Worksheet - Molecular Evolution
... passed on to the next generation over time (i.e., inherited), which is what really matters in evolution - long term change. The major forces/mechanisms of change implicit in evolution are mutations, recombination, migration (gene flow in & out of a population), non-random mating, natural selection & ...
... passed on to the next generation over time (i.e., inherited), which is what really matters in evolution - long term change. The major forces/mechanisms of change implicit in evolution are mutations, recombination, migration (gene flow in & out of a population), non-random mating, natural selection & ...
Ch 16 Summary
... of evolutionary change. In small populations, alleles can become more or less common simply by chance. This kind of change in allele frequency is called genetic drift. It occurs when individuals with a particular allele leave more descendants than other individuals, just by chance. Over time, this c ...
... of evolutionary change. In small populations, alleles can become more or less common simply by chance. This kind of change in allele frequency is called genetic drift. It occurs when individuals with a particular allele leave more descendants than other individuals, just by chance. Over time, this c ...
MedicalAspectsVariations
... • searching for markers with “significant” marker allele frequency differences between cases and controls; these marker signify regions of possible causative alleles ...
... • searching for markers with “significant” marker allele frequency differences between cases and controls; these marker signify regions of possible causative alleles ...
Biological information
... have lately been shown to take place for at least half of the genes among human and other eukaryotes. Differential splicing is probably more the rule than the exception. ...
... have lately been shown to take place for at least half of the genes among human and other eukaryotes. Differential splicing is probably more the rule than the exception. ...
Chapter 17 Review ppt
... day, 10 individuals with the genotype bb leave the area and cross a river into a new habitat. Which of these processes has changed the population’s gene pool? ...
... day, 10 individuals with the genotype bb leave the area and cross a river into a new habitat. Which of these processes has changed the population’s gene pool? ...
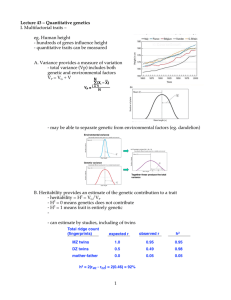
1 Lecture 43 â Quantitative genetics I. Multifactorial traits â eg
... - H2 = 0 means genetics does not contribute - H2 = 1 means trait is entirely genetic - can estimate by studies, including of twins ...
... - H2 = 0 means genetics does not contribute - H2 = 1 means trait is entirely genetic - can estimate by studies, including of twins ...
Genes and Health: Moving Beyond Race
... Discuss with students the roles genetics and environment play in many diseases. Use the following questions to generate a discussion. • What environmental conditions might play a role in a person’s tendency to contract a disease? (Answers may vary and could include: air pollution, water pollution, ...
... Discuss with students the roles genetics and environment play in many diseases. Use the following questions to generate a discussion. • What environmental conditions might play a role in a person’s tendency to contract a disease? (Answers may vary and could include: air pollution, water pollution, ...
Human Genome Project - College Heights Secondary School
... • Disseminate genome information • Consider ethical, legal, and social issues associated with this research ...
... • Disseminate genome information • Consider ethical, legal, and social issues associated with this research ...
Goal 3.05 Examine the Theory of Evolution by Natural
... Goal 3.04: Chapter 13 and 14 Genetic Engineering and The Human Genome Project 1. The Human Genome Project is an attempt to SEQUENCE HUMAN DNA. One of the goals is to help people with genetic disorders by replacing a faulty gene; this is calledGENE THERAPY 2. Selective breeding: 2 types are HYBRIDIZA ...
... Goal 3.04: Chapter 13 and 14 Genetic Engineering and The Human Genome Project 1. The Human Genome Project is an attempt to SEQUENCE HUMAN DNA. One of the goals is to help people with genetic disorders by replacing a faulty gene; this is calledGENE THERAPY 2. Selective breeding: 2 types are HYBRIDIZA ...
Genetics Study Notes
... plants on the island. One day there was a huge volcanic eruption which killed many, but not all of the birds on the island. A huge mountain formed which caused one side of the island to turn into a desert, with very little rainfall. Only the hardiest of plants survived and they only produced hard se ...
... plants on the island. One day there was a huge volcanic eruption which killed many, but not all of the birds on the island. A huge mountain formed which caused one side of the island to turn into a desert, with very little rainfall. Only the hardiest of plants survived and they only produced hard se ...
12 Cons Bio 2010
... 1. Biological diversity has many components (ecological, genetic, geographic). 2. Extinction is natural but its present rate is not. 3. Five types of human activities have accelerated the rate of extinction. 4. Rarity has multiple components (Geographic range, habitat specificity, local abundance). ...
... 1. Biological diversity has many components (ecological, genetic, geographic). 2. Extinction is natural but its present rate is not. 3. Five types of human activities have accelerated the rate of extinction. 4. Rarity has multiple components (Geographic range, habitat specificity, local abundance). ...
population genetics chapter 13
... What is the process by which one species splits into two or more species is a group of organisms of the same species that live in a localized place at the same time Genetic drift can result from Aside from founder effect, genetic drift can also result from this is the relative frequency of an allele ...
... What is the process by which one species splits into two or more species is a group of organisms of the same species that live in a localized place at the same time Genetic drift can result from Aside from founder effect, genetic drift can also result from this is the relative frequency of an allele ...
Chapter 16 Evolution of Populations Reading ONLY
... of evolutionary change. In small populations, alleles can become more or less common simply by chance. This kind of change in allele frequency is called genetic drift. It occurs when individuals with a particular allele leave more descendants than other individuals, just by chance. Over time, this c ...
... of evolutionary change. In small populations, alleles can become more or less common simply by chance. This kind of change in allele frequency is called genetic drift. It occurs when individuals with a particular allele leave more descendants than other individuals, just by chance. Over time, this c ...
1, 2, 5, 6, 7 Time: 08:00
... biological evolution. AL-COS 2015 14. Analyze and interpret data to evaluate adaptations resulting from natural and artificial selection that may cause changes in populations over time ...
... biological evolution. AL-COS 2015 14. Analyze and interpret data to evaluate adaptations resulting from natural and artificial selection that may cause changes in populations over time ...
natural selection
... point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total number of the alleles from the gene pool. ...
... point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total number of the alleles from the gene pool. ...
Defining evolution - Our eclass community
... traits being lost from small populations. unusual traits, not commonly found in the parent population, and that are often nonadaptive, becoming established. ...
... traits being lost from small populations. unusual traits, not commonly found in the parent population, and that are often nonadaptive, becoming established. ...
Document
... •When Science Takes the Witness Stand - Peter Neufeld (Innocence Project) - MAIN ARTICLE •The DNA Detectives (Newsweek) •Science on Trial in The Courtroom - Chapter 11 Introduction to Forensic DNA Analysis •Population & Evolutionary Genetics - Chapter 29 Introduction to Genetics •American Society of ...
... •When Science Takes the Witness Stand - Peter Neufeld (Innocence Project) - MAIN ARTICLE •The DNA Detectives (Newsweek) •Science on Trial in The Courtroom - Chapter 11 Introduction to Forensic DNA Analysis •Population & Evolutionary Genetics - Chapter 29 Introduction to Genetics •American Society of ...
The Margot Forde Forage Germplasm Centre
... dispatch 3,000 seed lots pa replenish 150-200 populations pa maintain database of 100,000 entries with www access back-up seed samples at -20° C ...
... dispatch 3,000 seed lots pa replenish 150-200 populations pa maintain database of 100,000 entries with www access back-up seed samples at -20° C ...
DISRUPTING GENETIC EQUILIBRIUM
... Gene Pool = the total genetic information stored in a population Adapting to new selection factors can only use existing genes found in the population Allele Frequency = the number of a certain allele in the population / the total number of all alleles The phenotype frequencies can change between ge ...
... Gene Pool = the total genetic information stored in a population Adapting to new selection factors can only use existing genes found in the population Allele Frequency = the number of a certain allele in the population / the total number of all alleles The phenotype frequencies can change between ge ...
File - Lucinda Supernavage
... a)Bottleneck effect may lead to reduced genetic variability following some large disturbance that removes a large portion of the population. b) Founder effect may lead to reduced variability when a few individuals from a large population colonize an isolated habitat. ...
... a)Bottleneck effect may lead to reduced genetic variability following some large disturbance that removes a large portion of the population. b) Founder effect may lead to reduced variability when a few individuals from a large population colonize an isolated habitat. ...
Genetic variation - Biology Courses Server
... Rates of significantly deleterious mutation have been estimated at 0.01-1 mutation per genome per generation, in various different species. A small minority of mutations are beneficial, at least under some conditions. Some of these are maintained as polymorphisms by selection. But most polymorphism ...
... Rates of significantly deleterious mutation have been estimated at 0.01-1 mutation per genome per generation, in various different species. A small minority of mutations are beneficial, at least under some conditions. Some of these are maintained as polymorphisms by selection. But most polymorphism ...
Populations evolution
... doesn’t evolve and genetic equilibrium has been reached. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium: condition in which a population’s allele frequencies for a given trait do not change ...
... doesn’t evolve and genetic equilibrium has been reached. Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium: condition in which a population’s allele frequencies for a given trait do not change ...
Chapter 23 Evolution of Populations
... • (2) the central role of natural selection as the most important mechanism of evolution • (3) the idea of gradualism to explain how large changes can evolve as an accumulation of small changes over long periods of time ...
... • (2) the central role of natural selection as the most important mechanism of evolution • (3) the idea of gradualism to explain how large changes can evolve as an accumulation of small changes over long periods of time ...
Part_2
... of genes or genomic patterns with human brain evolution is only tentative and based on suggestive evidence," says Bruce Lahn, a human geneticist at the University of Chicago, Illinois. "The situation may not change anytime soon due to the complexity of the questions and because we can't redo the exp ...
... of genes or genomic patterns with human brain evolution is only tentative and based on suggestive evidence," says Bruce Lahn, a human geneticist at the University of Chicago, Illinois. "The situation may not change anytime soon due to the complexity of the questions and because we can't redo the exp ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.