Physics in Everyday Life - Electricty and Magnetism
... • The protons and electrons in each atom carry a quantum property we call charge, which can be one of two “flavours” – positive or negative • The positive protons in the nucleus are relatively heavy, and cannot get out of the nucleus easily. They do not move much • The electrons, on the outside of t ...
... • The protons and electrons in each atom carry a quantum property we call charge, which can be one of two “flavours” – positive or negative • The positive protons in the nucleus are relatively heavy, and cannot get out of the nucleus easily. They do not move much • The electrons, on the outside of t ...
Cosmic Rays and Climate
... Particles from space (Cosmic Rays) influence Earths climate, ranging from days to 109 years. •The empirical evidence is large and strong Part of a physical mechanism has been demonstrated experimentally • Involving ions and aerosol formation • Linking to clouds and thereby the energy budget of the E ...
... Particles from space (Cosmic Rays) influence Earths climate, ranging from days to 109 years. •The empirical evidence is large and strong Part of a physical mechanism has been demonstrated experimentally • Involving ions and aerosol formation • Linking to clouds and thereby the energy budget of the E ...
Subduction zone backarcs, mobile belts, and orogenic heat
... backarc lithospheres is that, in addition to high temperatures, the mantle viscosity is lowered by incorporation of water expelled from the underlying subducting oceanic plate (e.g., Dixon et al., 2004; Honda and Saito, 2003). The amount of water supplied is estimated to be very large (e.g., Peacock ...
... backarc lithospheres is that, in addition to high temperatures, the mantle viscosity is lowered by incorporation of water expelled from the underlying subducting oceanic plate (e.g., Dixon et al., 2004; Honda and Saito, 2003). The amount of water supplied is estimated to be very large (e.g., Peacock ...
Acoustic Waves - The Evergreen State College
... atmosphere is no longer dense enough for them to propagate through. At an altitude where the pressure of the atmosphere is comparable to the pressure of the magnetic field, where ~1, these acoustic waves transform into magnetic waves. ...
... atmosphere is no longer dense enough for them to propagate through. At an altitude where the pressure of the atmosphere is comparable to the pressure of the magnetic field, where ~1, these acoustic waves transform into magnetic waves. ...
Virtual geomagnetic poles
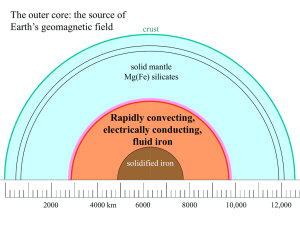
... 90% of the modern geomagnetic field is represented by a simple dipole at the center of the earth. The remaining 10%, the “non-dipole” components, have a more complicated spatial structure. Geomagneticians assume that in the past the earth’s field was also dominated by the dipole component. We can de ...
... 90% of the modern geomagnetic field is represented by a simple dipole at the center of the earth. The remaining 10%, the “non-dipole” components, have a more complicated spatial structure. Geomagneticians assume that in the past the earth’s field was also dominated by the dipole component. We can de ...
Continental drift: the history of an idea
... magnetic poles at the time of rock formation). 3. The inclination of the RMS (the inclination of the Earth's field which reflects the latitude at which the rock ...
... magnetic poles at the time of rock formation). 3. The inclination of the RMS (the inclination of the Earth's field which reflects the latitude at which the rock ...
flux linkage File
... If a coil is not at right angles to the uniform field then only a component of the flux passes through the coil ...
... If a coil is not at right angles to the uniform field then only a component of the flux passes through the coil ...
Van Allen radiation belt
A radiation belt is a layer of energetic charged particles that is held in place around a magnetized planet, such as the Earth, by the planet's magnetic field. The Earth has two such belts and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The discovery of the belts is credited to James Van Allen and as a result the Earth's belts bear his name. The main belts extend from an altitude of about 1,000 to 60,000 kilometers above the surface in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays. The belts are located in the inner region of the Earth's magnetosphere. The belts contain energetic electrons that form the outer belt and a combination of protons and electrons that form the inner belt. The radiation belts additionally contain less amounts of other nuclei, such as alpha particles. The belts endanger satellites, which must protect their sensitive components with adequate shielding if their orbit spends significant time in the radiation belts. In 2013, NASA reported that the Van Allen Probes had discovered a transient, third radiation belt, which was observed for four weeks until destroyed by a powerful, interplanetary shock wave from the Sun.