Formation of Active Regions on the Rising Slope of the 23rd Solar
... can only be done purely by empirical-statistical methods based on large uniform sequences of observations of different solar structures (mainly relative sunspot numbers). Solar activity forecast tasks are divided into three groups, depending on the task: short-term - of the order of a few days (but ...
... can only be done purely by empirical-statistical methods based on large uniform sequences of observations of different solar structures (mainly relative sunspot numbers). Solar activity forecast tasks are divided into three groups, depending on the task: short-term - of the order of a few days (but ...
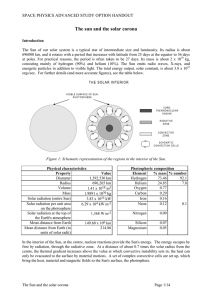
The sun and the solar corona
... established by purely theoretical considerations, based on the measured energy output (luminosity), radius and mass, using of course all the applicable laws of physics. Making some simplifying assumptions, such as spherical symmetry, no rotation and no magnetic fields, basic models of the Sun’s inte ...
... established by purely theoretical considerations, based on the measured energy output (luminosity), radius and mass, using of course all the applicable laws of physics. Making some simplifying assumptions, such as spherical symmetry, no rotation and no magnetic fields, basic models of the Sun’s inte ...
The Kuiper Belt: What We Know and What We Don`t - UCLA
... (“irregular” means that the orbit around the planet is large and eccentric and, in this case, the orbital motion is opposite to the direction of Saturn’s spin). Phoebe was captured from elsewhere in the Solar system but the source region and the mechanism of capture remain unknown. One possible sour ...
... (“irregular” means that the orbit around the planet is large and eccentric and, in this case, the orbital motion is opposite to the direction of Saturn’s spin). Phoebe was captured from elsewhere in the Solar system but the source region and the mechanism of capture remain unknown. One possible sour ...
Can We Successfully Apply A Solar Thin-Flux
... Spin up to different (0.25, 1, 4, 10, 25, 63, rigid rot. profile). Mainly PMS-stars, a few (sub)giants for comparison. ...
... Spin up to different (0.25, 1, 4, 10, 25, 63, rigid rot. profile). Mainly PMS-stars, a few (sub)giants for comparison. ...
Geomagnetism. - Brock University
... magnetic poles at the time of rock formation). 3. The inclination of the RMS (the inclination of the Earth's field which reflects the latitude at which the rock ...
... magnetic poles at the time of rock formation). 3. The inclination of the RMS (the inclination of the Earth's field which reflects the latitude at which the rock ...
Answers for Student notes page
... • Where is the motion of electric charges in a common bar magnet? • The magnet as a whole may be stationary, but it is composed of atoms whose electrons are in constant motion about atomic nuclei. • This moving charge constitutes a tiny current and produces a magnetic field. Most substances are not ...
... • Where is the motion of electric charges in a common bar magnet? • The magnet as a whole may be stationary, but it is composed of atoms whose electrons are in constant motion about atomic nuclei. • This moving charge constitutes a tiny current and produces a magnetic field. Most substances are not ...
Significance of the Kuiper Belt
... (“irregular” means that the orbit around the planet is large and eccentric and, in this case, the orbital motion is opposite to the direction of Saturn’s spin). Phoebe was captured from elsewhere in the Solar system but the source region and the mechanism of capture remain unknown. One possible sour ...
... (“irregular” means that the orbit around the planet is large and eccentric and, in this case, the orbital motion is opposite to the direction of Saturn’s spin). Phoebe was captured from elsewhere in the Solar system but the source region and the mechanism of capture remain unknown. One possible sour ...
Magnets and Magnetism
... Ferromagnets – magnets made with metals Electromagnets – produced by an electric current. Temporary magnets – made from materials that are easy to magnetize, but they lose their magnetization easily too. Permanent magnets – difficult to magnetize, but retain their magnetic properties better. ...
... Ferromagnets – magnets made with metals Electromagnets – produced by an electric current. Temporary magnets – made from materials that are easy to magnetize, but they lose their magnetization easily too. Permanent magnets – difficult to magnetize, but retain their magnetic properties better. ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... • The electric force between any two charged particles depends on the product of their charges and their distance of separation, as specified in Coulomb’s law. • If the charged particles are moving with respect to each other, there is an additional force between them, called the magnetic force. • Th ...
... • The electric force between any two charged particles depends on the product of their charges and their distance of separation, as specified in Coulomb’s law. • If the charged particles are moving with respect to each other, there is an additional force between them, called the magnetic force. • Th ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... • Earth is itself a huge magnet. • The magnetic poles of Earth are widely separated from the geographic poles. • The magnetic field of Earth is not due to a giant magnet in its interior—it is due to electric currents. • Most Earth scientists think that moving charges looping around within the molten ...
... • Earth is itself a huge magnet. • The magnetic poles of Earth are widely separated from the geographic poles. • The magnetic field of Earth is not due to a giant magnet in its interior—it is due to electric currents. • Most Earth scientists think that moving charges looping around within the molten ...
Van Allen radiation belt
A radiation belt is a layer of energetic charged particles that is held in place around a magnetized planet, such as the Earth, by the planet's magnetic field. The Earth has two such belts and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The discovery of the belts is credited to James Van Allen and as a result the Earth's belts bear his name. The main belts extend from an altitude of about 1,000 to 60,000 kilometers above the surface in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays. The belts are located in the inner region of the Earth's magnetosphere. The belts contain energetic electrons that form the outer belt and a combination of protons and electrons that form the inner belt. The radiation belts additionally contain less amounts of other nuclei, such as alpha particles. The belts endanger satellites, which must protect their sensitive components with adequate shielding if their orbit spends significant time in the radiation belts. In 2013, NASA reported that the Van Allen Probes had discovered a transient, third radiation belt, which was observed for four weeks until destroyed by a powerful, interplanetary shock wave from the Sun.