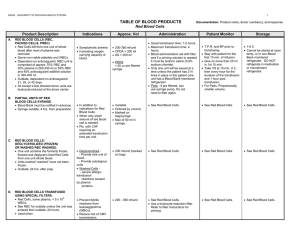
Table for Blood Products - University of Michigan : Pathology
... • In Peds - saline set-up optional. Only one unit will be issued at a time unless the patient has 2 IV lines in place or the patient care unit has a Blood Bank monitored refrigerator. ...
... • In Peds - saline set-up optional. Only one unit will be issued at a time unless the patient has 2 IV lines in place or the patient care unit has a Blood Bank monitored refrigerator. ...
Platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to stop bleeding by clumping and clogging blood vessel injuries. Platelets have no cell nucleus: they are fragments of cytoplasm which are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow, and then enter the circulation. These unactivated platelets are biconvex discoid (lens-shaped) structures, 2–3 µm in greatest diameter. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other animals (e.g. birds, amphibians) thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells.On a stained blood smear, platelets appear as dark purple spots, about 20% the diameter of red blood cells. The smear is used to examine platelets for size, shape, qualitative number, and clumping. The ratio of platelets to red blood cells in a healthy adult is 1:10 to 1:20. The main function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site of interrupted endothelium. They gather at the site and unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: adhesion. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: activation. Third, they connect to each other through receptor bridges: aggregation. Formation of this platelet plug (primary hemostasis) is associated with activation of the coagulation cascade with resultant fibrin deposition and linking (secondary hemostasis). These processes may overlap: the spectrum is from a predominantly platelet plug, or ""white clot"" to a predominantly fibrin clot, or ""red clot"" or the more typical mixture. The final result is the clot. Some would add the subsequent clot retraction and platelet inhibition as fourth and fifth steps to the completion of the process and still others a sixth step wound repair.Low platelet concentration is thrombocytopenia and is due to either decreased production or increased destruction. Elevated platelet concentration is thrombocytosis and is either congenital, reactive (to cytokines), or due to unregulated production: one of the myeloprolerative neoplasms or certain other myeloid neoplasms. A disorder of platelet function is a thrombocytopathy.Normal platelets can respond to an abnormality on the vessel wall rather than to hemorrhage, resulting in inappropriate platelet adhesion/activation and thrombosis: the formation of a clot within an intact vessel. These arise by different mechanisms than a normal clot. Examples are: extending the fibrin clot of venous thrombosis; extending an unstable or ruptured arterial plaque, causing arterial thrombosis; and microcirculatory thrombosis. An arterial thrombus may partially obstruct blood flow, causing downstream ischemia; or completely obstruct it, causing downstream tissue death.

![Erythrocytes [Red Blood Cells]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011997754_1-8692c5d89a78d41425c72abdd2615d43-300x300.png)