Tracing the Paths of the First Americans
... earlier indications that the Paleoindians, the and her colleagues analyzed mtDNA ancestors of today’s Native Americans, stem and archaeological evidence to confrom a single Asian source population. But clude that these Beringian populations the data also suggest that this population may might have b ...
... earlier indications that the Paleoindians, the and her colleagues analyzed mtDNA ancestors of today’s Native Americans, stem and archaeological evidence to confrom a single Asian source population. But clude that these Beringian populations the data also suggest that this population may might have b ...
Genetic pollution
... A controversial term for uncontrolled Gene flow into Wild Populations . This is undesirable according to groups such as “Greenpeace” & “TRAFFIC”. ...
... A controversial term for uncontrolled Gene flow into Wild Populations . This is undesirable according to groups such as “Greenpeace” & “TRAFFIC”. ...
Forces of Evolutionary Change
... INCREASE genetic diversity in a population? Mutations and Gene Flow • Which forces of evolutionary change DECREASE genetic diversity in a population? Genetic Drift and Natural Selection ...
... INCREASE genetic diversity in a population? Mutations and Gene Flow • Which forces of evolutionary change DECREASE genetic diversity in a population? Genetic Drift and Natural Selection ...
05 Lecture Evolution 09
... in population and natural selection favors alleles suitable for new environment. 2) The sources of genetic variation are mutation and sexual recombination. 3) Forces that influence evolution include: natural selection, gene flow (migration), small population size + chance (loss of genetic variation ...
... in population and natural selection favors alleles suitable for new environment. 2) The sources of genetic variation are mutation and sexual recombination. 3) Forces that influence evolution include: natural selection, gene flow (migration), small population size + chance (loss of genetic variation ...
Understanding Human Diversity
... in the world”1. On page 1299 of this issue2, in a paper from the International HapMap Consortium, we find a detailed account of one of the primary reasons why there is no ‘normal’ human type. The human genome has about 10 million ‘polymorphisms’, defined as genetic variants in which the minor gene f ...
... in the world”1. On page 1299 of this issue2, in a paper from the International HapMap Consortium, we find a detailed account of one of the primary reasons why there is no ‘normal’ human type. The human genome has about 10 million ‘polymorphisms’, defined as genetic variants in which the minor gene f ...
Principal Investigator Dr Eleftheria Zeggini Address Wellcome Trust
... region of origin, occupational activity, HRT information and smoking habits. We would also like to request data on OA severity (Kellgren-Lawrence score, if available), age at OA diagnosis, and information on total joint replacement surgery including joint site, and age at surgery. The focus of our ...
... region of origin, occupational activity, HRT information and smoking habits. We would also like to request data on OA severity (Kellgren-Lawrence score, if available), age at OA diagnosis, and information on total joint replacement surgery including joint site, and age at surgery. The focus of our ...
Class Starter
... • This will make the individual ‘more fit’ and therefore more likely to survive in their environment and pass on their DNA to future ...
... • This will make the individual ‘more fit’ and therefore more likely to survive in their environment and pass on their DNA to future ...
Reproduction and Evolution Exam
... 16. A reproductive strategy in which an animal expends all of it’s energy in one suicidal event is a. budding b. hermaphroditism c. parthenogenesis. d. semelparity e. iteroparity 17. If meiosis did NOT occur in sexually reproducing organisms, a. mitosis would be sufficient. b. eggs would be haploid ...
... 16. A reproductive strategy in which an animal expends all of it’s energy in one suicidal event is a. budding b. hermaphroditism c. parthenogenesis. d. semelparity e. iteroparity 17. If meiosis did NOT occur in sexually reproducing organisms, a. mitosis would be sufficient. b. eggs would be haploid ...
Can a population of animals continue to reproduce without
... Can a population of animals continue to reproduce without limit? ...
... Can a population of animals continue to reproduce without limit? ...
Polygenic and Multifactoral Traits
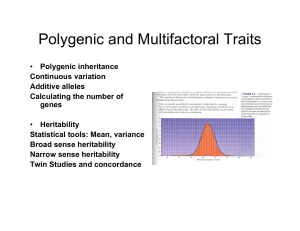
... variation vs discontinuous • Additive component • Distinct phenotypic classes • Quantitative traits: size, weight, height,IQ ...
... variation vs discontinuous • Additive component • Distinct phenotypic classes • Quantitative traits: size, weight, height,IQ ...
Genetic Drift
... Natural Selection How does natural selection work? Adaptation Selection of new beneficial traits according to selective pressures at the time Natural selection produces adaptation of an organism ...
... Natural Selection How does natural selection work? Adaptation Selection of new beneficial traits according to selective pressures at the time Natural selection produces adaptation of an organism ...
27_3 The Process of Evolution - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... e. Natural Selection i. The process by which some individuals produce more offspring than others ii. Evolution by natural selection requires: 1. Individual variation 2. Inheritance 3. Overproduction 4. Differential reproductive success iii. “fitness” in biology = the number of fertile offspring an ...
... e. Natural Selection i. The process by which some individuals produce more offspring than others ii. Evolution by natural selection requires: 1. Individual variation 2. Inheritance 3. Overproduction 4. Differential reproductive success iii. “fitness” in biology = the number of fertile offspring an ...
Name: AP Biology Driftworm Demo Evolution is the process by
... time (i.e., inherited), which is what really matters in evolution - long term change. The major forces/mechanisms of change implicit in evolution are mutations, recombination, migration (gene flow in & out of a population), non-random mating, natural selection & genetic drift. These forces cause cha ...
... time (i.e., inherited), which is what really matters in evolution - long term change. The major forces/mechanisms of change implicit in evolution are mutations, recombination, migration (gene flow in & out of a population), non-random mating, natural selection & genetic drift. These forces cause cha ...
Introduction to History of Life Biological evolution
... • The significance of this process of speciation is that the new species are likely to evolve independently from then on. • Some may give rise to yet other species, which ultimately may become exceedingly different from one another. • Successive speciation events, coupled with divergence, give rise ...
... • The significance of this process of speciation is that the new species are likely to evolve independently from then on. • Some may give rise to yet other species, which ultimately may become exceedingly different from one another. • Successive speciation events, coupled with divergence, give rise ...
Mechanisms of Non Mechanisms of Non
... alleles can enter population from other populations. This process leads to a migration load (the maintenance of deleterious alleles by migration). Migration load depends on the following: • Strength of selection on alleles • Rate of migration • Size of populations ...
... alleles can enter population from other populations. This process leads to a migration load (the maintenance of deleterious alleles by migration). Migration load depends on the following: • Strength of selection on alleles • Rate of migration • Size of populations ...
46556-2-12118
... observations n, precluding the direct application of classical multivariate techniques that start with a saturated model. Moreover, genetic effects emanating from discrete genotypes may act non-additively through allele dominance and/or mask each other between different loci, a phenomenon known as e ...
... observations n, precluding the direct application of classical multivariate techniques that start with a saturated model. Moreover, genetic effects emanating from discrete genotypes may act non-additively through allele dominance and/or mask each other between different loci, a phenomenon known as e ...
Population Genetics Sequence Diversity Molecular Evolution
... for HIV-1 is CCR-5. a 32-bp deletion mutation in the coding region of the human CCR5 gene has been found that results in an inactive protein. Homozygotes are highly resistant to HIV-1 infection. The allele is found predominantly on a single haplotype, consistent with the notion that it arose once in ...
... for HIV-1 is CCR-5. a 32-bp deletion mutation in the coding region of the human CCR5 gene has been found that results in an inactive protein. Homozygotes are highly resistant to HIV-1 infection. The allele is found predominantly on a single haplotype, consistent with the notion that it arose once in ...
Human Genetic Disorders
... There is no cure but there are medications to lesson the pain and other symtoms. ...
... There is no cure but there are medications to lesson the pain and other symtoms. ...
Paleoanthropologists use models to show humans may
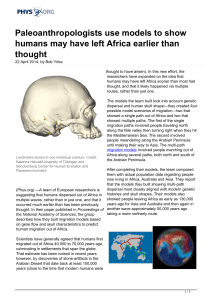
... dispersal and human skull shape—they created four possible model scenarios of migration—two that showed a single path out of Africa and two that showed multiple paths. The first of the single migration paths involved people traveling north along the Nile valley then turning right when they hit the M ...
... dispersal and human skull shape—they created four possible model scenarios of migration—two that showed a single path out of Africa and two that showed multiple paths. The first of the single migration paths involved people traveling north along the Nile valley then turning right when they hit the M ...
CH 13 * Microevolution - Chadwick School: Haiku Learning
... The Bottleneck Effect – The bottleneck effect • Is an example of genetic drift. • Results from a drastic reduction in population size. ...
... The Bottleneck Effect – The bottleneck effect • Is an example of genetic drift. • Results from a drastic reduction in population size. ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.