* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Haemostasis
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
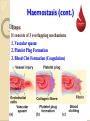
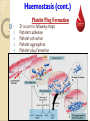
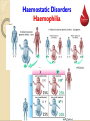
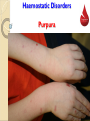
ﺼﺩﻕ ﺍﷲ ﺍﻟﻌﻅﻴﻡ ﺍﻻﺴﺭﺍﺀ ﺍﻴﺔ 58 Tests for Haemostasis Learning objectives: 1.Know mechanisms of haemostasis. 2.Know disorders of haemostasis. 3.Know how to test for haemostasis. 4.Know abnormalities of haemostasis. Haemostasis Def., Hemostasis („hemo”=blood; sta=„remain”) is the stoppage (arrest) of bleeding from damaged blood vessels. Haemostasis (cont.) Steps: Steps: It consists of 3 overlapping mechanisms 1. Vascular spasm 2. Platelet Plug Formation 3. Blood Clot Formation (Coagulation) 3. Blood Clot Formation (Coagulation) Haemostasis (cont.) (cont.) Vascular Spasm It is due to local spasm of the smooth muscle It can be maintained by platelet vasoconstrictors e.g. serotonin Haemostasis (cont.) (cont.) Platelet Plug Formation • 1. 2. 3. 4. It occurs in following steps; Platelets adhesion Platelet activation Platelet aggregation Platelet plug formation Haemostasis (cont.) (cont.) Blood Clot Formation Clotting Factors: These are plasma proteins Most of them are formed in the liver Vitamin Kdependent clotting factors are: II, VII, IX, X Most of them are present as proenzymes (inactive) Once activated, it induces a cascade reaction → to form blood clot Haemostasis (cont.) (cont.) Steps of Blood Clot Formation Coagulation mechanism is composed of an extrinsic and intrinsic pathway, which eventually merge into one Haemostasis (cont.) (cont.) Summary of steps of Blood Clot Formation Summary of steps of Blood Clot Formation Haemostatic Disorders There are 2 groups of haemostatic disorders: 1. Bleeding disorders •Haemophilia •Purpura •Vit. K deficiency 2. Intravascular clotting Haemostatic Disorders Purpura Haemophilia Def., It is a haemorhagic disease caused It is a congenital sex linked, by ↓ed platelet count or function. recessive disease carried on X chromosome Types and Causes a)Thrombocytopenic purpura→ due to ↓ of platelets count below 50,000/mm3 b)Non‐thrombocytopenic purpura → due to; i) ↓of functioning platelets (thromboasthenic purpura) ii) Defect in the vessel wall as in cases of severe vit. C deficiency or allergy, and called vascular purpura. Include 3 types; a) Haemophilia A: It is the classic haemophilia. It is caused by ↓of factor VIII b) Haemophilia B: It is due to ↓ of factor IX. c) Haemophilia C: It is due to ↓of factor XI. Manifestations many subcutaneous and submucosal hemorrhages (petichae) Excessive bleeding after mild trauma Investigations • prolonged bleeding time • normal clotting time • prolonged coagulation time • normal bleeding time Haemostatic Disorders Haemophilia Haemostatic Disorders Haemophilia Haemostatic Disorders Haemophilia Son of the last Tsar of Russia – Aleksy Romanow suffered from Hemophilia A Haemostatic Disorders Purpura Haemostatic Tests Haemostatic Tests Whole Blood Clotting Time It is the time needed by blood to form clot Procedure: -Clean the tip of the finger with an alcohol -Prick the finger tip with an automatic lancet -Note the time when blood first appears on the skin -Touch capillary tube to the drop of blood -Break gently 1cm of the tube at the end of 2 min, and every 30 sec these after When fibrin is formed between the two broken pieces of tube the coagulation or clotting time is noted Haemostatic Tests Whole Blood Clotting Time Normal Value: 4-8 min Causes of prolonged CT: 1. Haemophilia 2. Vit K deficiency 3. Liver diseases 4. Use of oral anticoagulants Haemostatic Tests Bleeding Time It is the time needed to stop bleeding from small injury Procedure: -Clean the earlobe with an alcohol -Prick the earlobe or tip of finger with an automatic lancet -Note the time when blood first appears on the skin -After half a minute (30sec) place the edge of the filter paper on the top of the drop of blood. Haemostatic Tests Bleeding Time Normal Value: 1-5 min Causes of prolonged BT: 1. Purpura 2. Platelets count deficiency 3. Von Willibrand disease 4. Disease of blood vessels. S K N A H T Dr. Abdel Aziz Hussein, Mansoura Faculty of Medicine