Genetic Drift and Gene Flow
... A founder effect occurs when a new colony is started by a few members of the original population. This small population size means that the colony may have: reduced genetic variation from the original population. a non-random sample of the genes in the original population. ...
... A founder effect occurs when a new colony is started by a few members of the original population. This small population size means that the colony may have: reduced genetic variation from the original population. a non-random sample of the genes in the original population. ...
Evolution Study Guide – Part I If natural selection is to take place
... 1. Stabilizing selection is the type of selection that favors average individuals in a population. 2. The allele frequency is the percentage of a particular allele in a population. 3. The alteration of allelic frequencies by chance is known as genetic drift. 4. The total number of genes present in a ...
... 1. Stabilizing selection is the type of selection that favors average individuals in a population. 2. The allele frequency is the percentage of a particular allele in a population. 3. The alteration of allelic frequencies by chance is known as genetic drift. 4. The total number of genes present in a ...
Chapter 16
... Variation and Gene Pools • Gene Pool :All genes (and diff’t alleles) present in a population • Relative frequency: how often an allele shows up in a gene pool • Evolution: is a group process “ any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population” ...
... Variation and Gene Pools • Gene Pool :All genes (and diff’t alleles) present in a population • Relative frequency: how often an allele shows up in a gene pool • Evolution: is a group process “ any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population” ...
Natural selection Differential survival or reproduction of individuals
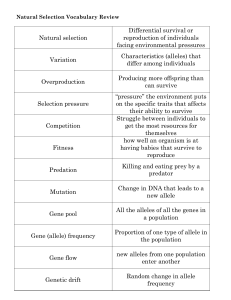
... Natural Selection Vocabulary Review ...
... Natural Selection Vocabulary Review ...
Nutritional Genomics
... The New Paradigm of Nutritional Genomics a. University programs b. Research Publications c. What’s Hot in Nutrition and Gene Science d. The Two Approaches ...
... The New Paradigm of Nutritional Genomics a. University programs b. Research Publications c. What’s Hot in Nutrition and Gene Science d. The Two Approaches ...
Evolution Bingo Review
... 6. _____________________ shows the geographically separated species may have descended from a common ancestor. 7. The strongest evidence for evolution and the best way to determine how closely species are related to each other is ________________________________________ (3 words). 8. A preserved rem ...
... 6. _____________________ shows the geographically separated species may have descended from a common ancestor. 7. The strongest evidence for evolution and the best way to determine how closely species are related to each other is ________________________________________ (3 words). 8. A preserved rem ...
LE - 7 - Genetic Engineering
... • By various methods (like particle guns) selected genes will combine with the natural DNA, therefore altering the original sequence. This phase of genetic engineering varies depending on the organism. ...
... • By various methods (like particle guns) selected genes will combine with the natural DNA, therefore altering the original sequence. This phase of genetic engineering varies depending on the organism. ...
Evo Notes 2b
... by only a small group of individuals – just by chance some rare alleles may be at high frequency; others may be missing – skew the gene pool of new population • human populations that started from small group of colonists • example: colonization of New World albino deer Seneca Army Depot ...
... by only a small group of individuals – just by chance some rare alleles may be at high frequency; others may be missing – skew the gene pool of new population • human populations that started from small group of colonists • example: colonization of New World albino deer Seneca Army Depot ...
Lesson Overview
... populations is mutations!! They occur randomly Only heritable mutations matter for evolution Other sources of variation include: 1. Genetic recombinationcrossing over and independent assortment in meiosis 2. Lateral gene transfer- (bacteria only) Bacteria swap plasmids between members of the same ge ...
... populations is mutations!! They occur randomly Only heritable mutations matter for evolution Other sources of variation include: 1. Genetic recombinationcrossing over and independent assortment in meiosis 2. Lateral gene transfer- (bacteria only) Bacteria swap plasmids between members of the same ge ...
A population
... phenotypes are more likely to survive and produce more offspring. Thus, passing traits to subsequent generations. Darwin’s idea was that resources are limited and that there is competition for those resources. Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. Population is the smallest unit in ...
... phenotypes are more likely to survive and produce more offspring. Thus, passing traits to subsequent generations. Darwin’s idea was that resources are limited and that there is competition for those resources. Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. Population is the smallest unit in ...
Population Genetics
... allele frequency in the original population. b) Founder effect may lead to reduced variability when a few individuals from a large population colonize an isolated habitat. ...
... allele frequency in the original population. b) Founder effect may lead to reduced variability when a few individuals from a large population colonize an isolated habitat. ...
Genetics
... •If either partner belongs to an ethnic group in which a genetic disorder occur frequently e.g. Sickle cell disease is common mainly in people whose families come from Africa, the Caribbean and eastern Mediterranean. •If there is a high rate of some forms of cancer within families •If the couple are ...
... •If either partner belongs to an ethnic group in which a genetic disorder occur frequently e.g. Sickle cell disease is common mainly in people whose families come from Africa, the Caribbean and eastern Mediterranean. •If there is a high rate of some forms of cancer within families •If the couple are ...
Activity 3: Mechanisms for Evolution
... frequency of certain alleles in the population. For instance, in the island scenario from the previous activity, what if two of the eleven individuals can overcome an infection (they carry the alleles to do this) that strikes all the people. However they decide to build a raft and leave the island. ...
... frequency of certain alleles in the population. For instance, in the island scenario from the previous activity, what if two of the eleven individuals can overcome an infection (they carry the alleles to do this) that strikes all the people. However they decide to build a raft and leave the island. ...
Introduction to How Designer Children Work
... When doctors first performed in vitro fertilization (IVF) in 1978, it gave many otherwise infertile couples a way to have a child of their own. IVF works by removing the eggs from the woman's uterus, fertilizing them in a laboratory and then, a few days later, transferring the fertilized egg, called ...
... When doctors first performed in vitro fertilization (IVF) in 1978, it gave many otherwise infertile couples a way to have a child of their own. IVF works by removing the eggs from the woman's uterus, fertilizing them in a laboratory and then, a few days later, transferring the fertilized egg, called ...
Genome variation informatics: SNP discovery, demographic
... mutations in a variety of new data types, representing both genetic and epigenetic changes ...
... mutations in a variety of new data types, representing both genetic and epigenetic changes ...
Logan Rayborns Biology CrosswordsM
... inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele. 4. assortment formation of random combinations of chromosomes in meiosis and of genes on different pairs of homologous chromosomes by the passage according to the laws of probability of one of ea ...
... inheritance in which one allele for a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele. 4. assortment formation of random combinations of chromosomes in meiosis and of genes on different pairs of homologous chromosomes by the passage according to the laws of probability of one of ea ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... directly into a person’s cells. For example, hemophilia might be treated by replacing the defective allele on the X chromosome. Some people are concerned about long-term effects of genetic engineering. For example, some people fear that genetically engineered crops may harm the environment or cause ...
... directly into a person’s cells. For example, hemophilia might be treated by replacing the defective allele on the X chromosome. Some people are concerned about long-term effects of genetic engineering. For example, some people fear that genetically engineered crops may harm the environment or cause ...
Wildlife Genetics: Concepts, Tools, Applications
... maternally inherited; thus, mitochondrial genes are haploid: they have only 1 form of the gene, not 2 as in nuclear genes). mtDNA accumulates mutations 5-10 times faster than nuclear genes, which is an important feature that it very useful for applied wildlife ecology (see pages 39 and 40 in Mills 2 ...
... maternally inherited; thus, mitochondrial genes are haploid: they have only 1 form of the gene, not 2 as in nuclear genes). mtDNA accumulates mutations 5-10 times faster than nuclear genes, which is an important feature that it very useful for applied wildlife ecology (see pages 39 and 40 in Mills 2 ...
Human Genetic Disorders
... Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about cloning. a. A clone has exactly the same genes as the organism from which it was produced. b. A cutting is one way to make a clone of an animal. c. It’s easier to clone an animal than it is to clone a plant. ...
... Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about cloning. a. A clone has exactly the same genes as the organism from which it was produced. b. A cutting is one way to make a clone of an animal. c. It’s easier to clone an animal than it is to clone a plant. ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.