Evolution Review Questions
... 22. If you were to plot the height of everyone in your class on a graph, the values would probably form a hill-shaped curve called a(n) ____________________ ______________________. 23. Sometimes, individuals prefer to mate with others that live nearby or are of their own phenotype, a situation calle ...
... 22. If you were to plot the height of everyone in your class on a graph, the values would probably form a hill-shaped curve called a(n) ____________________ ______________________. 23. Sometimes, individuals prefer to mate with others that live nearby or are of their own phenotype, a situation calle ...
Integration of chemical-genetic and genetic interaction data links
... • Confirmed interactions by serial-dilution spot assays to minimize false positives • Assessed false-negatives by comparing results for rapamycin screen to previously published ...
... • Confirmed interactions by serial-dilution spot assays to minimize false positives • Assessed false-negatives by comparing results for rapamycin screen to previously published ...
Meiosis Poster Project - Mercer Island School District
... Use stickers with letters to represent the different genes on the chromosomes. o The long homologous pair has the gene for flower color (R/r). Long chromosome 1 has the red flower color gene form (R) Long chromosome 2 has the white flower color gene form (r) o The short homologous pair has the gene ...
... Use stickers with letters to represent the different genes on the chromosomes. o The long homologous pair has the gene for flower color (R/r). Long chromosome 1 has the red flower color gene form (R) Long chromosome 2 has the white flower color gene form (r) o The short homologous pair has the gene ...
What is Evolution?
... 142/546 = .26 which represents q2 or gg In order to get the homozygous dominant & heterozygous we need to use the p + q = 1 equation. q2 = .26 take the square root of each side to get q which is .51 ...
... 142/546 = .26 which represents q2 or gg In order to get the homozygous dominant & heterozygous we need to use the p + q = 1 equation. q2 = .26 take the square root of each side to get q which is .51 ...
First debate of 2008
... If environment didn't play a part in determining an individual's traits and behaviors, then identical twins should, theoretically, be exactly the same in all respects, even if reared apart. But a number of studies show that they are never exactly alike, even though they are remarkably similar in mos ...
... If environment didn't play a part in determining an individual's traits and behaviors, then identical twins should, theoretically, be exactly the same in all respects, even if reared apart. But a number of studies show that they are never exactly alike, even though they are remarkably similar in mos ...
Russian Academy of Sciences, Kurchatov Sq.46,
... Figure l. Arrangement of genetic loci in the Pgd-KIO region of the Drosophila X chromosome. The orientation is from centromere-distal (left) to centromere-proximal (right). Added or changed loci are marked by asterisks (see text). Tolchkov 1985, Dros. Inf. Servo 61 :24; Alatortsev, V.E., LA. Kramero ...
... Figure l. Arrangement of genetic loci in the Pgd-KIO region of the Drosophila X chromosome. The orientation is from centromere-distal (left) to centromere-proximal (right). Added or changed loci are marked by asterisks (see text). Tolchkov 1985, Dros. Inf. Servo 61 :24; Alatortsev, V.E., LA. Kramero ...
UNIT PLAN- DNA and MITOSIS
... understanding this concept: 1. Students know why natural selection acts on the phenotype rather than the genotype of an organism. 2. Students know why alleles that are lethal in a homozygous individual may be carried in a heterozygote and thus maintained in a gene pool. 3. Students know new mutation ...
... understanding this concept: 1. Students know why natural selection acts on the phenotype rather than the genotype of an organism. 2. Students know why alleles that are lethal in a homozygous individual may be carried in a heterozygote and thus maintained in a gene pool. 3. Students know new mutation ...
Slide 1
... What Anthropologists Knew • No dramatic genetic discontinuities among humans • Little genetic variation when compared to other organisms young species with a single common origin in Africa ...
... What Anthropologists Knew • No dramatic genetic discontinuities among humans • Little genetic variation when compared to other organisms young species with a single common origin in Africa ...
Assignment1
... The sequences on the following page are part of the Cytochrome Oxidase Subunit I gene sequence (known as COX1 or CO1) from the mitochondrial genome of Gorilla, Human and Dog. There are no insertions and deletions in this region. The gaps have been put into the alignment to indicate the positions of ...
... The sequences on the following page are part of the Cytochrome Oxidase Subunit I gene sequence (known as COX1 or CO1) from the mitochondrial genome of Gorilla, Human and Dog. There are no insertions and deletions in this region. The gaps have been put into the alignment to indicate the positions of ...
C1. The first principle is that there is genetic variation within natural
... transition of fossil forms. The transition period in which environment pressure and genetic changes cause a previous species to evolve into a new species is thought to be so short that few, if any, of the transitional members would be preserved as fossils. Therefore, the fossil record primarily cont ...
... transition of fossil forms. The transition period in which environment pressure and genetic changes cause a previous species to evolve into a new species is thought to be so short that few, if any, of the transitional members would be preserved as fossils. Therefore, the fossil record primarily cont ...
E: Acronyms and Glossary
... insurance policy goes into effect and commonly defined as one which would cause an ordinarily prudent person to seek diagnosis, care, or treatment. Prenatal testing: Assay performed after conception but before birth-usually via amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling-to assess the status of the f ...
... insurance policy goes into effect and commonly defined as one which would cause an ordinarily prudent person to seek diagnosis, care, or treatment. Prenatal testing: Assay performed after conception but before birth-usually via amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling-to assess the status of the f ...
Document
... transition of fossil forms. The transition period in which environment pressure and genetic changes cause a previous species to evolve into a new species is thought to be so short that few, if any, of the transitional members would be preserved as fossils. Therefore, the fossil record primarily cont ...
... transition of fossil forms. The transition period in which environment pressure and genetic changes cause a previous species to evolve into a new species is thought to be so short that few, if any, of the transitional members would be preserved as fossils. Therefore, the fossil record primarily cont ...
HIV-1
... • Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) have invaded the germ-line cells of every species of vertebrate and are transmitted, like genes, as part of normal host reproduction. • 8% of the human genome consists of HERVs. • Host genomes are continually evolving new regulatory mechanisms to silence the mutageni ...
... • Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) have invaded the germ-line cells of every species of vertebrate and are transmitted, like genes, as part of normal host reproduction. • 8% of the human genome consists of HERVs. • Host genomes are continually evolving new regulatory mechanisms to silence the mutageni ...
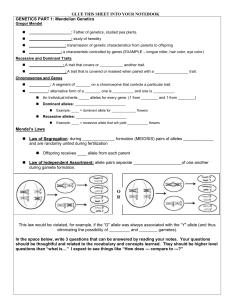
Fill-in Handout - Liberty Union High School District
... Law of Independent Assortment: allele pairs separate _____________________of one another during gamete formation. ...
... Law of Independent Assortment: allele pairs separate _____________________of one another during gamete formation. ...
Gene Mapping Linked traits can be unlinked if crossing over occurs
... individuals both heterozygous for the trait Dihybrid crosses involve two individuals both heterozygous for each of two traits A punnet square is a useful way to determine the genotypes and phenotypes from one and two trait crosses A test cross is a method for determining the genotype of an individua ...
... individuals both heterozygous for the trait Dihybrid crosses involve two individuals both heterozygous for each of two traits A punnet square is a useful way to determine the genotypes and phenotypes from one and two trait crosses A test cross is a method for determining the genotype of an individua ...
BIOLOGY STANDARD 4
... Co-dominant - a genetic pattern where the pair of alleles is equally expressed in the offspring for example a black chicken mated with a white chicken produce speckled offspring Cystic fibrosis - a genetic disorder caused by a recessive trait carried on the autosomes that caused mucus build up in th ...
... Co-dominant - a genetic pattern where the pair of alleles is equally expressed in the offspring for example a black chicken mated with a white chicken produce speckled offspring Cystic fibrosis - a genetic disorder caused by a recessive trait carried on the autosomes that caused mucus build up in th ...
genetics
... Greater variation within the species makes a population better suited to adaptation to changes in the environment. ...
... Greater variation within the species makes a population better suited to adaptation to changes in the environment. ...
WHAT WILL YOU KNOW? - Napa Valley College
... Variation of a gene or any of the possible forms in which a gene for a particular trait can occur Effects of variations vary greatly from causing lifethreatening conditions to having no detectable effect at all ...
... Variation of a gene or any of the possible forms in which a gene for a particular trait can occur Effects of variations vary greatly from causing lifethreatening conditions to having no detectable effect at all ...
Genes
... Variation of a gene or any of the possible forms in which a gene for a particular trait can occur Effects of variations vary greatly from causing lifethreatening conditions to having no detectable effect at all ...
... Variation of a gene or any of the possible forms in which a gene for a particular trait can occur Effects of variations vary greatly from causing lifethreatening conditions to having no detectable effect at all ...
A Case Study and Meta-Analysis of Type 2 Diabetes Research
... explain the heighted risk of T2D among those expressing rs12255372 if the mutation is, in fact, deleterious with respect to that function. Furthermore, another thread of research has emerged out of Iceland and Germany in 2006 concerning the association between rs7903146 and heightened risk of type 2 ...
... explain the heighted risk of T2D among those expressing rs12255372 if the mutation is, in fact, deleterious with respect to that function. Furthermore, another thread of research has emerged out of Iceland and Germany in 2006 concerning the association between rs7903146 and heightened risk of type 2 ...
geneflow - International Food Safety Consultancy
... > some way that might be important for its survival in some habitats or for > other organisms that depend on them for their survival," says Haygood. "The > potential ramifications are huge and diverse." > The research team starts with a simple model, where a wild population of > large and constant s ...
... > some way that might be important for its survival in some habitats or for > other organisms that depend on them for their survival," says Haygood. "The > potential ramifications are huge and diverse." > The research team starts with a simple model, where a wild population of > large and constant s ...
sheet_29
... some genes on Y chromosome and some genes on X chromosome. ●Homozygous: the same two alleles. ●Heterozygous: different alleles. ●Hemizygous: one allele only, Where can we find it? It's found on the x-chromosome , because only one xchromosome is active while the other is inactivated. ●Genotype: t ...
... some genes on Y chromosome and some genes on X chromosome. ●Homozygous: the same two alleles. ●Heterozygous: different alleles. ●Hemizygous: one allele only, Where can we find it? It's found on the x-chromosome , because only one xchromosome is active while the other is inactivated. ●Genotype: t ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.