Machine Evolution
... – Crossover (1-point) • A crossover point is selected at random and parts of the two parent chromosomes are swapped to create two offspring with a probability which is called crossover rate. ...
... – Crossover (1-point) • A crossover point is selected at random and parts of the two parent chromosomes are swapped to create two offspring with a probability which is called crossover rate. ...
Power Point 2 - G. Holmes Braddock
... A mutation may result in a phenotypic change if the mutation occurs at a point on the gene that determines the phenotype. Mutations don’t always result in phenotypic change. Phenotypic change is mostly seen when looking into evolution Evolution is the change of a species over time ...
... A mutation may result in a phenotypic change if the mutation occurs at a point on the gene that determines the phenotype. Mutations don’t always result in phenotypic change. Phenotypic change is mostly seen when looking into evolution Evolution is the change of a species over time ...
The making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation
... switch, a stretch of noncoding DNA sequence that functions to turn genes on or off. Mutations in gene switches that control developmental genes are an important evolutionary mechanism responsible for the diversity of animal forms. ...
... switch, a stretch of noncoding DNA sequence that functions to turn genes on or off. Mutations in gene switches that control developmental genes are an important evolutionary mechanism responsible for the diversity of animal forms. ...
Chapter 4: Evolution and Extinction
... o Molecular structure of DNA was determined by Watson and Crick (1950s) Natural selection acts on mutations, coupled with genetic recombination, to produce evolutionary change that results in new species 4.7 Evidence for Natural Selection Since Darwin’s time a number of well-documented cases of ...
... o Molecular structure of DNA was determined by Watson and Crick (1950s) Natural selection acts on mutations, coupled with genetic recombination, to produce evolutionary change that results in new species 4.7 Evidence for Natural Selection Since Darwin’s time a number of well-documented cases of ...
Print Name: UNR I.D. Number: BIOL 191 SPRING 2005 Midterm 1
... 6) Haldane’s rule of speciation: states that in crosses between individuals from different populations or species, it is the heterogametic sex that is more likely to be inviable or infertile (or exhibit reduced viability or fertility) (5 points). Males are the heterogametic sex in mammals and most i ...
... 6) Haldane’s rule of speciation: states that in crosses between individuals from different populations or species, it is the heterogametic sex that is more likely to be inviable or infertile (or exhibit reduced viability or fertility) (5 points). Males are the heterogametic sex in mammals and most i ...
discov5_lecppt_Ch17
... acts differently on two populations, they may emerge as two new species descended from one ancestral population • Microevolution focuses on evolutionary changes that occur over relatively short periods of time • Macroevolution studies the history of life from the perspective of the formation and ext ...
... acts differently on two populations, they may emerge as two new species descended from one ancestral population • Microevolution focuses on evolutionary changes that occur over relatively short periods of time • Macroevolution studies the history of life from the perspective of the formation and ext ...
Evol unit: part 1
... environmental pressure to change. 2. Stabilizing selection eliminates the extremes and reduces variation 3. Disruptive selection selects against the average and favors the extremes ...
... environmental pressure to change. 2. Stabilizing selection eliminates the extremes and reduces variation 3. Disruptive selection selects against the average and favors the extremes ...
Evolution of Populations
... • All members of a population can interbreed, they share a common group of genes, called a gene pool. – A gene pool is the combined genetic information of all the members of a particular population. • Typically contains two or more alleles—or forms of a certain gene—for each inheritable trait. ...
... • All members of a population can interbreed, they share a common group of genes, called a gene pool. – A gene pool is the combined genetic information of all the members of a particular population. • Typically contains two or more alleles—or forms of a certain gene—for each inheritable trait. ...
Mutations II
... • Since E. coli’s genome is 4.6 x 106 base pairs, this works out to one mutation every 2442 generations ...
... • Since E. coli’s genome is 4.6 x 106 base pairs, this works out to one mutation every 2442 generations ...
Evolution Review - Milan Area Schools
... Lamarck – _____________ _____________(not determined by genes) passed on to offspring. (Theory replaced by Wallace and Darwin) B. Natural Selection i. Alfred Wallace – contemporary of Darwin, proposed natural selection theory just prior to Darwin. ii. Charles Darwin – credited with theory of natural ...
... Lamarck – _____________ _____________(not determined by genes) passed on to offspring. (Theory replaced by Wallace and Darwin) B. Natural Selection i. Alfred Wallace – contemporary of Darwin, proposed natural selection theory just prior to Darwin. ii. Charles Darwin – credited with theory of natural ...
Evolution PowerPoint
... Describe how Mutations Occur • Describe the molecular processes (e.g., insertion, deletion, substitution) and/or environmental factors (e.g., UV radiation in sunlight) by which mutations can occur. ...
... Describe how Mutations Occur • Describe the molecular processes (e.g., insertion, deletion, substitution) and/or environmental factors (e.g., UV radiation in sunlight) by which mutations can occur. ...
Intro to Evolution updated 10
... Natural Selection – best adapted organisms survive and pass on their traits, population changes over time ◦ Fitness ...
... Natural Selection – best adapted organisms survive and pass on their traits, population changes over time ◦ Fitness ...
Notes Chapter 16 - Spring Branch ISD
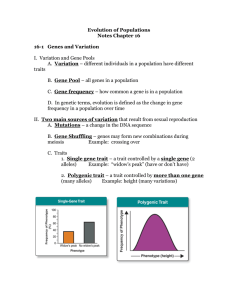
... C. Gene frequency – how common a gene is in a population D. In genetic terms, evolution is defined as the change in gene frequency in a population over time II. Two main sources of variation that result from sexual reproduction A. Mutations – a change in the DNA sequence B. Gene Shuffling – genes ma ...
... C. Gene frequency – how common a gene is in a population D. In genetic terms, evolution is defined as the change in gene frequency in a population over time II. Two main sources of variation that result from sexual reproduction A. Mutations – a change in the DNA sequence B. Gene Shuffling – genes ma ...
ppt - OHLL
... about ancient demographic events. • However, this information, may be qualitative rather than quantitative and does not allow us to determine whether other scenarios could have played a role (or selection). ...
... about ancient demographic events. • However, this information, may be qualitative rather than quantitative and does not allow us to determine whether other scenarios could have played a role (or selection). ...
Population
... favorable genes to the next generation. It is an ongoing process in nature and an important disruption to equilibrium. Three patterns of Natural Selection: ...
... favorable genes to the next generation. It is an ongoing process in nature and an important disruption to equilibrium. Three patterns of Natural Selection: ...
Genetic Mutations and Biotechnology
... • AlbinismAnother disorder where the offspring needs to inherit the bad gene from each parent. The gene is a defect in a protein to produce melanin, which is a pigment for skin, hair, and eyes. Albino animals and people can also have eye problems, prone to sunburn and skin cancer, and weak immune ...
... • AlbinismAnother disorder where the offspring needs to inherit the bad gene from each parent. The gene is a defect in a protein to produce melanin, which is a pigment for skin, hair, and eyes. Albino animals and people can also have eye problems, prone to sunburn and skin cancer, and weak immune ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... The knowledge and understanding of genetics and other fields of biology have been combined with Darwin’s theory of natural selection to form the modern evolutionary synthesis Biologists define evolution as changes in the gene pool of a species over time Gene Pool - The complete set of all allele ...
... The knowledge and understanding of genetics and other fields of biology have been combined with Darwin’s theory of natural selection to form the modern evolutionary synthesis Biologists define evolution as changes in the gene pool of a species over time Gene Pool - The complete set of all allele ...
File
... There are a few basic ways in which microevolutionary change happens. Mutation, migration, genetic drift, and natural selection are all processes that can directly affect gene frequencies in a population. ...
... There are a few basic ways in which microevolutionary change happens. Mutation, migration, genetic drift, and natural selection are all processes that can directly affect gene frequencies in a population. ...
Homo Species - WordPress.com
... 1. “A trait must be inherited if natural selection is to act on it (e.g. finch beak size; see Weiner). 2. Natural selection can’t occur without population variation in inherited characteristics. Selection can only work with variation that already exists (remember rule of large numbers and a normal d ...
... 1. “A trait must be inherited if natural selection is to act on it (e.g. finch beak size; see Weiner). 2. Natural selection can’t occur without population variation in inherited characteristics. Selection can only work with variation that already exists (remember rule of large numbers and a normal d ...
BIOLOGICAL EVOLUTION – UNITY AND DIVERSITY
... Standard or Performance Indicator Standard H.B.5: The student will demonstrate an understanding of biological evolution and the unity and diversity of life on Earth. H.B.5A. Conceptual Understanding: Scientific evidence from the fields of anatomy, embryology, biochemistry, and paleontology underlie ...
... Standard or Performance Indicator Standard H.B.5: The student will demonstrate an understanding of biological evolution and the unity and diversity of life on Earth. H.B.5A. Conceptual Understanding: Scientific evidence from the fields of anatomy, embryology, biochemistry, and paleontology underlie ...
gene pool
... Gene flow is the movement of genes into or out of a population. A) Emigration- when individuals leave a population decreasing the size of the gene pool. B) Immigration- when individuals from a different population enter a new population and begin breeding. This increases the size of the gene pool. ...
... Gene flow is the movement of genes into or out of a population. A) Emigration- when individuals leave a population decreasing the size of the gene pool. B) Immigration- when individuals from a different population enter a new population and begin breeding. This increases the size of the gene pool. ...
Related Document
... In humans, the gene for polydactyly (having extra fingers or toes) is dominant over the gene for the normal number of digits. If parents who are both homozygous dominant for polydactyly have four children, how many of these children would most likely have extra fingers or toes? ...
... In humans, the gene for polydactyly (having extra fingers or toes) is dominant over the gene for the normal number of digits. If parents who are both homozygous dominant for polydactyly have four children, how many of these children would most likely have extra fingers or toes? ...
q - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium • Condition #1 can be met. It is important to have large populations in order that the loss or addition of genes is not a factor. By contrast, small populations experience genetic drift. Additionally, if a small population moves to another area or becomes isolated, the ge ...
... Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium • Condition #1 can be met. It is important to have large populations in order that the loss or addition of genes is not a factor. By contrast, small populations experience genetic drift. Additionally, if a small population moves to another area or becomes isolated, the ge ...
Chapter 16 The Theory of Evolution
... Populations, not individuals, evolve • Natural selection acts on the range of phenotypes in a population. • Picture all of the alleles of the population’s genes as being together in a large pool called a gene pool. • The percentage of any specific allele in the gene pool is called the allelic frequ ...
... Populations, not individuals, evolve • Natural selection acts on the range of phenotypes in a population. • Picture all of the alleles of the population’s genes as being together in a large pool called a gene pool. • The percentage of any specific allele in the gene pool is called the allelic frequ ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.