If you have BRCA in the family (England and Wales)
... My maternal/paternal (select one) mother/father/grandmother/grandfather/uncle/aunt (select one) is a BRCA1/2 gene mutation carrier and there is a strong possibility that this gene mutation will have been passed on to me. According to NHS England policy E01/P/b, Clinical Commissioning Policy: Genetic ...
... My maternal/paternal (select one) mother/father/grandmother/grandfather/uncle/aunt (select one) is a BRCA1/2 gene mutation carrier and there is a strong possibility that this gene mutation will have been passed on to me. According to NHS England policy E01/P/b, Clinical Commissioning Policy: Genetic ...
Lecture notes for lecture 4. This lecture covers chapters 6 and 7 in
... I’m not worried about you understanding the details here, just the general idea that mutations can range from the very minor to the radically different. - Another source of variation in sexual organisms is recombination. This occurs in meosis when the two copies of the same chromosome (one from each ...
... I’m not worried about you understanding the details here, just the general idea that mutations can range from the very minor to the radically different. - Another source of variation in sexual organisms is recombination. This occurs in meosis when the two copies of the same chromosome (one from each ...
Lecture 9
... nature (otherwise evolution would not occur). • Organisms are subject to mutations, selective forces and they move about, or the allele frequencies may be different in males and females. • Gene frequencies are constantly changing in a population, but the effects of these processes can be assessed by ...
... nature (otherwise evolution would not occur). • Organisms are subject to mutations, selective forces and they move about, or the allele frequencies may be different in males and females. • Gene frequencies are constantly changing in a population, but the effects of these processes can be assessed by ...
Scylla and Charybdis - Minority Health Project
... This assumes that the environmental influences on the gene’s expression are the same in each group. However can we assume that safely in the US? ...
... This assumes that the environmental influences on the gene’s expression are the same in each group. However can we assume that safely in the US? ...
11.1. Introducing Gregor Mendel
... were different, offspring would possess traits intermediate between those of parents. • Found to be incorrect by Mendel!! ...
... were different, offspring would possess traits intermediate between those of parents. • Found to be incorrect by Mendel!! ...
Unit 3 Evolution Jeopardy 1
... Grade 11 University Biology – Unit 3 Evolution – Jeopardy 1 Darwin ...
... Grade 11 University Biology – Unit 3 Evolution – Jeopardy 1 Darwin ...
Name: Hour: ______ UNIT 2 – Genetics and Diversity Study Guide
... ii. What is a behavioral adaptation of a squirrel, and how does it help the squirrel survive and reproduce? ...
... ii. What is a behavioral adaptation of a squirrel, and how does it help the squirrel survive and reproduce? ...
ppt
... Relative fitness is a function of frequency in the population Negative frequency-dependence: fitness is negatively correlated with frequency Should maintain variation in the population Examples include predator-prey interactions, pollinatorfloral interactions, and differential use of nutrients b ...
... Relative fitness is a function of frequency in the population Negative frequency-dependence: fitness is negatively correlated with frequency Should maintain variation in the population Examples include predator-prey interactions, pollinatorfloral interactions, and differential use of nutrients b ...
Evidence of the Past
... He learned from plant and animal breeders. They could select for desirable traits by picking what animals will breed together. ...
... He learned from plant and animal breeders. They could select for desirable traits by picking what animals will breed together. ...
Chapter 16 notes
... ◦ Representation of all the alleles of all the genes within a population Relative frequency- How often something happens divided by all outcomes. Example: Your team has won 9 games from a total of 12 games played: the Frequency of winning is 9. the Relative Frequency of winning is 9/12 = 75% ...
... ◦ Representation of all the alleles of all the genes within a population Relative frequency- How often something happens divided by all outcomes. Example: Your team has won 9 games from a total of 12 games played: the Frequency of winning is 9. the Relative Frequency of winning is 9/12 = 75% ...
Document
... Like random mating, condition applies only to the locus under study. Genes are unlinked because of recombination or because they assort independently on different chromosomes. ...
... Like random mating, condition applies only to the locus under study. Genes are unlinked because of recombination or because they assort independently on different chromosomes. ...
Theories of Evolution
... Beneficial mutations give: rise to new genetic traits (adaptive traits) that give an organism an advantage in a changing environment and produce more offspring with those traits - natural selection. Through time these adaptive traits become more prevalent in a population. Evolution is the change in ...
... Beneficial mutations give: rise to new genetic traits (adaptive traits) that give an organism an advantage in a changing environment and produce more offspring with those traits - natural selection. Through time these adaptive traits become more prevalent in a population. Evolution is the change in ...
Psych8_Lecture_Ch02use
... • In each cell, some genes are expressed, or activated in some way, at any point in time and others are not. • Gene expression is controlled by the biochemical environment inside the cell, which is influenced by the organism’s: ...
... • In each cell, some genes are expressed, or activated in some way, at any point in time and others are not. • Gene expression is controlled by the biochemical environment inside the cell, which is influenced by the organism’s: ...
Evolution Review
... Two species of sea urchin release their gametes at the same time, but crossspecific fertilization does not occur. Two species of orchid have different length nectar tubes and are pollinated by different species of moths. Two species of mayflies emerge during different weeks in springtime. Two specie ...
... Two species of sea urchin release their gametes at the same time, but crossspecific fertilization does not occur. Two species of orchid have different length nectar tubes and are pollinated by different species of moths. Two species of mayflies emerge during different weeks in springtime. Two specie ...
Solution
... 2 Genetic drift is due to random _____ effects in the formation of successive generations. 5 The hip bone. 10 A location where australopithecines fossils were found. 11 The jaw bone. 12 A hominin species that lived in Europe during the last Ice Age. 13 Gene _____ is the transfer of genes from one po ...
... 2 Genetic drift is due to random _____ effects in the formation of successive generations. 5 The hip bone. 10 A location where australopithecines fossils were found. 11 The jaw bone. 12 A hominin species that lived in Europe during the last Ice Age. 13 Gene _____ is the transfer of genes from one po ...
Fundamentals of Lifespan Development
... Homozygous – Displays inherited trait because the alleles from both parents are alike Heterozygous – The relationship between dominant and recessive relationships determine the phenotype Incomplete Dominance – A pattern of inheritance in which both alleles are expressed in the phenotype, resulting i ...
... Homozygous – Displays inherited trait because the alleles from both parents are alike Heterozygous – The relationship between dominant and recessive relationships determine the phenotype Incomplete Dominance – A pattern of inheritance in which both alleles are expressed in the phenotype, resulting i ...
Chapter 6.1 Trashketball
... 9. Those with helpful traits survive to the next generation A. Adaptation B. Competition C. Variation D. Selection ...
... 9. Those with helpful traits survive to the next generation A. Adaptation B. Competition C. Variation D. Selection ...
Biology 2002 - Spring Branch ISD
... 2. In the theory of evolution, the term adaptation refers to random genetic changes in the DNA code of an organism, which increases an organism's ability to survive. (We often use the term adaptation incorrectly. For example - "Johnny adapted to the cold climate when he moved to Alaska." But since t ...
... 2. In the theory of evolution, the term adaptation refers to random genetic changes in the DNA code of an organism, which increases an organism's ability to survive. (We often use the term adaptation incorrectly. For example - "Johnny adapted to the cold climate when he moved to Alaska." But since t ...
Charles Darwin and Natural Selection
... bodies of dolphins and sharks. • The fins would be an example of analogous structures. ...
... bodies of dolphins and sharks. • The fins would be an example of analogous structures. ...
Unit 6: Evolution
... 5. Work out these practice problems. Find both the gene and genotype frequencies: a. In Drosophilia, the allele for normal length wings is dominant over the allele for vestigial wings. In a population of 1,000 individuals, 160 show the recessive phenotype. b. The allele for the hair pattern called " ...
... 5. Work out these practice problems. Find both the gene and genotype frequencies: a. In Drosophilia, the allele for normal length wings is dominant over the allele for vestigial wings. In a population of 1,000 individuals, 160 show the recessive phenotype. b. The allele for the hair pattern called " ...
Microevolution: Unique Gene Pools
... Artificial Selection When humans manipulate a gene pool it is called artificial selection. There are often consequences involved in such manipulations. For example in agriculture, farmers try to increase crop production, which may lead to many farmers growing only one variety of a particular crop s ...
... Artificial Selection When humans manipulate a gene pool it is called artificial selection. There are often consequences involved in such manipulations. For example in agriculture, farmers try to increase crop production, which may lead to many farmers growing only one variety of a particular crop s ...
What observations did Darwin make that lead him to the
... 24. What is the value of classical taxonomy in this age of phylogenetics? 25. Explain how scientific names are generated. What is the value in this system? 26. How do phylogenetic trees and cladograms illustrate relatedness? How does this relate to speciation? 27. Describe a phylogenetic tree. What ...
... 24. What is the value of classical taxonomy in this age of phylogenetics? 25. Explain how scientific names are generated. What is the value in this system? 26. How do phylogenetic trees and cladograms illustrate relatedness? How does this relate to speciation? 27. Describe a phylogenetic tree. What ...
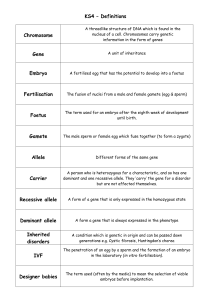
Definitions
... A threadlike structure of DNA which is found in the nucleus of a cell. Chromosomes carry genetic information in the form of genes ...
... A threadlike structure of DNA which is found in the nucleus of a cell. Chromosomes carry genetic information in the form of genes ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.