Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q
... occur most often in males because the ______chromosome only codes for maleness. ...
... occur most often in males because the ______chromosome only codes for maleness. ...
Introduction to Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
... forms whose characteristics arise as random variations ADAPTATION: adjustment to environmental conditions through the long term process of natural selection acting on the genotype. ...
... forms whose characteristics arise as random variations ADAPTATION: adjustment to environmental conditions through the long term process of natural selection acting on the genotype. ...
Complementation
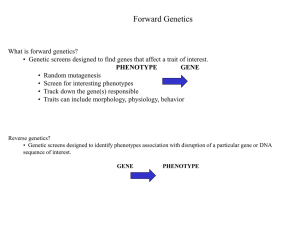
... • Genetic screens designed to identify phenotypes association with disruption of a particular gene or DNA sequence of interest. GENE ...
... • Genetic screens designed to identify phenotypes association with disruption of a particular gene or DNA sequence of interest. GENE ...
Mendelian Genetics in Populations II
... Nearly neutral theory – 2 • Imagine a species in which effective population size, N, is 500. If the selection coefficient, s, against a mutant heterozygote is 0.0005, then 4Ns = 1.0, which qualifies as “small”, and the mutation is effectively neutral • On the other hand, the same selection coeffici ...
... Nearly neutral theory – 2 • Imagine a species in which effective population size, N, is 500. If the selection coefficient, s, against a mutant heterozygote is 0.0005, then 4Ns = 1.0, which qualifies as “small”, and the mutation is effectively neutral • On the other hand, the same selection coeffici ...
Power Point
... – The GA creates a population of genomes – Then applies crossover and mutation to the individuals in the population to generate new individuals. – It uses various selection criteria so that it picks the best individuals for mating (and subsequent crossover). ...
... – The GA creates a population of genomes – Then applies crossover and mutation to the individuals in the population to generate new individuals. – It uses various selection criteria so that it picks the best individuals for mating (and subsequent crossover). ...
Evolution Exam practice - AP-Science-Experience-JMHS
... E) Allele frequency cannot be estimated from this information. 18) In peas, a gene controls flower color such that R = red and r = white. In an isolated pea patch, there were 36 red flowers and 64 white flowers. Assuming HardyWeinberg equilibrium, what is the value of q for this population? A) 0.60 ...
... E) Allele frequency cannot be estimated from this information. 18) In peas, a gene controls flower color such that R = red and r = white. In an isolated pea patch, there were 36 red flowers and 64 white flowers. Assuming HardyWeinberg equilibrium, what is the value of q for this population? A) 0.60 ...
Assessment Specifications
... Factors affecting the processes may include both direct and indirect availability of resources. Factors that affect enzyme activity within cells may include temperature, pH, substrate concentration, co-enzymes and enzyme inhibitors. Similarities and differences between cells may relate to the overal ...
... Factors affecting the processes may include both direct and indirect availability of resources. Factors that affect enzyme activity within cells may include temperature, pH, substrate concentration, co-enzymes and enzyme inhibitors. Similarities and differences between cells may relate to the overal ...
Population Genetics - Bev Facey Community High
... • Gene pool all the alleles of all the genes of all the individuals in a population • Evolution cumulative changes in the gene pool (and therefore changes in characteristics of populations) of organisms from one generation to the next ...
... • Gene pool all the alleles of all the genes of all the individuals in a population • Evolution cumulative changes in the gene pool (and therefore changes in characteristics of populations) of organisms from one generation to the next ...
Descent With Modification
... I2. Individuals best suited to the environment will be the ones most successful at producing offspring. I3. Unequal reproduction will lead to gradual change, with favorable characteristics accumulating over time. ...
... I2. Individuals best suited to the environment will be the ones most successful at producing offspring. I3. Unequal reproduction will lead to gradual change, with favorable characteristics accumulating over time. ...
Changes Over Time
... gene in a given population leads to a change in a population and may result in the emergence of a new species. • Natural selection operates on populations over many generations. ...
... gene in a given population leads to a change in a population and may result in the emergence of a new species. • Natural selection operates on populations over many generations. ...
Exam 3
... _____ 13. Small changes in the DNA code over time have given us complex features such as the human eye. What is this process of small gradual changes called? A. B. C. D. ...
... _____ 13. Small changes in the DNA code over time have given us complex features such as the human eye. What is this process of small gradual changes called? A. B. C. D. ...
Goal 3.05 II EOC Review Questions
... life and the changes of organisms over time. 3.05 Examine the development of the theory of evolution by natural selection including: development of the theory, the origin and history of life, fossil and biochemical evidence, mechanisms of evolution, and applications (pesticide and antibiotic resista ...
... life and the changes of organisms over time. 3.05 Examine the development of the theory of evolution by natural selection including: development of the theory, the origin and history of life, fossil and biochemical evidence, mechanisms of evolution, and applications (pesticide and antibiotic resista ...
BIOL 6617
... 7. Genetics of human personality, behavior and intelligence 8. Duplicate genes: origin, adaptive and evolutionary importance. Consider the hemoglobin family in detail. 9. Genetic control of sex determination (5 hrs.): single locus systems, polygenic and multiple allelic systems, sex chromosomes, hap ...
... 7. Genetics of human personality, behavior and intelligence 8. Duplicate genes: origin, adaptive and evolutionary importance. Consider the hemoglobin family in detail. 9. Genetic control of sex determination (5 hrs.): single locus systems, polygenic and multiple allelic systems, sex chromosomes, hap ...
2. Be sure that your exam has 9 pages including this cover sheet.
... _____1. A key point in Darwin's explanation of evolution is that A. biological structures most likely inherited are those that have become better suited to the environment by their constant use. B. mutations that occur are those that will help future generations fit into their environments. C. sligh ...
... _____1. A key point in Darwin's explanation of evolution is that A. biological structures most likely inherited are those that have become better suited to the environment by their constant use. B. mutations that occur are those that will help future generations fit into their environments. C. sligh ...
Plant Breeding is the actual application of the genetics research
... produce vigorous hybrid plants. ...
... produce vigorous hybrid plants. ...
Vocabulary Words for the first Evolution Quiz Adaptation Inherited
... Adaptation Inherited characteristics of a species that develops over time in response to an environmental factor, enabling the species to survive Adaptive Radiation/Divergent Evolution Diversification of a species into a number of different species, often over a relatively short time span Analogous ...
... Adaptation Inherited characteristics of a species that develops over time in response to an environmental factor, enabling the species to survive Adaptive Radiation/Divergent Evolution Diversification of a species into a number of different species, often over a relatively short time span Analogous ...
Unit1EvolutionReview
... 19. What do we mean when we describe an organism as “more fit” than some other organism? 20. How might natural selection have produced the modern giraffe from short-necked ancestors? 21. How does sexual reproduction benefit a species? 22. Explain the difference between homologous and analogous. Give ...
... 19. What do we mean when we describe an organism as “more fit” than some other organism? 20. How might natural selection have produced the modern giraffe from short-necked ancestors? 21. How does sexual reproduction benefit a species? 22. Explain the difference between homologous and analogous. Give ...
Genetics Syllabus.pages - Maranacook Area Schools
... LS3-1. Develop and use a model to describe why structural changes to genes (mutations) located on chromosomes may affect proteins and may result in harmful, beneficial, or neutral effects to the structure and function of the organism. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on conceptual understanding ...
... LS3-1. Develop and use a model to describe why structural changes to genes (mutations) located on chromosomes may affect proteins and may result in harmful, beneficial, or neutral effects to the structure and function of the organism. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on conceptual understanding ...
Early Ideas About Evolution
... Natural selection explains how evolution can occur. There are four main principles to natural selection: Variation: heritable _______________________________________ are the basis for natural selection Overproduction: __________________________________________________________________ ___________ ...
... Natural selection explains how evolution can occur. There are four main principles to natural selection: Variation: heritable _______________________________________ are the basis for natural selection Overproduction: __________________________________________________________________ ___________ ...
Lecture 5
... mutates) to weak (only one gene mutates) • May mean adding a new gene entirely • Mutation prevents fixation • Mutation is a source of diversity and discovery ...
... mutates) to weak (only one gene mutates) • May mean adding a new gene entirely • Mutation prevents fixation • Mutation is a source of diversity and discovery ...
Examples of Gene flow File
... Gene flow is the exchange of genes between two separate populations. This is most often accomplished when animals or spores from plants migrate to a new area. Any time a gene is introduced into a population where that gene once did not exist, gene flow has occurred. ...
... Gene flow is the exchange of genes between two separate populations. This is most often accomplished when animals or spores from plants migrate to a new area. Any time a gene is introduced into a population where that gene once did not exist, gene flow has occurred. ...
Mechanisms of Evolution part 2
... A gene pool is the total number of genes of every individual in an interbreeding population. ...
... A gene pool is the total number of genes of every individual in an interbreeding population. ...
Review Quizzes
... a. stabilizing selection b. directional selection c. sympatric selection d. allopatric selection e. disruptive selection 9. mortality in an annual plant is highest among the extreme variants A 10. favors selection of both larger and smaller snails relative to intermediate variants E 11. favors sele ...
... a. stabilizing selection b. directional selection c. sympatric selection d. allopatric selection e. disruptive selection 9. mortality in an annual plant is highest among the extreme variants A 10. favors selection of both larger and smaller snails relative to intermediate variants E 11. favors sele ...
S-B-9-1_Principles of Natural Selection
... shorter-necked relatives. These animals live longer, through more breeding seasons, and so they can have more offspring. In the next generation, there are more long-neck genes than short-neck genes in the population. If this continued over very many generations, then in time the average neck length ...
... shorter-necked relatives. These animals live longer, through more breeding seasons, and so they can have more offspring. In the next generation, there are more long-neck genes than short-neck genes in the population. If this continued over very many generations, then in time the average neck length ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.